J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Sep;22(Suppl):S122-S128. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.S.S122.
Analysis of Changes in the Total Lymphocyte and Eosinophil Count during Immunotherapy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Correlation with Response and Survival
- Affiliations
-
- 1Urologic Oncology Clinic, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. cjs5225@ncc.re.kr
- 2National Cancer Control Research Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1785800
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.S.S122
Abstract
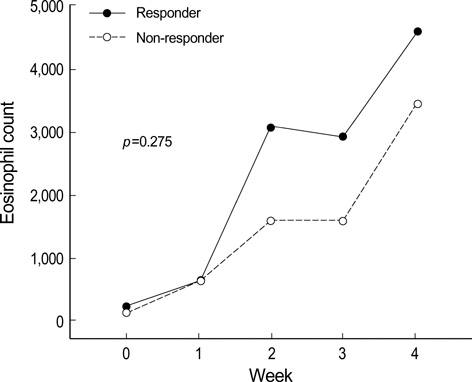
- The aims of this study were to analyze lymphocyte and eosinophil counts in consecutive peripheral blood samples taken during immunotherapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) and to correlate the findings with objective response and survival. A total of 40 patients with mRCC who received immunotherapy with interleukin-2, interferon-alpha, and 5-fluorouracil were analyzed. Objective responses were observed in 14 patients, including 2 (5%) who showed a complete response (CR) and 12 (30%) who showed a partial response (PR). Eleven patients (27%) achieved stable disease (SD), and 15 patients (38%) had progressive disease (PD). Changes from baseline in the total lymphocyte counts were significantly higher in the responding patients (CR+PR+SD) than in the non-responding patients (PD) (p=0.017), but no difference was seen in the total eosinophil counts (p=0.275). Univariate analysis identified the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (p=0.017), the presence of a primary renal tumor (p<0.001) and the peripheral lymphocyte counts at week 4 (p=0.034) as prognostic factors, but a low ECOG performance status (p=0.003) and the presence of a primary renal tumor (p=0.001) were identified as independent poor prognostic factors by multivariate analysis. This study provides further evidence that changes in blood lymphocyte counts may serve as an objective indicator of objective responses.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Carcinoma, Renal Cell/blood/*immunology/secondary/*therapy
Eosinophils
Female
Fluorouracil/administration & dosage
Humans
*Immunotherapy
Interferon Type I, Recombinant/administration & dosage
Interleukin-2/administration & dosage
Kidney Neoplasms/blood/*immunology/*therapy
Leukocyte Count
*Lymphocyte Count
Male
Middle Aged
Prognosis
Survival Rate
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bukowski RM. Natural history and therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: the role of interleukin-2. Cancer. 1997. 80:1198–1220.2. Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul LM, Leitman S, Chang AE, Ettinghausen SE, Matory YL, Skibber JM, Shiloni E, Vetto JT. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985. 313:1485–1492.
Article3. Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, White DE, Steinberg SM. Durability of complete responses in patients with metastatic cancer treated with high-dose interleukin-2: identification of the antigens mediating response. Ann Surg. 1998. 228:307–319.
Article4. Parkinson DR, Abrams JS, Wiernik PH, Rayner AA, Margolin KA, Van Echo DA, Sznol M, Dutcher JP, Aronson FR, Doroshow JH. Interleukin-2 therapy in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 1990. 8:1650–1656.
Article5. Atzpodien J, Lopez Hanninen E, Kirchner H, Bodenstein H, Pfreundschuh M, Rebmann U, Metzner B, Illiger HJ, Jakse G, Niesel T. Multiinstitutional home-therapy trial of recombinant human interleukin-2 and interferon alfa-2 in progressive metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1995. 13:497–501.
Article6. Negrier S, Escudier B, Lasset C, Douillard JY, Savary J, Chevreau C, Ravaud A, Mercatello A, Peny J, Mousseau M, Philip T, Tursz T. Groupe Francais d'Immunothérapie. Recombinant human interleukin-2, recombinant human interferon alfa-2a, or both in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1998. 338:1272–1278.
Article7. Atzpodien J, Hoffmann R, Franzke M, Stief C, Wandert T, Reitz M. Thirteen-year, long-term efficacy of interferon 2alpha and interleukin 2-based home therapy in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2002. 95:1045–1050.8. Yang JC, Sherry RM, Steinberg SM, Topalian SL, Schwartzentruber DJ, Hwu P, Seipp CA, Rogers-Freezer L, Morton KE, White DE, Liewehr DJ, Merino MJ, Rosenberg SA. Randomized study of high-dose and low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with metastatic renal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003. 21:3127–3132.
