Korean J Radiol.
2006 Jun;7(2):97-105. 10.3348/kjr.2006.7.2.97.
Radio Frequency Ablation in the Rabbit Lung Using Wet Electrodes: Comparison of Monopolar and Dual Bipolar Electrode Mode
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Research Institute of Clincal Medicine, Chonbuk, Korea. gyjin@chonbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of internal Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Research Institute of Clincal Medicine, Chonbuk, Korea.
- KMID: 1782182
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2006.7.2.97
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
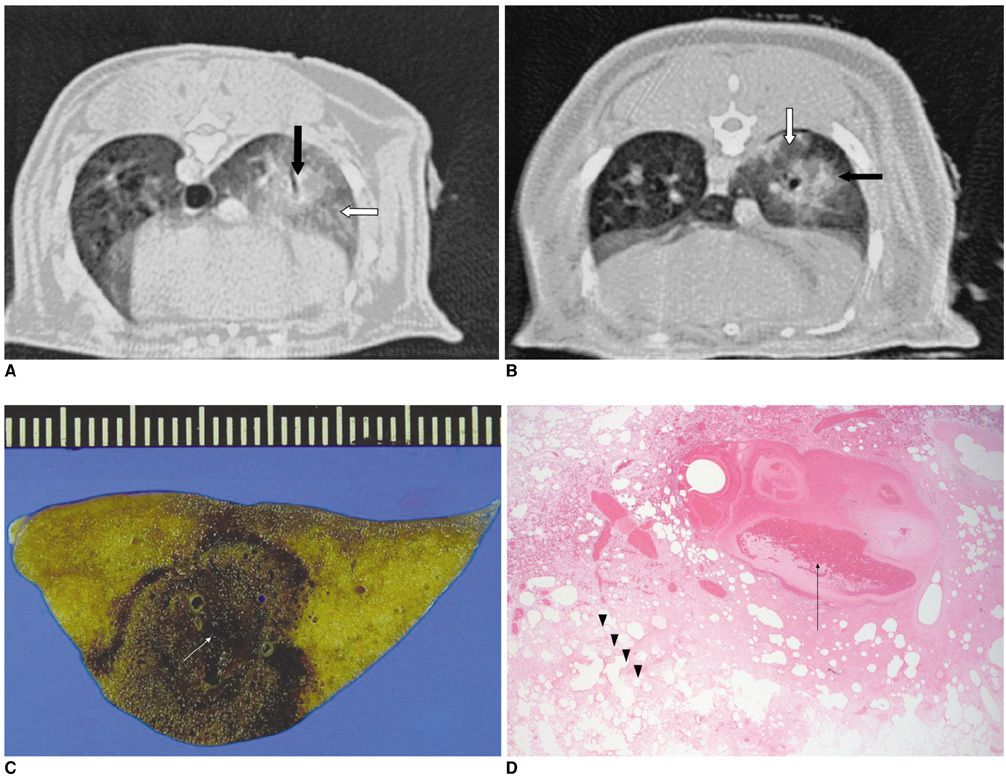
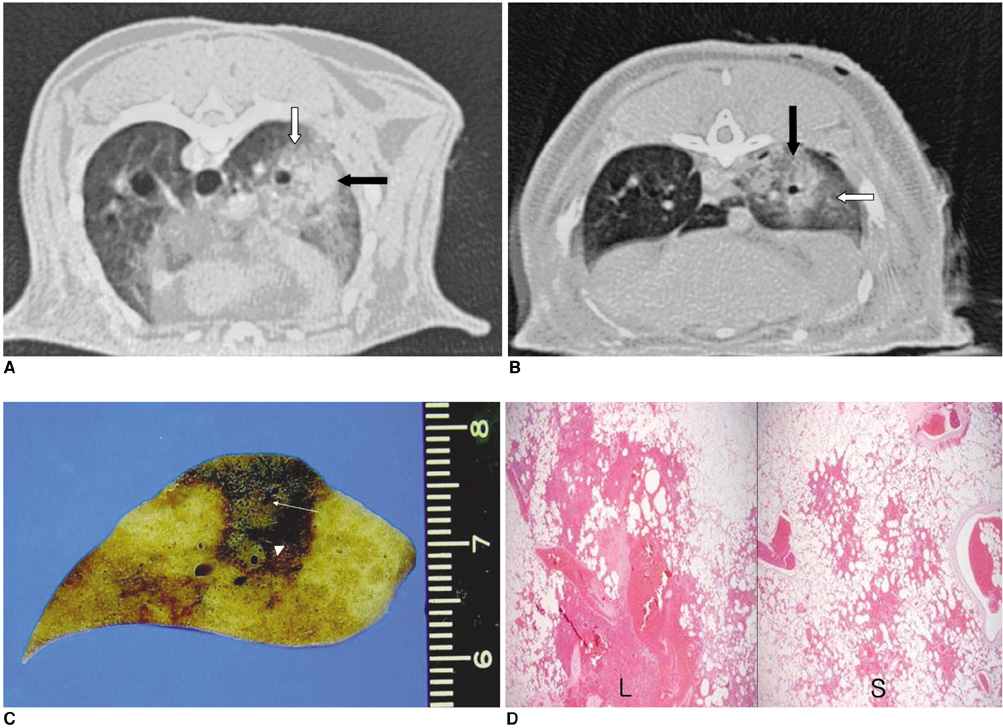
To compare the effect of radio frequency ablation (RFA) on the dimensions of radio frequency coagulation necrosis in a rabbit lung using a wet electrode in monopolar mode with that in dual electrode bipolar mode at different infusion rates (15 mm/hr versus 30 ml/hr) and saline concentrations (0.9% normal versus 5.8% hypertonic saline) . MATERIALS AND METHODS: Fifty ablation zones (one ablation zone in each rabbit) were produced in 50 rabbits using one or two 16-guage wet electrodes with a 1-cm active tip. The RFA system used in the monopolar and dual electrode wet bipolar RFA consisted of a 375-kHz generator (Elektrotom HiTT 106, Berchtold, Medizinelektronik, Germany). The power used was 30 watts and the exposure time was 5 minutes. The rabbits were assigned to one of five groups. Group A (n = 10) was infused with 0.9% NaCl used at a rate of 30 ml/hr in a monopolar mode. Groups B (n = 10) and C (n = 10) were infused with 0.9% NaCl at a rate of 15 and 30 ml/hr, respectively in dual electrode bipolar mode; groups D (n = 10) and E (n = 10) were infused with 5.8% NaCl at a rate of 15 and 30 ml/hr, respectively in a dual electrode bipolar mode. The dimensions of the ablation zones in the gross specimens from the groups were compared using one-way analysis of variance by means of the Scheffe test (post-hoc testing). RESULTS: The mean largest diameter of the ablation zones was larger in dual electrode bipolar mode (30.9+/-4.4 mm) than in monopolar mode (22.5+/-3.5 mm). The mean smallest diameter of the ablation zones was larger in dual electrode bipolar mode (22.3+/-2.5 mm) than in monopolar mode (19.5+/-3.5 mm). There were significant differences in the largest and smallest dimension between the monopolar (group A) and dual electrode wet bipolar mode (groups B-E). In dual electrode bipolar mode, the mean largest diameter of the ablation zones was larger at an infusion rate of 15 ml/hr (34.2+/-4.0 mm) than at 30 ml/hr (27.6+/-0.1 mm), and the mean smallest diameter of the ablation zones was larger at an infusion rate of 15 ml/hr (27.2+/-7.5 mm) than at an infusion rate of 30 ml/hr (24+/-2.9 mm). CONCLUSION: Using a wet electrode, dual electrode bipolar RFA can create a larger ablation zone more efficiently than monopolar RFA.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jin GY, Lee JM, Lee YC, Han YM, Lim YS. Primary and secondary lung malignancies treated with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: evaluation with follow-up helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:1013–1020.2. Jin GY, Lee JM, Lee YC, Han YM. Acute cerebral infarction after radiofrequency ablation of an atypical carcinoid pulmonary tumor. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 182:990–992.3. Lee JM, Jin GY, Goldberg SN, Lee YC, Chung GH, Han YM, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for inoperable non-small cell lung cancer and metastases: preliminary report. Radiology. 2004. 230:125–134.4. Belfiore G, Moggio G, Tedeschi E, Greco M, Cioffi R, Cincotti F, et al. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation: a potential complementary therapy for patients with unresectable primary lung cancer-a preliminary report of 33 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:1003–1011.5. Steinke K, King J, Glenn DW, Morris DL. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors with expandable needle electrodes: tips from preliminary experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:605–611.6. Gadaleta C, Mattioli V, Colucci G, Cramarossa A, Lorusso V, Canniello E, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of 40 lung neoplasms: preliminary results. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:361–368.7. Steinke K, Glenn D, King J, Clark W, Zhao J, Clingan P, et al. Percutaneous imaging-guided radiofrequency ablation in patients with colorectal pulmonary metastases: 1-year follow-up. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004. 11:207–212.8. Lee JM, Han JK, Kim SH, Shin KS, Lee JY, Park HS, et al. Comparison of wet radiofrequency ablation with dry radiofrequency ablation and radiofrequency ablation using hypertonic saline preinjection: ex vivo bovine liver. Korean J Radiol. 2004. 5:258–265.9. Lee JM, Kim SW, Li CA, Youk JH, Kim YK, Jin Z, et al. Saline-enhanced radiofrequency thermal ablation of the lung: a feasibility study in rabbits. Korean J Radiol. 2002. 3:245–253.10. Lee JM, Han JK, Kim SH, Sohn KL, Lee KH, Ah SK, et al. A comparative experimental study of the in-vitro efficiency of hypertonic saline-enhanced hepatic bipolar and monopolar radiofrequency ablation. Korean J Radiol. 2003. 4:163–169.11. Burdio F, Guemes A, Burdio JM, Castiella T, De Gregorio MA, Lozano R, et al. Hepatic lesion ablation with bipolar saline-enhanced radiofrequency in the audible spectrum. Acad Radiol. 1999. 6:680–686.12. Burdio F, Burdio JM, Navarro A, Ros P, Guemes A, Sousa R, et al. Electric influence of NaCl concentration into the tissue in radiofrequency ablation. Radiology. 2004. 232:932.13. Denys AL, De Baere T, Kuoch V, Dupas B, Chevallier P, Madoff DC, et al. Radio-frequency tissue ablation of the liver: in vivo and ex vivo experiments with four different systems. Eur Radiol. 2003. 13:2346–2352.14. Gazelle GS, Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Livraghi T. Tumor ablation with radio-frequency energy. Radiology. 2000. 217:633–646.15. Choi D, Lim HK, Kim MJ, Lee J, Kim SK, Kim EY, et al. Overlapping ablation using a coaxial radiofrequency electrode and multiple cannulae system: experimental study in ex-vivo bovine liver. Korean J Radiol. 2003. 