J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2010 Dec;40(6):276-282. 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.6.276.
The effect of Er:YAG laser irradiation on the surface microstructure and roughness of hydroxyapatite-coated implant
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Kyung Hee University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. yherr@khu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Oral Biology, Kyung Hee University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1783572
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2010.40.6.276
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The present study was performed to evaluate the effect of erbium:yttrium-aluminium-garnet (Er:YAG) laser irradiation on the change of hydroxyapatite (HA)-coated implant surface microstructure according to the laser energy and the application time.
METHODS
The implant surface was irradiated by Er:YAG laser under combination condition using the laser energy of 100 mJ/pulse, 140 mJ/pulse and 180 mJ/pulse and application time of 1 minute, 1.5 minutes and 2 minutes. The specimens were examined by surface roughness evaluation and scanning electron microscopic observation.
RESULTS
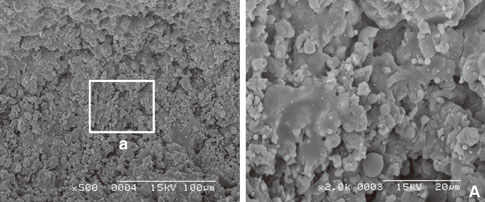
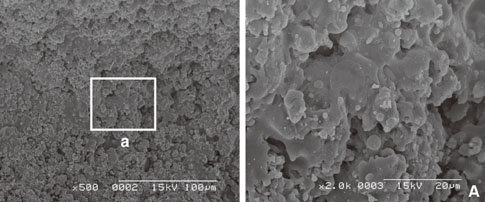
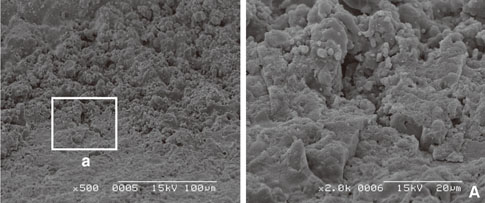
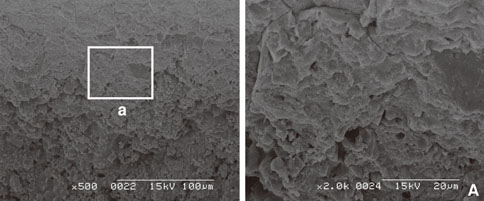
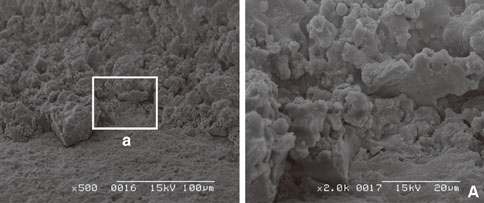
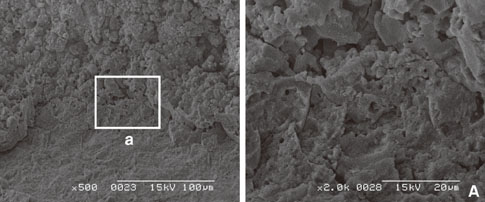
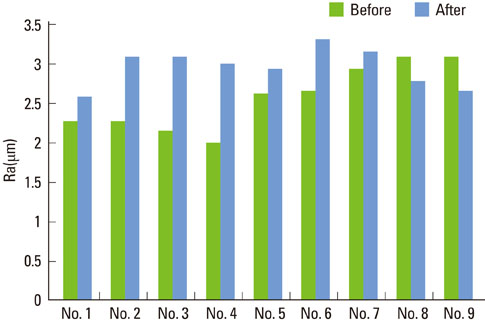
In scanning electron microscope, HA-coated implant surface was not altered by Er:YAG laser irradiation under experimental condition on 100 mJ/pulse, 1 minute. Local areas with surface melting and cracks were founded on 100 mJ/pulse, 1.5 minutes and 2 minutes. One hundred forty mJ/pulse and 180 mJ/pulse group had surface melting and peeling area of HA particles, which condition was more severe depending on the increase of application time. Under all experimental condition, the difference of surface roughness value on implant surface was not statistically significant.
CONCLUSIONS
Er:YAG laser on HA-coated implant surface is recommended to be irradiated below 100 mJ/pulse, 1 minute for detoxification of implant surface without surface alteration.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pjetursson BE, Tan K, Lang NP, Bragger U, Egger M, Zwahlen M. A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of fixed partial dentures (FPDs) after an observation period of at least 5 years. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004. 15:667–676.
Article2. Esposito M, Hirsch JM, Lekholm U, Thomsen P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (I). Success criteria and epidemiology. Eur J Oral Sci. 1998. 106:527–551.
Article3. Mombelli A, Buser D, Lang NP. Colonization of osseointegrated titanium implants in edentulous patients. Early results. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1988. 3:113–120.
Article4. Becker W, Becker BE, Newman MG, Nyman S. Clinical and microbiologic findings that may contribute to dental implant failure. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1990. 5:31–38.5. Apse P, Ellen RP, Overall CM, Zarb GA. Microbiota and crevicular fluid collagenase activity in the osseointegrated dental implant sulcus: a comparison of sites in edentulous and partially edentulous patients. J Periodontal Res. 1989. 24:96–105.
Article6. Quaranta A, Maida C, Scrascia A, Campus G, Quaranta M. Er:Yag Laser application on titanium implant surfaces contaminated by Porphyromonas gingivalis: an histomorphometric evaluation. Minerva Stomatol. 2009. 58:317–330.7. Baier RE, Meyer AE. Implant surface preparation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1988. 3:9–20.8. Sennerby L, Lekholm U. The soft tissue response to titanium abutments retrieved from humans and reimplanted in rats. A light microscopic study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1993. 4:23–27.
Article9. Meffert RM, Langer B, Fritz ME. Dental implants: a review. J Periodontol. 1992. 63:859–870.
Article10. Zablotsky MH, Diedrich DL, Meffert RM. Detoxification of endotoxin-contaminated titanium and hydroxyapatite-coated surfaces utilizing various chemotherapeutic and mechanical modalities. Implant Dent. 1992. 1:154–158.
Article11. Fox SC, Moriarty JD, Kusy RP. The effects of scaling a titanium implant surface with metal and plastic instruments: an in vitro study. J Periodontol. 1990. 61:485–490.
Article12. Matarasso S, Quaremba G, Coraggio F, Vaia E, Cafiero C, Lang NP. Maintenance of implants: an in vitro study of titanium implant surface modifications subsequent to the application of different prophylaxis procedures. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1996. 7:64–72.
Article13. Augthun M, Tinschert J, Huber A. In vitro studies on the effect of cleaning methods on different implant surfaces. J Periodontol. 1998. 69:857–864.
Article14. Kreisler M, Kohnen W, Christoffers AB, Gotz H, Jansen B, Duschner H, et al. In vitro evaluation of the biocompatibility of contaminated implant surfaces treated with an Er : YAG laser and an air powder system. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005. 16:36–43.
Article15. Van de Velde E, Thielens P, Schautteet H, Vanclooster R. Subcutaneous emphysema of the oral floor during cleaning of a bridge fixed on an IMZ implant. Case report. Rev Belge Med Dent. 1991. 46:64–71.16. Mouhyi J, Sennerby L, Pireaux JJ, Dourov N, Nammour S, Van Reck J. An XPS and SEM evaluation of six chemical and physical techniques for cleaning of contaminated titanium implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998. 9:185–194.
Article17. Krozer A, Hall J, Ericsson I. Chemical treatment of machined titanium surfaces. An in vitro study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1999. 10:204–211.
Article18. Romanos GE, Everts H, Nentwig GH. Effects of diode and Nd:YAG laser irradiation on titanium discs: a scanning electron microscope examination. J Periodontol. 2000. 71:810–815.
Article19. Kreisler M, Gotz H, Duschner H. Effect of Nd:YAG, Ho:YAG, Er:YAG, CO2, and GaAIAs laser irradiation on surface properties of endosseous dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002. 17:202–211.20. Schwarz F, Sculean A, Berakdar M, Szathmari L, Georg T, Becker J. In vivo and in vitro effects of an Er:YAG laser, a GaAlAs diode laser, and scaling and root planing on periodontally diseased root surfaces: a comparative histologic study. Lasers Surg Med. 2003. 32:359–366.
Article21. Tucker D, Cobb CM, Rapley JW, Killoy WJ. Morphologic changes following in vitro CO2 laser treatment of calculus-ladened root surfaces. Lasers Surg Med. 1996. 18:150–156.
