J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Apr;21(2):236-241. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.236.
Surgical Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Isolated Synchronous Brain Metastases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jkim@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781828
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.236
Abstract
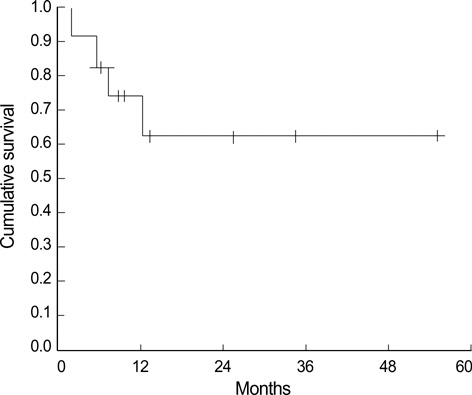
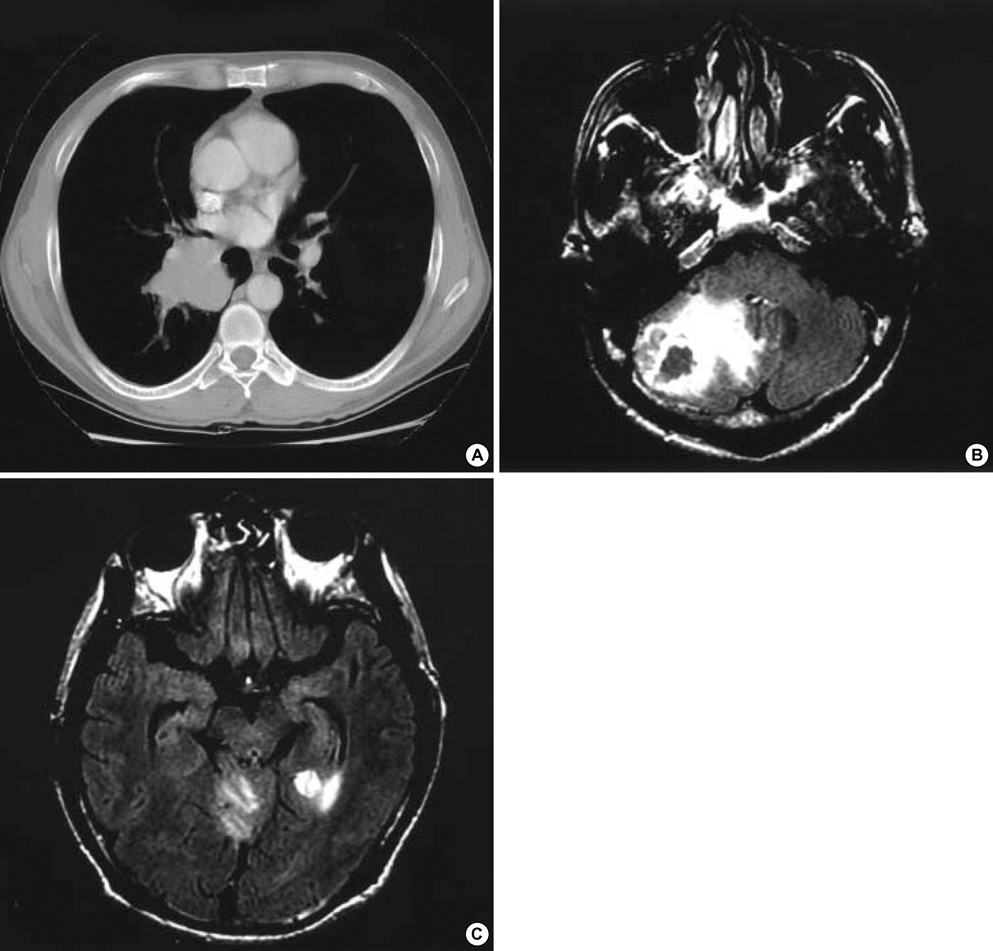
- This study is a retrospective examination of our experiences with patients who underwent treatment of isolated synchronous brain metastases coupled with primary non-small cell lung cancer. From January 1995 to June 2004, 12 patients presented with isolated synchronous brain metastases coupled with primary non-small cell lung cancer. The patient was comprised of 8 men and 4 women. The median age was 52 yr, in a range of 32 to 75 yr. Median follow-up duration was 10.6 months, in a range of 2 to 55.8 months. Recurrence developed in 7 patients, and the median interval from 1st treatment to recurrence was 4.5 months (2.8-6.5 months). The overall 1-yr survival rate was 61.7%. The 1-yr survival rates for pathologic N0 and N1 cases were 75% and 66.7%, respectively. The median survival duration for pathologic N2 was 6.2 months (95% CI, 4.8-7.5 months). The 1-yr survival rate for cases of single brain metastasis was 75%. Based on our current observations, we could speculate that aggressive management of primary non-small cell lung cancer and isolated synchronous brain metastases was beneficial in a selected group of patients, as long as the brain lesions and pulmonary lesions were limited or resectable.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Poggi MM, Sullivan FJ. Pass HI, Carbone DP, Johnson DH, Minna JD, Turrisi AT, editors. Palliative radiotherapy. Lung cancer principles and practice. 2005. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;777–793.2. Lee JL, Shin CJ, Kang HJ, Oh HA, Lee G, Choi JH, Bae SH, Lee KH, Hyun MS, Shin SO, Ryoo HM. Brain metastasis: Clinical characteristics and prognosis. Korean J Med. 2002. 62:444–452.3. Kelly K, Bunn PA Jr. Is it time to reevaluate our approach to the treatment of brain metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer? Lung Cancer. 1998. 20:85–91.
