J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Oct;20(5):821-828. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.5.821.
Adefovir Dipivoxil Alone or in Combination with Ongoing Lamivudine in Patients with Decompensated Liver Disease and Lamivudine-resistant Hepatitis B Virus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Centre, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. djsuh@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University International Hospital, University of Dongguk College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1781766
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.5.821
Abstract
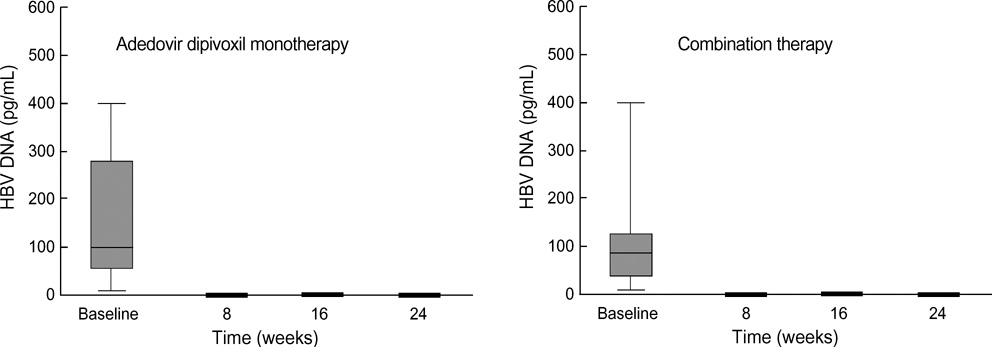
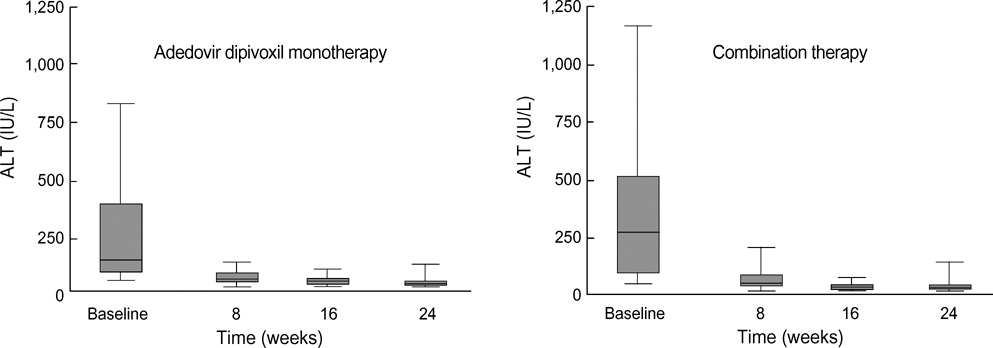
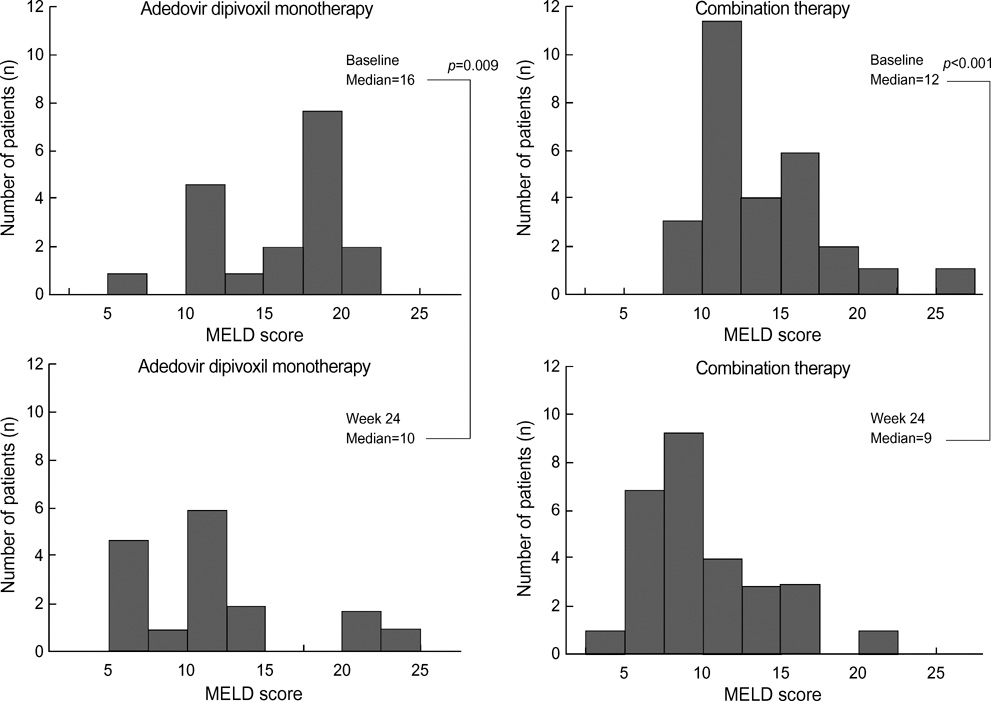
- The purpose of this prospective study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of adefovir dipivoxil with or without ongoing lamivudine in decompensated lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients. Forty-six hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-positive patients with decompensated liver function and lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus (HBV) were assigned to adefovir dipivoxil monotherapy (n=18) or combination therapy with ongoing lamivudine (n=28) according to their own preference. After 24 weeks of treatment, 83% of monotherapy and 86% of combination therapy showed serum HBV DNA below detection limit (<0.5 pg/mL). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) normalized in 78% and 82% respectively. Median Child-Pugh-Turcotte (CPT) score or Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score reduced significantly by 3 or 5 point in monotherapy and 2 or 2 point in combination therapy respectively. There were no significant differences in rate of undetectable serum HBV DNA, median change of ALT and median reduction of CPT or MELD scores between the two groups. In conclusion, both adefovir dipivoxil monotherapy and combination therapy with ongoing lamivudine result in comparable virologic, biochemical, and clinical improvements in HBeAg-positive patients with decompensated liver function and lamivudine-resistant HBV. Combination with lamivudine showed no additional benefit over monotherapy during 24 weeks of treatment in these patients.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenine/administration and dosage/*analogs and derivatives
Adolescent
Adult
Anti-HIV Agents/administration and dosage
Antiviral Agents/administration and dosage
Drug Combinations
Drug Resistance, Viral/drug effects
Female
Hepatitis B/*complications/*drug therapy
Humans
Lamivudine/*administration and dosage
Liver Cirrhosis/*etiology/*prevention and control
Male
Middle Aged
Phosphonic Acids/*administration and dosage
Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1997. 337:1733–1745.
