J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Oct;23(5):916-919. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.5.916.
Complete Remission of Unresectable Colon Cancer after Preoperative Chemotherapy Selected by Adenosine Triphosphate-Based Chemotherapy Response Assay
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yongdong Severance Hospital, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea. sksohn@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pathology, Yongdong Severance Hospital, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1783085
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.5.916
Abstract
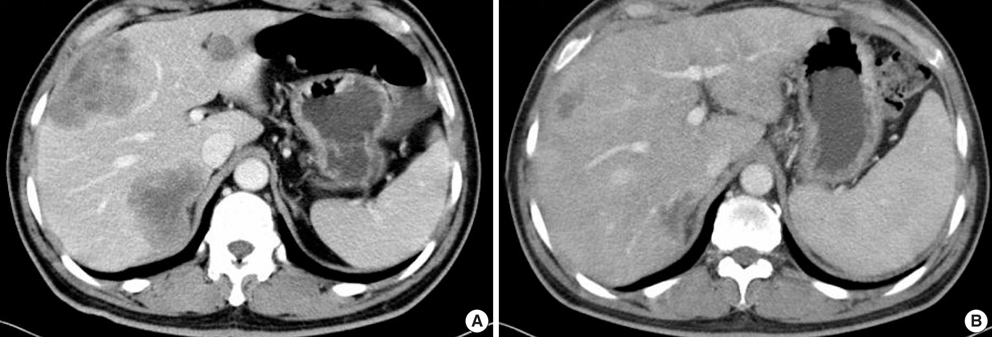
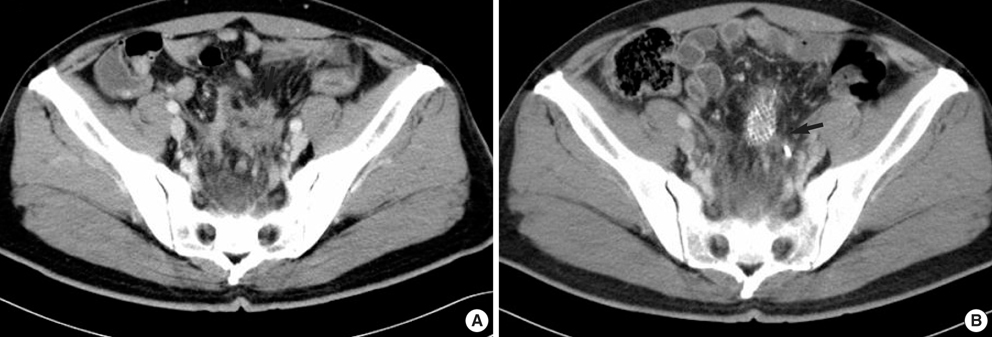
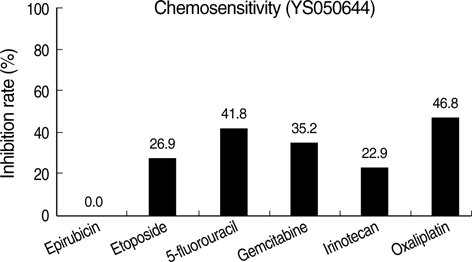
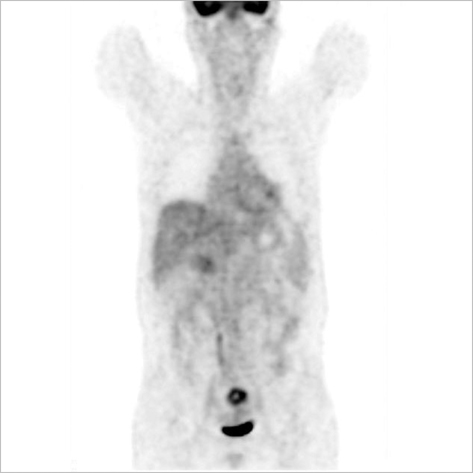
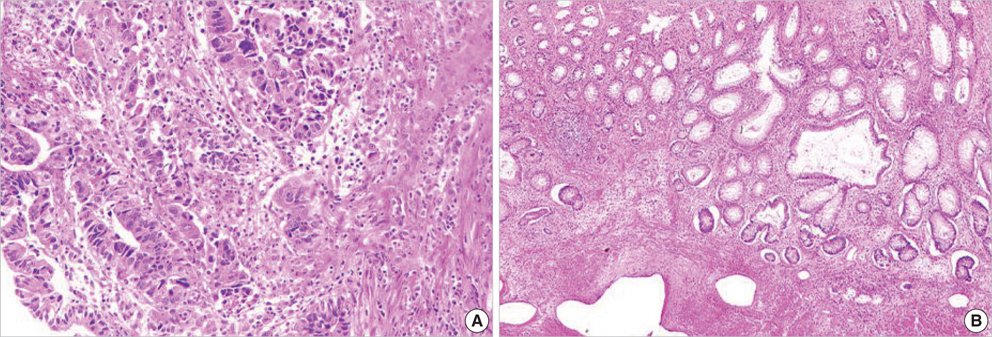
- The adenosine triphosphate-based chemotherapy response assay (ATP-CRA) is a chemosensitivity test that offers the potential of selecting cancer treatments based on the responsiveness of individual tumors. We report a case of 47-yr-old male, presented with sigmoid colon cancer with multiple liver and peritoneal metastases, in which there was a complete response for the primary colon cancer after administration of preoperative chemotherapy selected by ATP-CRA. Oxaliplatin was the most sensitive drug based on the ATP-CRA where the specimen obtained by ultrasound- guided percutaneous liver biopsy was used. After twelve cycles of oxaliplatincapecitabine chemotherapy, abdominopelvic computed tomography revealed marked shrinkage of the liver metastases and positron emission tomography showed no uptake of (18)F-fluoro-deoxy-glucose (FDG) either in the liver or peritoneum except localized uptake in the sigmoid colon. The patient underwent an anterior resection and radiofrequency ablation of the liver metastases, which resulted in a macroscopic curative resection of the cancer cells. Histological examination revealed no residual cancer cells in the resected specimen of the sigmoid colon. This result suggested that preoperative chemotherapy chosen by ATP-CRA may be useful for treating advanced colon cancer with unresectable liver and peritoneal metastases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenosine Triphosphate/*metabolism
Antineoplastic Agents/*pharmacology
Antineoplastic Combined Chemotherapy Protocols/therapeutic use
Colonic Neoplasms/*diagnosis/*drug therapy
Deoxycytidine/administration & dosage/analogs & derivatives
Fluorouracil/administration & dosage/analogs & derivatives
Humans
Liver Neoplasms/drug therapy/secondary
Male
Medical Oncology/methods
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Metastasis
Organoplatinum Compounds/administration & dosage
Positron-Emission Tomography
Remission Induction
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Clinical value of an adenosine triphosphate-based chemotherapy response assay in resectable stage III colorectal cancer
Chan Dong Kim, So Hyun Kim, Sang Hoon Jung, Jae Hwang Kim
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019;97(2):93-102. doi: 10.4174/astr.2019.97.2.93.Heterogeneity of Adenosine Triphosphate-Based Chemotherapy Response Assay in Colorectal Cancer - Secondary Publication
Jung Wook Huh, Yoon Ah Park, Kang Young Lee, Seung-Kook Sohn
Yonsei Med J. 2009;50(5):697-703. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.5.697.
Reference
-
1. Adam R, Delvart V, Pascal G, Valeanu A, Castaing D, Azoulay D, Giacchetti S, Paule B, Kunstlinger F, Ghemard O, Levi F, Bismuth H. Rescue surgery for unresectable colorectal liver metastases downstaged by chemotherapy: a model to predict long-term survival. Ann Surg. 2004. 240:644–657.2. Cortazar P, Johnson BE. Review of the efficacy of individualized chemotherapy selected by in vitro drug sensitivity testing for patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:1625–1631.
