J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Oct;20(5):908-911. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.5.908.
Acrodermatitis Enteropathica-like Eruption Associated with Combined Nutritional Deficiency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Kangnam St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yymmpark@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Kangnam St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781784
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.5.908
Abstract
- We present here a case of acrodermatitis enteropathica-like eruption associated with essential free fatty acid and protein deficiencies as well as borderline zinc deficiency that occurred after Whipple's operation in a 31-yr-old woman. Her eruptions were improved not by zinc supplements alone, but her condition was improved by total parenteral nutrition including amino acids, albumin, lipid and zinc. Although we could not exactly decide which of the nutrients contributed the most to her manifestations, we inferred that all three elements in concert caused her dermatoses. This case shows that even though the patient's skin manifestations and laboratory results are suggestive of acrodermatitis enteropathica, the physicians should keep in mind the possibility that this disease can be associated with other nutritional deficiencies such as free fatty acid or protein deficiency.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
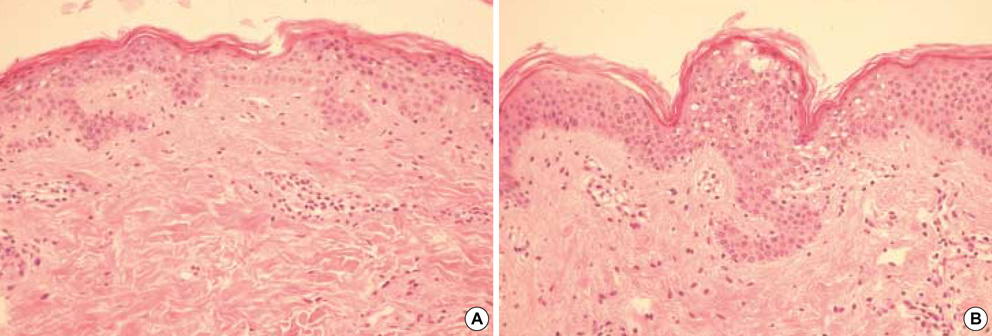
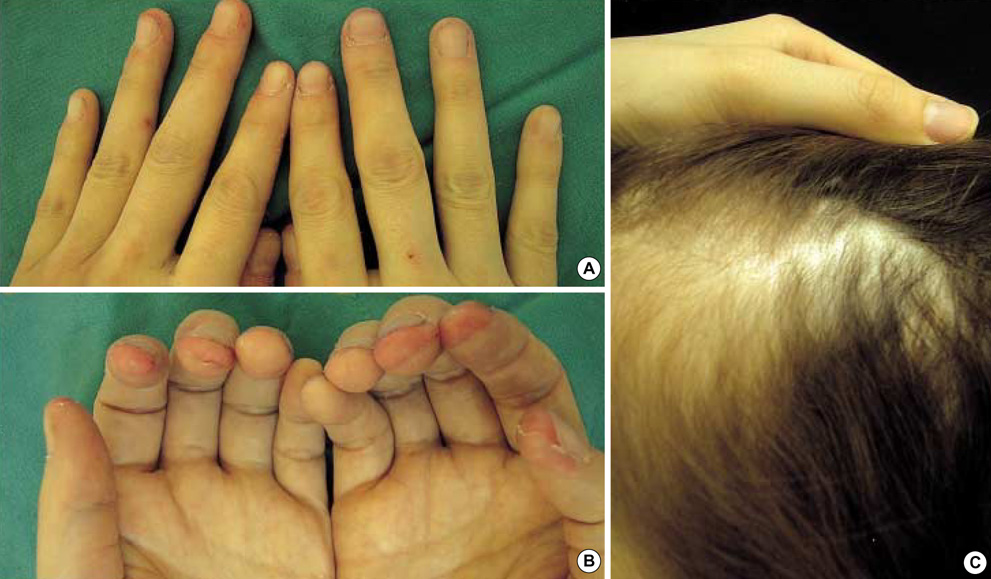
Figure
Reference
-
1. Perafan-Riveros C, Franca LF, Alves AC, Sanches JA Jr. Acrodermatitis enteropathica: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002. 19:426–431.2. Miller SJ. Nutritional deficiency and the skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989. 21:1–30.