Article4. Horton J, Baxter DH, Olson KB. The management of metastases to the brain by irradiation and corticosteroids. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1971. 111:334–336.
Article5. Posner JB. Management of central nervous system metastases. Semin Oncol. 1977. 4:81–91.6. Penel N, Brichet A, Prevost B, Duhamel A, Assaker R, Dubois F, Lafitte JJ. Prognostic factors of synchronous brain metastases from lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2001. 33:143–154.7. Magilligan DJ Jr, Duvernoy C, Malik G, Lewis JW Jr, Knighton R, Ausman JI. Surgical approach to lung cancer with solitary cerebral metastasis: twenty-five years' experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1986. 42:360–364.
Article8. Read RC, Boop WC, Yoder G, Schaefer R. Management of non-small cell lung carcinoma with solitary brain metastasis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1989. 98:884–890.
Article9. Burt M, Wronski M, Arbit E, Galicich JH. Resection of brain metastases from non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Results of therapy. Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Thoracic Surgical Staff. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1992. 103:399–410.10. Mountain CF. Revisions in the International System for Staging Lung Cancer. Chest. 1997. 111:1710–1717.
Article11. Detterbeck FC, Jones DR, Molina PL. Detterbeck FC, Rivera MP, Socinski MA, Rosenman JG, editors. Extrathoracic staging. Diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer / an evidence-based guide for the practicing clinician. 2001. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co.;94–110.12. Hankins JR, Miller JE, Salcman M, Ferraro F, Green DC, Attar S, McLaughlin JS. Surgical management of lung cancer with solitary cerebral metastasis. Ann Thorac Surg. 1988. 46:24–28.
Article13. Macheers SK, Mansour KA. Management of isolated splenic metastases from carcinoma of the lung: a case report and review of the literature. Am Surg. 1992. 58:683–685.14. Macchiarini P, Buonaguidi R, Hardin M, Mussi A, Angeletti CA. Results and prognostic factors of surgery in the management of non-small cell lung cancer with solitary brain metastasis. Cancer. 1991. 68:300–304.
Article15. Bonnette P, Puyo P, Gabriel C, Giudicelli R, Regnard JF, Riquet M, Brichon PY. Groupe Thorax. Surgical management of non-small cell lung cancer with synchronous brain metastases. Chest. 2001. 119:1469–1475.
Article16. Olak J, Ferguson MK. Pass HI, Mitchell JB, Johnson DH, Turrisi AT, Minna JD, editors. Surgical management of second primary and metastatic lung cancer. Lung cancer: principles and practice. 2000. 2nd edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;730–741.17. Lang FF, Chang EL, Abi-said D, Wildrick DM, Sawaya R. Richard WH, Youmans JR, editors. Metastatic brain tumors. Neurological surgery. Vol. 1. 2004:5th edition. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger;1077–1097.
Article18. Loeffler JS, Alexander ER. Alexander E, Loeffler JS, Lunsford LD, editors. Radiosurgery for the treatment of intracranial metastases. Stereotactic radiosurgery. 1993. New York: McGraw-Hill;197–206.19. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD. Apuzzo MLJ, editor. Brain metastases. Brain surgery: complication avoidance and management. 1993. Vol. 1. New York: Churchill Livingstone;615–641.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiotherapy of Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer
- Outcome of Surgical Resection of Symptomatic Cerebral Lesions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Multiple Brain Metastases
- Clinical Analysis on the Brain Metastases of Bronchogenic Carcinoma
- Radiological and Histological Clues in the Diagnosis of Solitary and Synchronous Breast Metastasis From Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
- Prognosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Synchronous Brain Metastases Treated with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery