Yonsei Med J.
2008 Dec;49(6):965-972. 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.965.
Point Mutation of Hoxd12 in Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division in Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Department of Oral Biology, Research Center for Orofacial Hard Tissue Regeneration, Brain Korea 21 Project, Oral Science Research Center, College of Dentistry, Yonsei Center of Biotechnology, Yonsei Universit
- 2Department of Biochemistry, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Laboratory of Toxicogenomics, Korea Institute of Toxicology, Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology, Deajeon, Korea.
- KMID: 1782945
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.965
Abstract
- PURPOSE
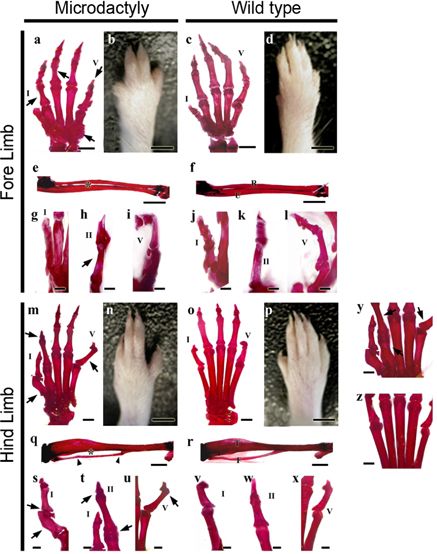
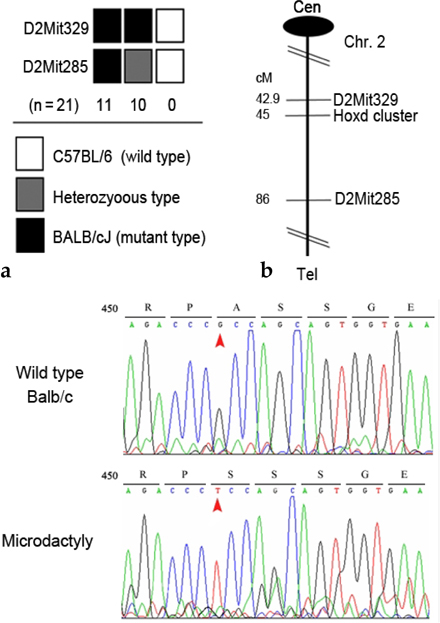
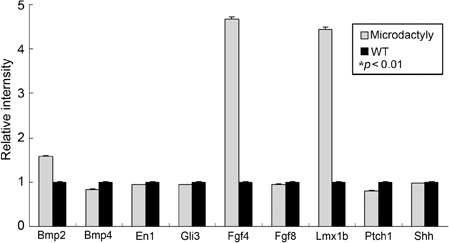
Genes of the HoxD cluster play a major role in vertebrate limb development, and changes that modify the Hoxd12 locus affect other genes also, suggesting that HoxD function is coordinated by a control mechanism involving multiple genes during limb morphogenesis. In this study, mutant phenotypes were produced by treatment of mice with a chemical mutagen, N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU). We analyzed mutant mice exhibiting the specific microdactyly phenotype and examined the genes affected. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We focused on phenotype characteristics including size, bone formation, and digit morphology of ENU-induced microdactyly mice. The expressions of several molecules were analyzed by genome-wide screening and quantitative real-time PCR to define the affected genes. RESULTS: We report on limb phenotypes of an ENU-induced A-to-C mutation in the Hoxd12 gene, resulting in alanine-to-serine conversion. Microdactyly mice exhibited growth defects in the zeugopod and autopod, shortening of digits, a missing tip of digit I, limb growth affected, and dramatic increases in the expressions of Fgf4 and Lmx1b. However, the expression level of Shh was not changed in Hoxd12 point mutated mice. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that point mutation rather than the entire deletion of Hoxd12, such as in knockout and transgenic mice, causes the abnormal limb phenotype in microdactyly mice. The precise nature of the spectrum of differences requires further investigation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Balling R. ENU mutagenesis: analyzing gene function in mice. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2002. 2:463–492.2. Clark AT, Bertram JF. Advances in renal development. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2000. 9:247–251.
Article3. Godinho SI, Nolan PM. The role of mutagenesis in defining genes in behaviour. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006. 14:651–659.
Article4. Niswander L. Pattern formation: old models out on a limb. Nat Rev Genet. 2003. 4:133–143.
Article5. Tickle C. Patterning systems--from one end of the limb to the other. Dev Cell. 2003. 4:449–458.
Article6. Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Harris MP, Simandl BK, Li Y, Beachy PA, et al. Manifestation of the limb prepattern: limb development in the absence of sonic hedgehog function. Dev Biol. 2001. 236:421–435.
Article7. Kraus P, Fraidenraich D, Loomis CA. Some distal limb structures develop in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog signaling. Mech Dev. 2001. 100:45–58.
Article8. Sanz-Ezquerro JJ, Tickle C. Digital development and morphogenesis. J Anat. 2005. 202:51–58.
Article9. Zhu J, Nakamura E, Nguyen MT, Bao X, Akiyama H, Mackem S. Uncoupling Sonic hedgehog control of pattern and expansion of the developing limb bud. Dev Cell. 2008. 14:624–632.