Article9. Donskov F, Bennedsgaard KM, Von Der Maase H, Marcussen N, Fisker R, Jensen JJ, Naredi P, Hokland M. Intratumoural and peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma undergoing interleukin-2 based immunotherapy: association to objective response and survival. Br J Cancer. 2002. 87:194–201.
Article10. Fumagalli LA, Vinke J, Hoff W, Ypma E, Brivio F, Nespoli A. Lymphocyte counts independently predict overall survival in advanced cancer patients: a biomarker for IL-2 immunotherapy. J Immunother. 2003. 26:394–402.
Article11. Upton MP, Parker RA, Youmans A, McDermott DF, Atkins MB. Histologic predictors of renal cell carcinoma response to interleukin-2-based therapy. J Immunother. 2005. 28:488–495.
Article12. Donskov F, von der Maase H. Impact of immune parameters on long-term survival in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:1997–2005.
Article13. Parmiani G. An explanation of the variable clinical response to interleukin 2 and LAK cells. Immunol Today. 1990. 11:113–115.
Article14. Forni G, Giovarelli M, Santoni A, Modesti A, Forni M. Interleukin 2 activated tumor inhibition in vivo depends on the systemic involvement of host immunoreactivity. J Immunol. 1987. 138:4033–4041.15. Buzio C, Andrulli S, Santi R, Pavone L, Passalacqua R, Potenzoni D, Ferrozzi F, Giacosa R, Vaglio A. Long-term immunotherapy with low-dose interleukin-2 and interferon-alpha in the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2001. 92:2286–2296.16. Hofmockel G, Langer W, Theiss M, Gruss A, Frohmuller HG. Immunochemotherapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma using a regimen of interleukin-2, interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil. J Urol. 1996. 156:18–21.
Article17. Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M, Winkler A. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer. 1981. 47:207–214.
Article18. Gez E, Rubinov R, Gaitini D, Meretyk S, Best LA, Native O, Stein A, Erlich N, Beny A, Zidan J, Haim N, Kuten A. Interleukin-2, interferon-alpha, 5-fluorouracil, and vinblastine in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a prospective phase II study: the experience of Rambam and Lin Medical Centers 1996-2000. Cancer. 2002. 95:1644–1649.19. McDermott DF, Regan MM, Clark JI, Flaherty LE, Weiss GR, Logan TF, Kirkwood JM, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, Ernstoff MS, Tretter CP, Urba WJ, Smith JW, Margolin KA, Mier JW, Gollob JA, Dutcher JP, Atkins MB. Randomized phase III trial of high-dose interleukin-2 versus subcutaneous interleukin-2 and interferon in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:133–141.
Article20. Atzpodien J, Kirchner H, Jonas U, Bergmann L, Schott H, Heynemann H, Fornara P, Loening SA, Roigas J, Muller SC, Bodenstein H, Pomer S, Metzner B, Rebmann U, Oberneder R, Siebels M, Wandert T, Puchberger T, Reitz M. Interleukin-2- and interferon alfa-2a-based immunochemotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a Prospectively Randomized Trial of the German Cooperative Renal Carcinoma Chemoimmunotherapy Group (DGCIN). J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:1188–1194.
Article21. Konrad MW, Hemstreet G, Hersh EM, Mansell PW, Mertelsmann R, Kolitz JE, Bradley EC. Pharmacokinetics of recombinant interleukin 2 in humans. Cancer Res. 1990. 50:2009–2017.22. Fumagalli L, Lissoni P, Di Felice G, Meregalli S, Valsuani G, Mengo S, Rovelli F. Pretreatment serum markers and lymphocyte response to interleukin-2 therapy. Br J Cancer. 1999. 80:407–411.
Article23. Donskov F, Bennedsgaard KM, Hokland M, Marcussen N, Fisker R, Madsen HH, Fode K, von der Maase H. Leukocyte orchestration in blood and tumour tissue following interleukin-2 based immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2004. 53:729–739.
Article24. Rodgers S, Rees RC, Hancock BW. Changes in the phenotypic characteristics of eosinophils from patients receiving recombinant human interleukin-2 (rhIL-2) therapy. Br J Haematol. 1994. 86:746–753.
Article25. Moroni M, Porta C, De Amici M, Quaglini S, Cattabiani MA, Buzio C. Eosinophils and C4 predict clinical failure of combination immunotherapy with very low dose subcutaneous interleukin-2 and interferon in renal cell carcinoma patients. Haematologica. 2000. 85:298–303.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Combined Effect of Angioinfarction with Immunotherapy in Patients with Stage IV Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Application of Autologous Tumor Vaccine as an Adjuvant Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Novel immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma in the Paranasal Sinus: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Surgical Resection of Pulmonary Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma