J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2011 Oct;41(5):211-217. 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.5.211.
A short-term clinical study of marginal bone level change around microthreaded and platform-switched implants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. kscho@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1783615
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2011.41.5.211
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The marginal bone levels around implants following restoration are used as a reference for evaluating implant success and survival. Two design concepts that can reduce crestal bone resorption are the microthread and platform-switching concepts. The aims of this study were to analyze the placement of microthreaded and platform-switched implants and their short-term survival rate, as well as the level of bone around the implants.
METHODS
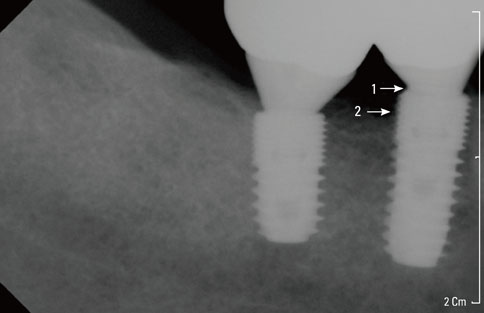
The subjects of this study were 27 patients (79 implants) undergoing treatment with microthreaded and platform-switched implants between October 2008 and July 2009 in the Dental Hospital of Yonsei University Department of Periodontology. The patients received follow-up care more than 6 months after the final setting of the prosthesis, at which time periapical radiographs were taken. The marginal bone level was measured from the reference point to the lowest observed point of contact between the marginal bone and the fixture. Comparisons were made between radiographs taken at the time of fixture installation and those taken at the follow-up visit.
RESULTS
During the study period (average of 11.8 months after fixture installation and 7.4 months after the prosthesis delivery), the short-term survival rate of microthreaded and platform-switched implants was 100% and the marginal bone loss around implants was 0.16+/-0.08 mm, the latter of which is lower than the previously reported values.
CONCLUSIONS
This short-term clinical study has demonstrated the successful survival rates of a microthread and platform-switched implant system, and that this system is associated with reduced marginal bone loss.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effects of implant collar design on marginal bone and soft tissue
Hyun-Sang Yoo, Sun-Nyo Kang, Chang-Mo Jeong, Mi-Jung Yun, Jung-Bo Huh, Young-Chan Jeon
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2012;50(1):21-28. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2012.50.1.21.
Reference
-
1. Brånemark PI, Adell R, Breine U, Hansson BO, Lindström J, Ohlsson A. Intra-osseous anchorage of dental prostheses. I. Experimental studies. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1969. 3:81–100.2. Atwood DA. Some clinical factors related to rate of resorption of residual ridges. 1962. J Prosthet Dent. 2001. 86:119–125.3. Lekholom U, Zarb GA. Brånemark PI, Zarb GA, Albrektsson T, editors. Patient selection and preparation. Tissue-integrated prostheses: osseointegration in clinical dentistry. 1985. Chicago: Quintessence;199–220.4. Ahlqvist J, Borg K, Gunne J, Nilson H, Olsson M, Astrand P. Osseointegrated implants in edentulous jaws: a 2-year longitudinal study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1990. 5:155–163.5. Albrektsson T, Zarb G, Worthington P, Eriksson AR. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: a review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1986. 1:11–25.6. Berglundh T, Persson L, Klinge B. A systematic review of the incidence of biological and technical complications in implant dentistry reported in prospective longitudinal studies of at least 5 years. J Clin Periodontol. 2002. 29:Suppl 3. 197–212.
Article7. Chang M, Wennström JL, Odman P, Andersson B. Implant supported single-tooth replacements compared to contralateral natural teeth. Crown and soft tissue dimensions. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1999. 10:185–194.
Article8. Lazzara RJ, Porter SS. Platform switching: a new concept in implant dentistry for controlling postrestorative crestal bone levels. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2006. 26:9–17.9. Schrotenboer J, Tsao YP, Kinariwala V, Wang HL. Effect of microthreads and platform switching on crestal bone stress levels: a finite element analysis. J Periodontol. 2008. 79:2166–2172.
Article10. Friberg B, Grondahl K, Lekholm U. A new self-tapping Brånemark implant: clinical and radiographic evaluation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1992. 7:80–85.11. Gonshor A, Goveia G, Sotirakis E. A prospective, multicenter, 4-year study of the ACE Surgical resorbable blast media implant. J Oral Implantol. 2003. 29:174–180.
Article12. Buser D, Weber HP, Lang NP. Tissue integration of non-submerged implants. 1-year results of a prospective study with 100 ITI hollow-cylinder and hollow-screw implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1990. 1:33–40.
Article13. Brägger U, Häfeli U, Huber B, Hämmerle CH, Lang NP. Evaluation of postsurgical crestal bone levels adjacent to non-submerged dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998. 9:218–224.
Article14. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Coulthard P, Thomsen P, Worthington HV. A 5-year follow-up comparative analysis of the efficacy of various osseointegrated dental implant systems: a systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005. 20:557–568.15. Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, Brånemark PI. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg. 1981. 10:387–416.
Article16. Guo E. Mechanical properities of cortical bone and cancellous bone tissue. 2001. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press;1–23.17. Lee DW, Choi YS, Park KH, Kim CS, Moon IS. Effect of microthread on the maintenance of marginal bone level: a 3-year prospective study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007. 18:465–470.
Article18. Oh TJ, Yoon J, Misch CE, Wang HL. The causes of early implant bone loss: myth or science? J Periodontol. 2002. 73:322–333.
Article19. Jung YC, Han CH, Lee KW. A 1-year radiographic evaluation of marginal bone around dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1996. 11:811–818.20. Hansson S. The implant neck: smooth or provided with retention elements. A biomechanical approach. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1999. 10:394–405.
Article21. Abrahamsson I, Berglundh T. Tissue characteristics at microthreaded implants: an experimental study in dogs. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2006. 8:107–113.
Article22. Quirynen M, Bollen CM, Eyssen H, van Steenberghe D. Microbial penetration along the implant components of the Brånemark system. An in vitro study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1994. 5:239–244.
Article23. Ericsson I, Persson LG, Berglundh T, Marinello CP, Lindhe J, Klinge B. Different types of inflammatory reactions in peri-implant soft tissues. J Clin Periodontol. 1995. 22:255–261.
Article24. Waerhaug J. Subgingival plaque and loss of attachment in periodontosis as evaluated on extracted teeth. J Periodontol. 1977. 48:125–130.
Article25. Hürzeler M, Fickl S, Zuhr O, Wachtel HC. Peri-implant bone level around implants with platform-switched abutments: preliminary data from a prospective study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007. 65:7 Suppl 1. 33–39.
Article26. López-Marí L, Calvo-Guirado JL, Martín-Castellote B, Gomez-Moreno G, López-Marí M. Implant platform switching concept: an updated review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009. 14:e450–e454.27. Kwon HJ, Lee DW, Park KH, Kim CK, Moon IS. Influence of the tooth- and implant-side marginal bone level on the interproximal papilla dimension in a single implant with a microthread, conical seal, and platform-switched design. J Periodontol. 2009. 80:1541–1547.
Article28. Calandriello R, Tomatis M, Vallone R, Rangert B, Gottlow J. Immediate occlusal loading of single lower molars using Brånemark System Wide-Platform TiUnite implants: an interim report of a prospective open-ended clinical multicenter study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003. 5:Suppl 1. 74–80.
Article29. Glauser R, Lundgren AK, Gottlow J, Sennerby L, Portmann M, Ruhstaller P, et al. Immediate occlusal loading of Brånemark TiUnite implants placed predominantly in soft bone: 1-year results of a prospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003. 5:Suppl 1. 47–56.
Article30. Vanden Bogaerde L, Pedretti G, Dellacasa P, Mozzati M, Rangert B, Wendelhag I. Early function of splinted implants in maxillas and posterior mandibles, using Brånemark System Tiunite implants: an 18-month prospective clinical multicenter study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2004. 6:121–129.
Article31. Wennström JL, Ekestubbe A, Gröndahl K, Karlsson S, Lindhe J. Implant-supported single-tooth restorations: a 5-year prospective study. J Clin Periodontol. 2005. 32:567–574.
Article32. Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, Brånemark PI, Lindhe J, Eriksson B, et al. Marginal tissue reactions at osseointegrated titanium fixtures (I). A 3-year longitudinal prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1986. 15:39–52.33. Siegele D, Soltesz U. Numerical investigations of the influence of implant shape on stress distribution in the jaw bone. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1989. 4:333–340.34. Hollender L, Rockler B. Radiographic evaluation of osseointegrated implants of the jaws. Experimental study of the influence of radiographic techniques on the measurement of the relation between the implant and bone. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1980. 9:91–95.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of marginal bone loss around platform-switched implants by digital subtraction radiography
- Marginal bone level change during sequential loading periods of partial edentulous rehabilitation using immediately loaded selftapping implants: a 6.5-year retrospective study
- Marginal bone level changes in association with different vertical implant positions: a 3-year retrospective study
- Three-dimensional finite element analysis of platform switched implant
- Success rate and marginal bone loss of Osstem USII plus implants; Short term clinical study