Article3. Krasovec M, Frenk E. Acrodermatitis enteropathica secondary to Crohn's disease. Dermatology. 1996. 193:361–363.
Article4. Kim BC, Joo KR, Lee HS, Jeong YK, Suh HS, Kim DH, Park NM, Park JH. A case of chronic pancreatitis associated with liver infarction and acrodermatitis enteropathica. Korean J Intern Med. 2002. 17:263–265.
Article5. Sawai T, Sugiura H, Danno K, Uchiyama M, Ohta S. Acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica during chemotherapy for acute lymphocytic leukemia in a child with Down syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1996. 135:659–660.6. Jang MS, Kim YJ, Chae YS, Suh KS, Kim ST. A case of necrolytic migratory erythema induced by a pancreatic insufficiency. Korean J Dermatol. 1996. 34:166–170.7. Park MA, Ha SG, Won YH, Chun IK. A case of protein energy malnutrition after Whipple's operation. Korean J Dermatol. 1994. 32:130–133.8. Seo KH, Park JH, Jang HS, Kwon KS, Chung TA. A case of pseudoglucagonoma syndrome treated with medium-chain triglyceride. Korean J Dermatol. 1997. 35:593–599.9. Krieger J, Evans GW. Acrodermatitis enteropathica without hypozincemia: therapeutic effect of a pancreatic enzyme preparation due to zinc binding ligand. J Pediatr. 1980. 96:32–35.10. Neldner KN, Hambidge KM. Zinc therapy of acrodermatitis enteropathica. N Eng J Med. 1975. 292:879–882.
Article11. Kang JD, You DO, Park SD. A case of transient acrodermatitis enteropathica. Korean J Dermatol. 2003. 41:786–789.12. McLaren DS. Skin in protein energy malnutrition. Arch Dermatol. 1987. 123:1674–1676.
Article13. Hansen RC, Lynch PJ, Morrow GM. Proteolytic deficiency causing acrodermatitis enteropathica. Clin Res. 1976. 24:168.14. Golden MH, Golden BE, Jackson AA. Skin breakdown in kwashiorkor responds to zinc. Lancet. 1980. 1:1256.
Article15. Schreiner V, Gooris GS, Pfeiffer S, Lanzendorfer G, Wenck H, Diembeck W, Proksch E, Bouwstra J. Barrier characteristics of different human skin types investigated with X-ray diffraction, lipid analysis, and electron microscopy imaging. J Invest Dermatol. 2000. 114:654–660.
Article16. Lowe NJ, Stoughton RB. Essential fatty acid deficient hairless mouse: a model of chronic epidermal hyperproliferation. Br J Dermatol. 1977. 96:155–162.
Article17. Ziboh VA, Cho Y, Mani I, Xi S. Biological significance of essential fatty acids/prostanoids/lipoxygenase-derived monohydroxy fatty acids in the skin. Arch Pharm Res. 2002. 25:747–758.18. Ginsburg R, Robertson A Jr, Michel B. Acrodermatitis enteropathico: abnormalities of fat metabolism and integumental ultrastructures in infants. Arch Dermatol. 1976. 112:653–660.
Article19. Horrobin DF, Cunnane SC. Interactions between zinc, essential fatty acids and prostaglandins: relevance to acrodermatitis enteropathica, total parenteral nutrition, the glucagonoma syndrome, diabetes, anorexia nervosa and sickle cell anemia. Med Hypotheses. 1980. 6:277–296.20. Schroeter AL, Tucker SB, Minn R. Essential fatty acid deficiency. Arch Dermatol. 1978. 114:800–801.
Article21. Schwartz RA. Glucagonoma and pseudoglucagonoma syndromes. Int J Dermatol. 1997. 36:81–89.
Article22. Blackford S, Wright S, Robert DL. Necrolytic migratory erythema without glucagonoma: the role of dietary essential fatty acids. Br J Dermatol. 1991. 125:460–462.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Transient Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
- Acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica caused by zinc deficiency in a heavy drinker: A case report
- A Case of Acrodermatitis Enteropathica with Normal Serum Zinc Level in a Breastfed Preterm Infant
- A Case of Acrodermatitis Enteropathica Localized on the Hands and Feet with a Normal Serum Zinc Level
- A Case of Acquired Acrodermatitis Enteropathica Caused by Zinc Deficiency in a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patient