4:117–123.16. Lee JM, Youk JH, Kim YK, Han YM, Chung GH, Lee SY, et al. Radio-frequency thermal ablation with hypertonic saline solution injection of the lung: ex vivo and in vivo feasibility studies. Eur Radiol. 2003. 13:2540–2547.17. Goldberg SN, Ahmed M, Gazelle GS, Kruskal JB, Huertas JC, Halpern EF, et al. Radio-frequency thermal ablation with NaCl solution injection: effect of electrical conductivity on tissue heating and coagulation-phantom and porcine liver study. Radiology. 2001. 219:157–165.18. Ni Y, Miao Y, Mulier S, Yu J, Baert AL, Marchal G. A novel "cooled-wet" electrode for radiofrequency ablation. Eur Radiol. 2000. 10:852–854.19. McGahan JP, Gu WZ, Brock JM, Tesluk H, Jones CD. Hepatic ablation using bipolar radiofrequency electrocautery. Acad Radiol. 1996. 3:418–422.20. Curley SA, Davidson BS, Fleming RY, Izzo F, Stephens LC, Tinkey P, et al. Laparoscopically guided bipolar radiofrequency ablation of areas of porcine liver. Surg Endosc. 1997. 11:729–733.21. Haemmerich D, Tungjitkusolmun S, Staelin ST, Lee FT Jr, Mahvi DM, Webster JG. Finite-element analysis of hepatic multiple probe radio-frequency ablation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2002. 49:836–842.22. Haemmerich D, Staelin ST, Tungjitkusolmun S, Lee FT Jr, Mahvi DM, Webster JG. Hepatic bipolar radio-frequency ablation between separated multiprong electrodes. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2001. 48:1145–1152.23. Miao Y, Ni Y, Yu J, Zhang H, Baert A, Marchal G. An ex vivo study on radiofrequency tissue ablation: increased lesion size by using an "expandable-wet" electrode. Eur Radiol. 2001. 11:1841–1847.24. Lobo SM, Afzal KS, Ahmed M, Kruskal JB, Lenkinski RE, Goldberg SN. Radiofrequency ablation: modeling the enhanced temperature response to adjuvant NaCl pretreatment. Radiology. 2004. 230:175–182.25. Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Solbiati L, Rittman WJ, Mueller PR. Radiofrequency tissue ablation: increased lesion diameter with a perfusion electrode. Acad Radiol. 1996. 3:636–644.26. Cosman ER, Nashold BS, Ovelman-Levitt J. Theoretical aspects of radiofrequency lesions in the dorsal root entry zone. Neurosurgery. 1984. 15:945–950.27. Burdio F, Guemes A, Burdio JM, Navarro A, Sousa R, Castiella T, et al. Bipolar saline-enhanced electrode for radiofrequency ablation: results of experimental study of in vivo porcine liver. Radiology. 2003. 229:447–456.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Saline-Enhanced Hepatic Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Perfused-Cooled Electrode: Comparison of Dual Probe Bipolar Mode with Monopolar and Single Probe Bipolar Modes
- A Comparative Experimental Study of the, In-vitro Efficiency of Hypertonic, Saline-Enhanced Hepatic Bipolar and, Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation
- Dual Switching Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Separable Clustered Electrode: Comparison with Consecutive and Switching Monopolar Modes in Ex Vivo Bovine Livers
- Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Dual-Switching System and a Separable Clustered Electrode: Evaluation of the In Vivo Efficiency
- Ablative Outcomes of Various Energy Modes for No-Touch and Peripheral Tumor-Puncturing Radiofrequency Ablation: An Ex Vivo Simulation Study