Article3. Moon YW, Choi SH, Kim YT, Sohn JH, Chang J, Kim SK, Park MS, Chung KY, Lee HJ, Kim JH. Adenosine triphosphate-based chemotherapy response assay (ATP-CRA)-guided platinum-based 2-drug chemotherapy for unresectable nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2007. 109:1829–1835.
Article4. Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Twelves C, Brunet R, Butts C, Conroy T, Debraud F, Figer A, Grossmann J, Sawada N, Schoffski P, Sobrero A, Van Cutsem E, Diaz-Rubio E. XELOX (capecitabine plus oxalipatin): active first-line therapy for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:2084–2091.5. Guillem JG, Puig-La Calle J Jr, Akhurst T, Tickoo S, Ruo L, Minsky BD, Gollub MJ, Kilmstra DS, Mazumdar M, Paty PB, Macapinlac H, Yeung H, Saltz L, Finn RD, Erdi Y, Humm J, Cohen AM, Larson S. Prospective assessment of primary rectal cancer response to preoperative radiation and chemotherapy using 18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000. 43:18–24.
Article6. Kaneki T, Koizumi T, Kawashima A, Tsushima K, Kubo K, Fujimoto K, Honda T, Akamatsu T. Double cancer (lung and colon cancer) that showed complete remission with irinotecan and cisplatin combined chemotherapy. J Gastroenterol. 2000. 35:864–869.
Article7. Brandi G, Pantaleo MA, Calabrese C, Di Battista M, Poggi R, Bajetta E, Biasco G. Complete remission of primary colon cancer in a metastatic patient treated with CPT-11 plus capecitabine. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2004. 19:599–602.
Article8. Huh JW, Park YA, Sohn SK, Choi SH. In-vitro chemosensitivity test for colorectal cancer using an adenosine-triphosphate-based chemotherapy response assay (ATP-CRA). J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2007. 23:172–179.
Article9. Meta-analysis Group in Cancer. Efficacy of intravenous continuous infusion of fluorouracil compared with bolus administration in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1998. 16:301–308.10. Goldberg RM, Sargent DJ, Morton RF, Fuchs CS, Ramanathan RK, Williamson SK, Findlay BP, Pitot HC, Alberts SR. A randomized controlled trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin combinations in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:23–30.
Article11. Tournigand C, Andre T, Achille E, Lledo G, Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D, Quinaux E, Couteau C, Buyse M, Ganem G, Landi B, Colin P, Louvet C, de Gramont A. FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:229–237.
Article12. Schrag D, Garewal HS, Burstein HJ, Samson DJ, Von Hoff DD, Somerfield MR. American Society of Clinical Oncology Technology Assessment: chemotherapy sensitivity and resistance assays. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:3631–3638.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- In Vitro Adenosine Triphosphate-Based Chemotherapy Response Assay as a Predictor of Clinical Response to Fluorouracil-Based Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Stage II Colorectal Cancer
- The Role of Chemotherapy Sensitivity and Resistance Assays in Ovarian Cancer
- Correlation between the molecular subtype of breast cancer and the in vitro adenosine triphosphate-based chemosensitivity assay
- Predictive Value of In Vitro Adenosine Triphosphate-Based Chemotherapy Response Assay in Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients Who Received Oral 5-Fluorouracil after Curative Resection
- The Results of the ATP Based Chemotherapy Response Assay in Gastric Cancer Tissues