Article22. Moritz A, Schoop U, Goharkhay K, Schauer P, Doertbudak O, Wernisch J, et al. Treatment of periodontal pockets with a diode laser. Lasers Surg Med. 1998. 22:302–311.
Article23. Bach G, Neckel C, Mall C, Krekeler G. Conventional versus laser-assisted therapy of periimplantitis: a five-year comparative study. Implant Dent. 2000. 9:247–251.24. Ando Y, Aoki A, Watanabe H, Ishikawa I. Bactericidal effect of erbium YAG laser on periodontopathic bacteria. Lasers Surg Med. 1996. 19:190–200.
Article25. Friedmann A, Antic L, Bernimoulin JP, Purucker P. In vitro attachment of osteoblasts on contaminated rough titanium surfaces treated by Er:YAG laser. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006. 79:53–60.
Article26. Schwarz F, Rothamel D, Sculean A, Georg T, Scherbaum W, Becker J. Effects of an Er:YAG laser and the Vector ultrasonic system on the biocompatibility of titanium implants in cultures of human osteoblast-like cells. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003. 14:784–792.
Article27. Kreisler M, Al Haj H, d'Hoedt B. Temperature changes at the implant-bone interface during simulated surface decontamination with an Er:YAG laser. Int J Prosthodont. 2002. 15:582–587.28. Porras R, Anderson GB, Caffesse R, Narendran S, Trejo PM. Clinical response to 2 different therapeutic regimens to treat peri-implant mucositis. J Periodontol. 2002. 73:1118–1125.
Article29. Rimondini L, Cicognani Simoncini F, Carrassi A. Micromorphometric assessment of titanium plasma-sprayed coating removal using burs for the treatment of peri-implant disease. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000. 11:129–138.
Article30. Kreisler M, Kohnen W, Marinello C, Gotz H, Duschner H, Jansen B, et al. Bactericidal effect of the Er:YAG laser on dental implant surfaces: an in vitro study. J Periodontol. 2002. 73:1292–1298.
Article31. Geesink RG, de Groot K, Klein CP. Bonding of bone to apatite-coated implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988. 70:17–22.
Article32. Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 1--review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int J Prosthodont. 2004. 17:536–543.33. Cook SD. Hydroxyapatite-coated total hip replacement. Dent Clin North Am. 1992. 36:235–238.34. Artzi Z, Carmeli G, Kozlovsky A. A distinguishable observation between survival and success rate outcome of hydroxyapatite-coated implants in 5-10 years in function. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006. 17:85–93.
Article35. Folwaczny M, Thiele L, Mehl A, Hickel R. The effect of working tip angulation on root substance removal using Er:YAG laser radiation: an in vitro study. J Clin Periodontol. 2001. 28:220–226.
Article36. Eriksson AR, Albrektsson T. Temperature threshold levels for heat-induced bone tissue injury: a vital-microscopic study in the rabbit. J Prosthet Dent. 1983. 50:101–107.
Article37. Burkes EJ Jr, Hoke J, Gomes E, Wolbarsht M. Wet versus dry enamel ablation by Er:YAG laser. J Prosthet Dent. 1992. 67:847–851.
Article38. Visuri SR, Walsh JT Jr, Wigdor HA. Erbium laser ablation of dental hard tissue: effect of water cooling. Lasers Surg Med. 1996. 18:294–300.
Article39. Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T. Suggested guidelines for the topographic evaluation of implant surfaces. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000. 15:331–344.40. Dong SP, Mainsah E, Sullivan PJ, Stout KJ. Stout KJ, Dong WP, editors. Instruments and measurement techniques of 3-dimensional surface topography. Three dimensional surface topography: measurement, interpretation, and applications: a survey and bibliography. 1994. London: Penton Press;3–63.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of Er:YAG laser irradiation on the surface microstructure and roughness of TiO2 implant
- The effect of erbium-doped: yttrium, aluminium and garnet laser irradiation on the surface microstructure and roughness of double acid-etched implants
- Effect of erbium-doped: yttrium, aluminium and garnet laser irradiation on the surface microstructure and roughness of sand-blasted, large grit, acid-etched implants
- TEMPERATURE CHANGES OF IMPLANT SURFACE IN SECOND STAGE SURGERY WITH DETAL LASER : IN VITRO STUDY
- Micromorphometric change of implant surface conditioned with tetracycline-HCl: Hydroxyapatite surface