Article2. Ganem D, Prince AM. Hepatitis B virus infection-natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:1118–1129.3. Conjeevaram HS, Lok AS. Management of chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2003. 38:Suppl 1. S90–S103.
Article4. Dienstag JL, Goldin RD, Heathcote EJ, Hann HW, Woessner M, Stephenson SL, Gardner S, Gray DF, Schiff ER. Histological outcome during long-term lamivudine therapy. Gastroenterology. 2003. 124:105–117.
Article5. Liaw YF, Sung JJ, Chow WC, Farrell G, Lee CZ, Yuen H, Tanwandee T, Tao QM, Shue K, Keene ON, Dixon JS, Gray DF, Sabbat J. Cirrhosis Asian Lamivudine Multicentre Study Group. Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2004. 351:1521–1531.
Article6. Jung S, Suh DJ, Park HJ, Park YH, Song HG, Lee HC, Chung YH, Lee YS. Therapeutic efficacy of lamivudine in patients with hepatitis B virus-related decompensated cirrhosis in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2002. 8:418–427.7. Kapoor D, Guptan RC, Wakil SM, Kazim SN, Kaul R, Agarwal SR, Raisuddin S, Hasnain SE, Sarin SK. Beneficial effects of lamivudine in hepatitis B virus-related decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2000. 33:308–312.
Article8. Hann HW, Fontana RJ, Wright T, Everson G, Baker A, Schiff ER, Riely C, Anschuetz G, Gardner SD, Brown N, Griffiths D. United States Lamivudine Compassionate Use Study Group. A United States compassionate use study of lamivudine treatment in nontransplantation candidates with decompensated hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis. Liver Transpl. 2003. 9:49–56.
Article9. Villeneuve JP, Condreay LD, Willems B, Pomier-Layrargues G, Fenyves D, Bilodeau M, Leduc R, Peltekian K, Wong F, Margulies M, Heathcote EJ. Lamivudine treatment for decompensated cirrhosis resulting from chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2000. 31:207–210.
Article10. Yao FY, Bass NM. Lamivudine treatment in patients with severely decompensated cirrhosis due to replicating hepatitis B infection. J Hepatol. 2000. 33:301–307.
Article11. Yao FY, Terrault NA, Freise C, Maslow L, Bass NM. Lamivudine treatment is beneficial in patients with severely decompensated cirrhosis and actively replicating hepatitis B infection awaiting liver transplantation: a comparative study using a matched, untreated cohort. Hepatology. 2001. 34:411–416.
Article12. Liaw YF, Leung NW, Chang TT, Guan R, Tai DI, Ng KY, Chien RN, Dent J, Roman L, Edmundson S, Lai CL. Effects of extended lamivudine therapy in Asian patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2000. 119:172–180.
Article13. Chang TT, Lai CL, Chien RN, Guan R, Lim SG, Lee CM, Ng KY, Nicholls GJ, Dent JC, Leung NW. Four years of lamivudine treatment in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. 19:1276–1282.
Article14. Wong VW, Chan HL, Wong ML, Tam JS, Leung NW. Clinical course after stopping lamivudine in chronic hepatitis B patients with lamivudine-resistant mutants. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004. 19:323–329.
Article15. Angus P, Locarnini S. Lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus and ongoing lamivudine therapy: stop the merry-go-round, it's time to get off! Antivir Ther. 2004. 9:145–148.16. Kagawa T, Watanabe N, Kanouda H, Takayama I, Shiba T, Kanai T, Kawazoe K, Takashimizu S, Kumaki N, Shimamura K, Matsuzaki S, Mine T. Fatal liver failure due to reactivation of lamivudine-resistant HBV mutant. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. 10:1686–1687.
Article17. Kim JW, Lee HS, Woo GH, Yoon JH, Jang JJ, Chi JG, Kim CY. Fatal submassive hepatic necrosis associated with tyrosine-methionine-aspartate-aspartate-motif mutation of hepatitis B virus after long-term lamivudine therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2001. 33:403–405.
Article18. Samuel D, Muller R, Alexander G, Fassati L, Ducot B, Benhamou JP, Bismuth H. Liver transplantation in European patients with the hepatitis B surface antigen. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:1842–1847.
Article19. Marcellin P, Chang TT, Lim SG, Tong MJ, Sievert W, Shiffman ML, Jeffers L, Goodman Z, Wulfsohn MS, Xiong S, Fry J, Brosgart CL. Adefovir Dipivoxil 437 Study Group. Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:808–816.
Article20. Hadziyannis SJ, Tassopoulos NC, Heathcote EJ, Chang TT, Kitis G, Rizzetto M, Marcellin P, Lim SG, Goodman Z, Wulfsohn MS, Xiong S, Fry J, Brosgart CL. Adefovir Dipivoxil 438 Study Group. Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:800–807.
Article21. Peters MG, Hann Hw, Martin P, Heathcote EJ, Buggisch P, Rubin R, Bourliere M, Kowdley K, Trepo C, Gray Df, Sullivan M, Kleber K, Ebrahimi R, Xiong S, Brosgart CL. Adefovir dipivoxil alone or in combination with lamivudine in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2004. 126:91–101.22. Schiff ER, Lai CL, Hadziyannis S, Neuhaus P, Terrault N, Colombo M, Tillmann HL, Samuel D, Zeuzem S, Lilly L, Rendina M, Villeneuve JP, Lama N, James C, Wulfsohn MS, Namini H, Westland C, Xiong S, Choy GS, Van Doren S, Fry J, Brosgart CL. Behalf of the Adefovir Dipovoxil Study 435 International Investigators Group. Adefovir dipivoxil therapy for lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B in pre- and post-liver transplantation patients. Hepatology. 2003. 38:1419–1427.
Article23. Perrillo R, Hann HW, Mutimer D, Willems B, Leung N, Lee WM, Moorat A, Gardner S, Woessner M, Bourne E, Brosgart CL, Schiff E. Adefovir dipivoxil added to ongoing lamivudine in chronic hepatitis B with YMDD mutant hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterology. 2004. 126:81–90.
Article24. Schiff E, Neuhaus P, Tillman HL, Samuel D, Terrault N, Marcellin P, Lama N. Safety and efficacy of adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of lamivudine resistant HBV in patients post liver transplantation [abstract]. Hepatology. 2001. 34:446A.25. Hong SP, Kim NK, Hwang SG, Chung HJ, Kim S, Han JH, Kim HT, Rim KS, Kang MS, Yoo W, Kim SO. Detection of hepatitis B virus YMDD variants using mass spectrometric analysis of oligonucleotide fragments. J Hepatol. 2004. 40:837–844.26. Murray KK. DNA sequencing by mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom. 1996. 31:1203–1215.
Article27. Chien RN, Liaw YF, Atkins M. Pretherapy alanine transaminase level as a determinant for hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion during lamivudine therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 1999. 30:770–774.
Article28. Lai CL, Chien RN, Leung NW, Chang TT, Guan R, Tai DI, Ng KY, Wu PC, Dent JC, Barber J, Stephenson SL, Gray DF. A one-year trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 1998. 339:61–68.
Article29. Honkoop P, de Man RA, Niesters HG, Zondervan PE, Schalm SW. Acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B virus infection after withdrawal of lamivudine therapy. Hepatology. 2000. 32:635–639.
Article30. Lai CL, Dienstag J, Schiff E, Leung NW, Atkins M, Hunt C, Brown N, Woessner M, Boehme R, Condreay L. Prevalence and clinical correlates chronic hepatitis B. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. 36:687–696.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of New Anti-viral Agent in the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B
- Application and Efficacy of Adefovir Dipivoxil in Hepatitis B Virus-assoicated Chronic Liver Diseases
- Efficacy and Safety of Adefovir Dipivoxil in Patients with Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis with Lamivudine Resistance Compared to Patients with Compensated Liver Disease
- Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of lamivudine resistant hepatitis B mutants
- Adefovir plus lamivudine combination therapy in lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B