J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Oct;23(5):814-818. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.5.814.
Quantitation of BK Virus DNA for Diagnosis of BK Virus-Associated Nephropathy in Renal Transplant Recipients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. mnkim@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1783066
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.5.814
Abstract
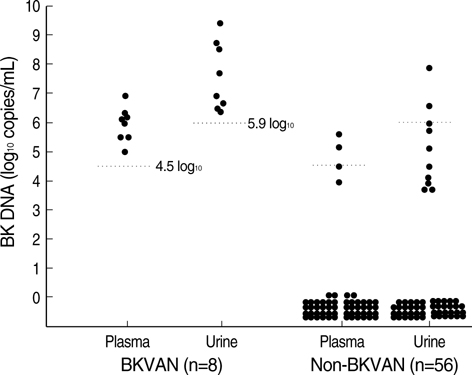
- Quantitative measurement of BK virus DNA (Q-BKDNA) has been used for the early diagnosis and monitoring of BK virus-associated nephropathy (BKVAN). This study was designed to determine the BKDNA cutoff for the diagnosis of BKVAN. Between June 2005 and February 2007, 64 renal transplant recipients taken renal biopsies due to renal impairment submitted plasma and urine for Q-BKDNA. Eight BKVAN patients (12.5%) had median viral loads of 6.0 log(10) copies/mL in plasma and 7.3 log(10) copies/mL in urine. Among 56 non-BKVAN patients, 45 were negative for Q-BKDNA; 4 were positive in plasma with a median viral load of 4.8 log(10) copies/ mL, and 10 were positive in urine with a median viral load of 4.8 log(10) copies/mL. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that a cutoff of 4.5 log(10) copies/mL in plasma and a cutoff of 5.9 log(10) copies/mL in urine had a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 96.4%, respectively. A combined cutoffs of 4 log(10) copies/ mL in plasma and 6 log(10) copies/mL in urine had better performance with a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 98.2% than each cutoff of urine or plasma. QBKDNA with the combined cutoffs could reliably diagnose BKVAN in renal transplant recipients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Randhawa P, Ho A, Shapiro R, Vats A, Swalsky P, Finkelstein S, Uhrmacher J, Weck K. Correlates of quantitative measurement of BK polyomavirus (BKV) DNA with clinical course of BKV infection in renal transplant patients. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:1176–1180.
Article2. Lin PL, Vats AN, Green M. BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients. Pediatr Transplant. 2001. 5:398–405.
Article3. Hirsch HH, Knowles W, Dickenmann M, Passweg J, Klimkait T, Mihatsch MJ, Steiger J. Prospective study of polyomavirus type BK replication and nephropathy in renal-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:488–496.
Article4. Hirsch HH. BK virus: opportunity makes a pathogen. Clin Infect Dis. 2005. 41:354–360.
Article5. Trofe J, Gordon J, Roy-Chaudhury P, Koralnik I, Atwood W, Eash S, Alloway RR, Khalili K, Alexander JW, Woodle ES. Basic and clinical research in polyomavirus nephropathy. Exp Clin Transplant. 2004. 2:162–173.6. Randhawa PS, Finkelstein S, Scantlebury V, Shapiro R, Vivas C, Jordan M, Picken MM, Demetris AJ. Human polyoma virus-associated interstitial nephritis in the allograft kidney. Transplantation. 1999. 67:103–109.7. Major EO, Ryschkewitsch C, Valsamakis A, Hou J. Murray PR, Baron EJ, Jorgensen JH, Landry ML, Pfaller MA, editors. Human polyomaviruses. Manual of clinical microbiology. 2007. 9th ed. Washington DC: ASM Press;1612–1621.8. Hirsch HH. Polyomavirus BK nephropathy: a (re-)emerging complication in renal transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2002. 2:25–30.
Article9. Nickeleit V, Hirsch HH, Binet IF, Gudat F, Prince O, Dalquen P, Thiel G, Mihatsch MJ. Polyomavirus infection of renal allograft recipients: from latent infection to manifest disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. 10:1080–1089.10. Mannon RB. Polyomavirus nephropathy: what have we learned? Transplantation. 2004. 77:1313–1318.11. Binet I, Nickeleit V, Hirsch HH, Prince O, Dalquen P, Gudat F, Mihatsch MJ, Thiel G. Polyomavirus disease under new immunosuppressive drugs: a cause of renal graft dysfunction and graft loss. Transplantation. 1999. 67:918–922.12. Lee WH, Kim BS, Jeong HJ, Kim YS, Kim HS. BK virus detection by polymerase chain reaction in renal transplant recipients and healthy donors. Korean J Lab Med. 2003. 23:263–267.13. Limaye AP, Jerome KR, Kuhr CS, Ferrenberg J, Huang ML, Davis CL, Corey L, Marsh CL. Quantitation of BK virus load in serum for the diagnosis of BK virus-associated nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 2001. 183:1669–1672.
Article14. Leung AY, Suen CK, Lie AK, Liang RH, Yuen KY, Kwong YL. Quantification of polyoma BK viruria in hemorrhagic cystitis complicating bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 2001. 98:1971–1978.
Article15. Basse G, Mengelle C, Kamar N, Guitard J, Ribes D, Esposito L, Rostaing L. Prospective evaluation of BK virus DNAemia in renal transplant patients and their transplant outcome. Transplant Proc. 2007. 39:84–87.
Article16. Ahuja M, Cohen EP, Dayer AM, Kampalath B, Chang CC, Bresnahan BA, Hariharan S. Polyoma virus infection after renal transplantation. Use of immunostaining as a guide to diagnosis. Transplantation. 2001. 71:896–899.17. Fogeda M, Munoz P, Luque A, Morales MD, Bouza E; BKV Study Group. Cross-sectional study of BK virus infection in pediatric kidney transplant recipients. Pediatr Transplant. 2007. 11:394–401.
Article18. Bressollette-Bodin C, Coste-Burel M, Hourmant M, Sebille V, Andre-Garnier E, Imbert-Marcille BM. A prospective longitudinal study of BK virus infection in 104 renal transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2005. 5:1926–1933.
Article19. Benavides CA, Pollard VB, Mauiyyedi S, Podder H, Knight R, Kahan BD. BK virus-associated nephropathy in sirolimus-treated renal transplant patients: incidence, course, and clinical outcomes. Transplantation. 2007. 84:83–88.
Article20. Tang YW, Sefers SE, Li H, Kohn DJ, Procop GW. Comparative evaluation of three commercial systems for nucleic acid extraction from urine specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:4830–4833.
Article21. Gardner SD, MacKenzie EF, Smith C, Porter AA. Prospective study of the human polyomaviruses BK and JC and cytomegalovirus in renal transplant recipients. J Clin Pathol. 1984. 37:578–586.
Article22. Hirsch HH, Steiger J. Polyomavirus BK. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003. 3:611–623.
Article23. Hirsch HH, Brennan DC, Drachenberg CB, Ginevri F, Gordon J, Limaye AP, Mihatsch MJ, Nickeleit V, Ramos E, Randhawa P, Shapiro R, Steiger J, Suthanthiran M, Trofe J. Polyomavirus-associated nephropathy in renal transplantation: interdisciplinary analyses and recommendations. Transplantation. 2005. 79:1277–1286.
Article24. Ramos E, Drachenberg CB, Portocarrero M, Wali R, Klassen DK, Fink JC, Farney A, Hirsch H, Papadimitriou JC, Cangro CB, Weir MR, Bartlett ST. BK virus nephropathy diagnosis and treatment: experience at the University of Maryland Renal Transplant Program. Clin Transpl. 2002. 143–153.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- BK Virus Detection by Polymerase Chain Reaction in Renal Transplant Recipients and Healthy Donors
- Treatment of Presumptive BK Nephropathy with Ciprofloxain in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Three Case Reports
- High-level viruria as a screening tool for BK virus nephropathy in renal transplant recipients
- Genotypes and Clinical Characteristics of BK Virus in Kidney Transplant Recipients
- Clinical Manifestations of BK Virus Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Single Center Experience