J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Oct;20(5):892-894. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.5.892.
Polypoid Endobronchial Lung Cyst with Bronchoscopic Removal: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. mdcspark@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pathology, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1781779
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.5.892
Abstract
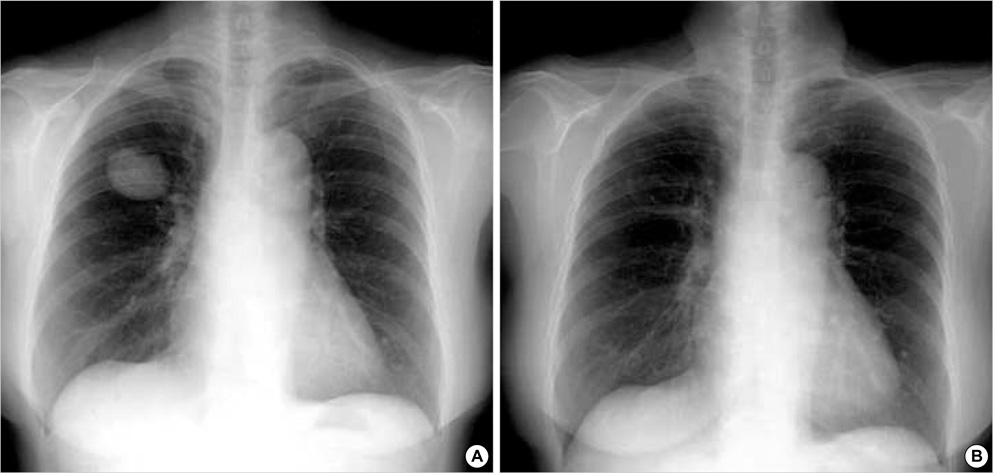
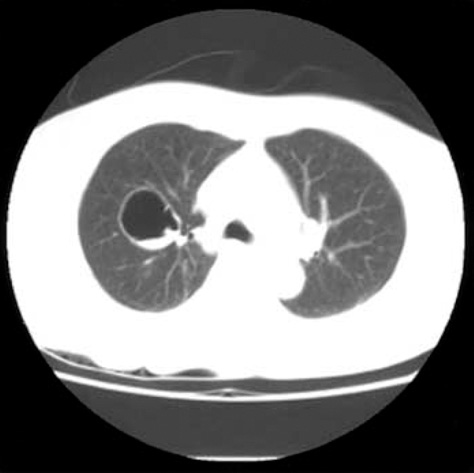
- Pulmonary bronchogenic cyst in adults is rare and the typical appearance is a sharply circumscribed, round or oval nodule or mass, usually in the medial third of the lungs. Bronchial polyps are rare histopathologically distinct nonneoplastic endobronchial lesions and are classified as multiple papillomas, solitary papillomas, and inflammatory polyps. We herein report a patient with polypoid endobronchial lung cyst. A 68-yr-old woman presented with a discomfort and pain in the right upper chest of four weeks' duration. Chest radiography revealed a cystic lesion in the right upper lung. Computed tomography revealed a 4x5 cm sized large cyst. Neither enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes nor extrabronchial involvements were observed. Flexible bronchoscopy revealed a peduncular polyp about 2 cm in length originating from the anterior segment of right upper lung. After bronchoscopic removal of polyp, cystic lesion of the right upper lung disappeared.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rogers LF, Osmer JC. Bronchogenic cyst: A review of 46 cases. Am J Roentgenol. 1964. 91:273–290.2. Ribet ME, Copin MC, Gosselin B. Bronchogenic cysts of the mediastinum. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1995. 109:1003–1010.
Article3. Dream JM, Douglas AC. Solitary papilloma of a bronchus. J Clin Pathol. 1965. 18:401–402.4. Beecham JE. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of peripheral congenital bronchial cyst. Acta Cytol. 1987. 32:663–666.5. Niimi A, Ikeda AT, Kubo Y, Tanaka E, Kuze F. Inflammatory bronchial polyps associated with asthma: resolution with inhaled corticosteroid. Eur Respir J. 1995. 8:1237–1239.
Article6. Roberts C, Devenny AM, Brooker R, Cockburn JS, Kerr KM. Inflammatory endobronchial polyposis with bronchiectasis in cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2001. 18:612–615.
Article7. Yong SJ, Won PS, Min KH, Soo KJ. A case of intratracheal polyp simulating asthma. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2002. 12:231–235.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of tumorous type of endobronchial tuberculosis simulating bronchial adenoma
- Endobronchial actinomycosis simulating endobronchial tuberculosis: a case report
- Endobronchial Chondroid Hamartoma Removed by Segmentectomy: Surgical Experience of One Case
- A Case of Endobronchial Carcinoid Tumor Treated by Flexible Bronchoscopic Resection
- Endobronchial Chondroid Hamartoma : A case report