Article10. Zákány J, Kmita M, Duboule DA. A dual role for Hox genes in limb anterior-posterior asymmetry. Science. 2004. 304:1669–1672.11. Tarchini B, Duboule D. Control of Hoxd genes' collinearity during early limb development. Dev Cell. 2006. 10:93–103.12. Galis F, Kundrát M, Metz JA. Hox genes, digit identities and the theropod/bird transition. J Exp Zoolog B Mol Dev Evol. 2005. 304:198–205.13. Pera EM, Ikeda A, Eivers E, De Robertis EM. Integration of IGF, FGF, and anti-BMP signals via Smad1 phosphorylation in neural induction. Genes Dev. 2003. 17:3023–3028.14. Silver LM, editor. Classical linkage analysis and mapping panels. Mouse genetics: concepts and applications. 1995. New York: Oxford University Press;195–263.15. Quwailid MM, Hugill A, Dear N, Vizor L, Wells S, Horner E, et al. A gene-driven ENU-based approach to generating an allelic series in any gene. Mamm Genome. 2004. 15:585–591.
Article16. Patton EE, Zon LI. The art and design of genetic screens: zebrafish. Nat Rev Genet. 2001. 2:956–966.
Article17. Hérault Y, Beckers J, Kondo T, Fraudeau N, Duboule D. Genetic analysis of a Hoxd-12 regulatory element reveals global versus local modes of controls in the HoxD complex. Development. 1998. 125:1669–1677.
Article18. Rijli FM, Chambon P. Genetic interactions of Hox genes in limb development: learning from compound mutants. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1997. 7:481–487.
Article19. Zákány J, Duboule D. Synpolydactyly in mice with a targeted deficiency in the HoxD complex. Nature. 1996. 384:69–71.
Article20. Caronia G, Goodman FR, McKeown CM, Scambler PJ, Zappavigna V. An I47L substitution in the HOXD13 homeodomain causes a novel human limb malformation by producing a selective loss of function. Development. 2003. 130:1701–1712.
Article21. Dillon R, Gadgil C, Othmer HG. Short- and long-range effects of Sonic hedgehog in limb development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. 100:10152–10157.22. Drossopoulou G, Lewis KE, Sanz-Ezquerro JJ, Nikbakht N, McMahon AP, Hofmann C, et al. A model for anteroposterior patterning of the vertebrate limb based on sequential long- and short-range Shh signalling and Bmp signalling. Development. 2000. 127:1337–1348.
Article23. Davis AP, Capecchi MR. A mutational analysis of the 5' HoxD genes: dissection of genetic interactions during limb development in the mouse. Development. 1996. 122:1175–1185.
Article24. Knezevic V, De Santo R, Schughart K, Huffstadt U, Chiang C, Mahon KA, et al. Hoxd-12 differentially affects preaxial and postaxial chondrogenic branches in the limb and regulates Sonic hedgehog in a positive feedback loop. Development. 1997. 124:4523–4536.
Article25. Chen Y, Knezevic V, Ervin V, Hutson R, Ward Y, Mackem S. Direct interaction with Hoxd proteins reverses Gli3-repressor function to promote digit formation downstream of Shh. Development. 2004. 131:2339–2347.
Article26. Ngo-Muller V, Muneoka K. Influence of FGF4 on digit morphogenesis during limb development in the mouse. Dev Biol. 2000. 219:224–236.
Article27. Wada N, Kawakami Y, Nohno T. Sonic hedgehog signaling during digit pattern duplication after application of recombinant protein and expressing cells. Dev Growth Differ. 1999. 41:567–574.
Article28. Chen H, Johnson RL. Interactions between dorsal-ventral patterning genes lmx1b, engrailed-1 and wnt-7a in the vertebrate limb. Int J Dev Biol. 2002. 46:937–941.29. Omi M, Fisher M, Maihle NJ, Dealy CN. Studies on epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in vertebrate limb patterning. Dev Dyn. 2005. 233:288–300.
Article30. Sun X, Mariani FV, Martin GR. Functions of FGF signalling from the apical ectodermal ridge in limb development. Nature. 2002. 418:501–508.
Article31. Lu P, Minowada G, Martin GR. Increasing Fgf4 expression in the mouse limb bud causes polysyndactyly and rescues the skeletal defects that result from loss of Fgf8 function. Development. 2006. 133:33–42.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rapid and efficient identification of the mouse leptin receptor mutation (C57BL/KsJ-db/db) by tetra-primer amplification refractory mutation system-polymerase chain reaction (ARMS-PCR) analysis
- A Case of Leber's Hereditary Optic Nouropathy Showing 11778 Point Mutation of Mitochondrial DNA
- OPTN gene Mutation in Normal-Tension Glaucoma
- Patterns of p53 and H-ras Mutations related to Invasiveness and Differentiation of Transitional Cell Carcinoma in Human bladder
- Point mutation of c-K-ras oncogene and p21 protein expression of v-K-ras & v-H-ras of dimethylhydrazine-induced colon cancer in rats