J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Sep;27(9):1037-1043. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.9.1037.
Suppressive Effect of 19-nor-1alpha-25-Dihydroxyvitamin D2 on Gastric Cancer Cells and Peritoneal Metastasis Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hematology-Oncology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. drwookyun@jnu.ac.kr
- 2Chonnam National University Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1782136
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.9.1037
Abstract
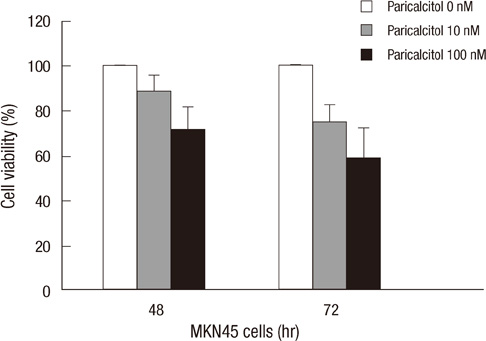
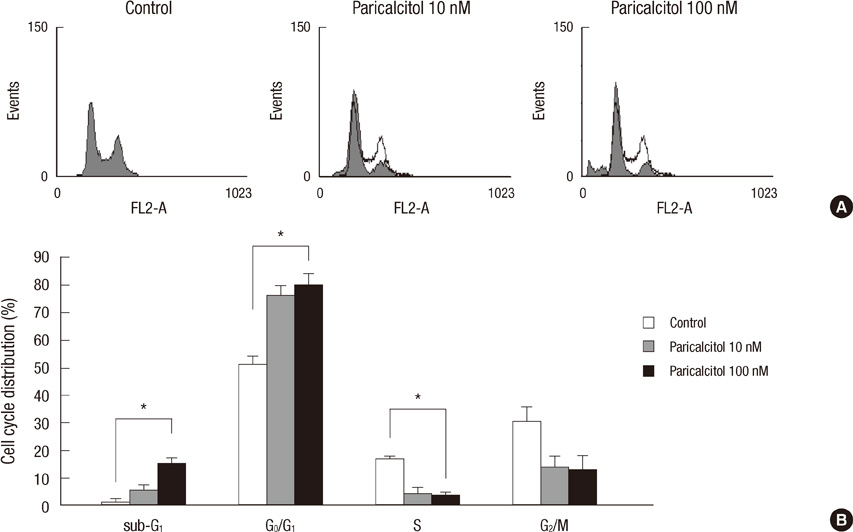
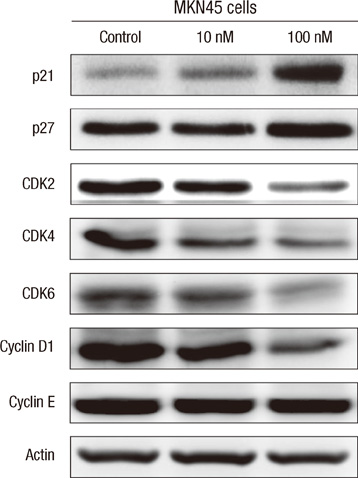
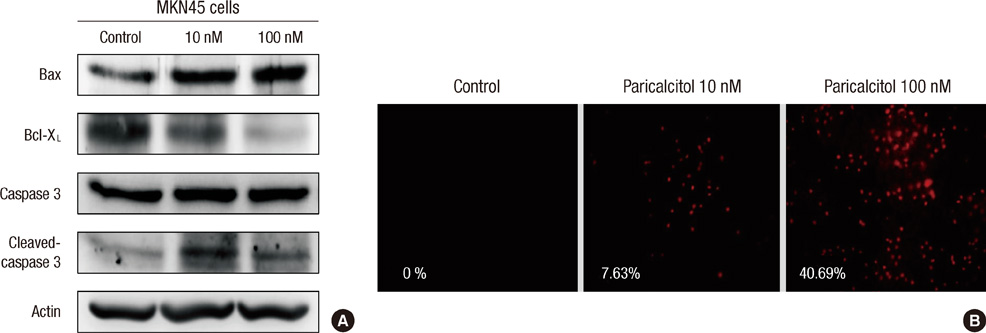
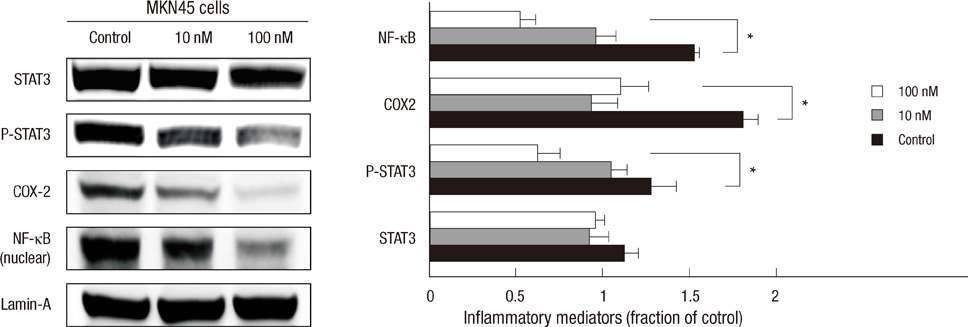
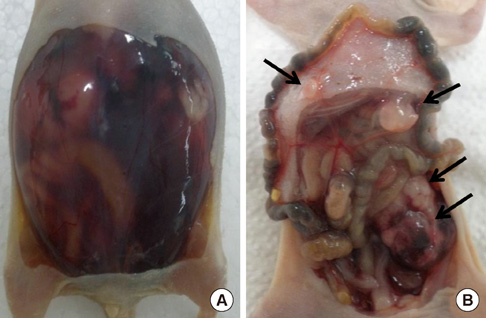
- The active metabolite of vitamin D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol), inhibits the growth of several types of human cancer cells in vitro, but its therapeutic use is limited because it causes hypercalcemia. Among its analogs, 19-nor-1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2 (paricalcitol), has fewer calcemic effects and exhibits an activity equipotent to that of calcitriol. We assessed the antitumor and anti-inflammatory effects of paricalcitol in gastric cancer cells, and evaluated the potential role of vitamin D in the treatment of peritoneal metastatic gastric cancer. In this study, treatment with paricalcitol inhibited gastric cancer cell growth and induced cell cycle arrest. Paricalcitol also induced apoptosis and showed anti-inflammatory activity. Moreover, the growth of intraperitoneal metastases in vivo was reduced in mice treated with paricalcitol. 18F-FDG uptake was significantly lower in the paricalcitol group compared to control group (SUV; control group 13.2 +/- 5.3 vs paricalcitol group 4.5 +/- 3.0). Intraperitoneal tumor volume was significantly lower in paricalcitol treated mice (control group 353.2 +/- 22.9 mm3 vs paricalcitol group 252.0 +/- 8.4 mm3). These results suggest that the vitamin D analog, paricalcitol, has anticancer activity on gastric cancer cells by regulation of the cell cycle, apoptosis, and inflammation.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antineoplastic Agents/chemistry/*pharmacology/therapeutic use
Apoptosis/drug effects
Cell Cycle Checkpoints/drug effects
Cell Cycle Proteins/metabolism
Cell Line, Tumor
Cell Proliferation/drug effects
Disease Models, Animal
Ergocalciferols/chemistry/*pharmacology/therapeutic use
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18/chemistry/diagnostic use
Humans
Mice
Mice, Inbred BALB C
Peritoneal Neoplasms/drug therapy/*secondary
Positron-Emission Tomography
Stomach Neoplasms/drug therapy/*pathology
Transplantation, Heterologous
Antineoplastic Agents
Cell Cycle Proteins
Ergocalciferols
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18
Figure
Reference
-
1. Reichel H, Koeffler HP, Norman AW. The role of the vitamin D endocrine system in health and disease. N Engl J Med. 1989. 320:980–991.2. Evans RM. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988. 240:889–895.3. Holick MF. Vitamin D: a millenium perspective. J Cell Biochem. 2003. 88:296–307.4. Carlberg C. Current understanding of the function of the nuclear vitamin D receptor in response to its natural and synthetic ligands. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2003. 164:29–42.5. Issa LL, Leong GM, Eisman JA. Molecular mechanism of vitamin D receptor action. Inflamm Res. 1998. 47:451–475.6. Christakos S, Raval-Pandya M, Wernyj RP, Yang W. Genomic mechanisms involved in the pleiotropic actions of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Biochem J. 1996. 316:361–371.7. Johnson CS, Hershberger PA, Trump DL. Vitamin D-related therapies in prostate cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2002. 21:147–158.8. Getzenberg RH, Light BW, Lapco PE, Konety BR, Nangia AK, Acierno JS, Dhir R, Shurin Z, Day RS, Trump DL, et al. Vitamin D inhibition of prostate adenocarcinoma growth and metastasis in the Dunning rat prostate model system. Urology. 1997. 50:999–1006.9. Shabahang M, Buras RR, Davoodi F, Schumaker LM, Nauta RJ, Evans SR. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor as a marker of human colon carcinoma cell line differentiation and growth inhibition. Cancer Res. 1993. 53:3712–3718.10. Colston KW, James SY, Ofori-Kuragu EA, Binderup L, Grant AG. Vitamin D receptors and anti-proliferative effects of vitamin D derivatives in human pancreatic carcinoma cells in vivo and in vitro. Br J Cancer. 1997. 76:1017–1020.11. Ylikomi T, Laaksi I, Lou YR, Martikainen P, Miettinen S, Pennanen P, Purmonen S, Syvala H, Vienonen A, Tuohimaa P. Antiproliferative action of vitamin D. Vitam Horm. 2002. 64:357–406.12. Mantell DJ, Owens PE, Bundred NJ, Mawer EB, Canfield AE. 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Circ Res. 2000. 87:214–220.13. Simboli-Campbell M, Narvaez CJ, Tenniswood M, Welsh J. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces morphological and biochemical markers of apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. 58:367–376.14. Gross C, Stamey T, Hancock S, Feldman D. Treatment of early recurrent prostate cancer with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol). J Urol. 1998. 159:2035–2039.15. Kubota T, Koshizuka K, Koike M, Uskokovic M, Miyoshi I, Koeffler HP. 19-nor-26,27-bishomo-vitamin D3 analogs: a unique class of potent inhibitors of proliferation of prostate, breast, and hematopoietic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1998. 58:3370–3375.16. Hisatake J, Kubota T, Hisatake Y, Uskokovic M, Tomoyasu S, Koeffler HP. 5,6-trans-16-ene-vitamin D3: a new class of potent inhibitors of proliferation of prostate, breast, and myeloid leukemic cells. Cancer Res. 1999. 59:4023–4029.17. Hisatake J, O'Kelly J, Uskokovic MR, Tomoyasu S, Koeffler HP. Novel vitamin D(3) analog, 21-(3-methyl-3-hydroxy-butyl)-19-nor D(3), that modulates cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, cell cycle, and induction of PTEN in leukemic cells. Blood. 2001. 97:2427–2433.18. Llach F, Keshav G, Goldblat MV, Lindberg JS, Sadler R, Delmez J, Arruda J, Lau A, Slatopolsky E. Suppression of parathyroid hormone secretion in hemodialysis patients by a novel vitamin D analogue: 19-nor-1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998. 32:S48–S54.19. Martin KJ, Gonzalez EA, Gellens M, Hamm LL, Abboud H, Lindberg J. 19-Nor-1-alpha-25-dihydroxyvitamin D2 (Paricalcitol) safely and effectively reduces the levels of intact parathyroid hormone in patients on hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998. 9:1427–1432.20. Liu M, Lee MH, Cohen M, Bommakanti M, Freedman LP. Transcriptional activation of the Cdk inhibitor p21 by vitamin D3 leads to the induced differentiation of the myelomonocytic cell line U937. Genes Dev. 1996. 10:142–153.21. Wang X, Studzinski GP. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) defines the first phase of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced differentiation of HL60 cells. J Cell Biochem. 2001. 80:471–482.22. Yang ZY, Perkins ND, Ohno T, Nabel EG, Nabel GJ. The p21 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor suppresses tumorigenicity in vivo. Nat Med. 1995. 1:1052–1056.23. Sherr CJ. Cancer cell cycles. Science. 1996. 274:1672–1677.24. Alexander WS. Suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS) in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002. 2:410–416.25. Kubo M, Hanada T, Yoshimura A. Suppressors of cytokine signaling and immunity. Nat Immunol. 2003. 4:1169–1176.26. Chen Z, Han ZC. STAT3: a critical transcription activator in angiogenesis. Med Res Rev. 2008. 28:185–200.27. Dong Z, Bonfil RD, Chinni S, Deng X, Trindade Filho JC, Bernardo M, Vaishampayan U, Che M, Sloane BF, Sheng S, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase activity and osteoclasts in experimental prostate cancer bone metastasis tissue. Am J Pathol. 2005. 166:1173–1186.28. Benevolo M, Mottolese M, Cosimelli M, Tedesco M, Giannarelli D, Vasselli S, Carlini M, Garofalo A, Natali PG. Diagnostic and prognostic value of peritoneal immunocytology in gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1998. 16:3406–3411.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- In Vitro Effects of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on the Production of Interleukin-1alpha by Ultraviolet B Irradiation in Cultured Human Keratinocyte Cell Line HaCaT Cells
- The Usefulness of Serum Tumor Markers as a Predictor of Peritoneal Metastasis in Patients with Gastric Carcinoma: CA 19-9 and CEA
- CD31 and D2-40 Contribute to Peritoneal Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer by Promoting Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
- A Clinical Analysis of the Characteristics of the Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients with Gastrics Cancer
- Effect of Radical Removal of Primary and Metastatic Lesions in Gastric Cancer with Peritoneal Seeding