Korean J Lab Med.
2010 Aug;30(4):388-393. 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.4.388.
Novel Influenza A (H1N1) Infection in Immunocompromised Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pathology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. kesong@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1781645
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.4.388
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Since April 2009, novel influenza A (H1N1) infection is spreading throughout the world. This infection might be fatal for immunocompromised patients who are at a potentially high risk of developing infectious complications. We investigated the detection rate and features of H1N1 infection in immunocompromised patients.
METHODS
Between August 2009 and February 2010, we examined 8,112 subjects, including 390 immunocompromised patients, for H1N1. Swab samples were taken from the nose and throat of the participants. Real-time PCR was performed to identify H1N1 viral genes.
RESULTS
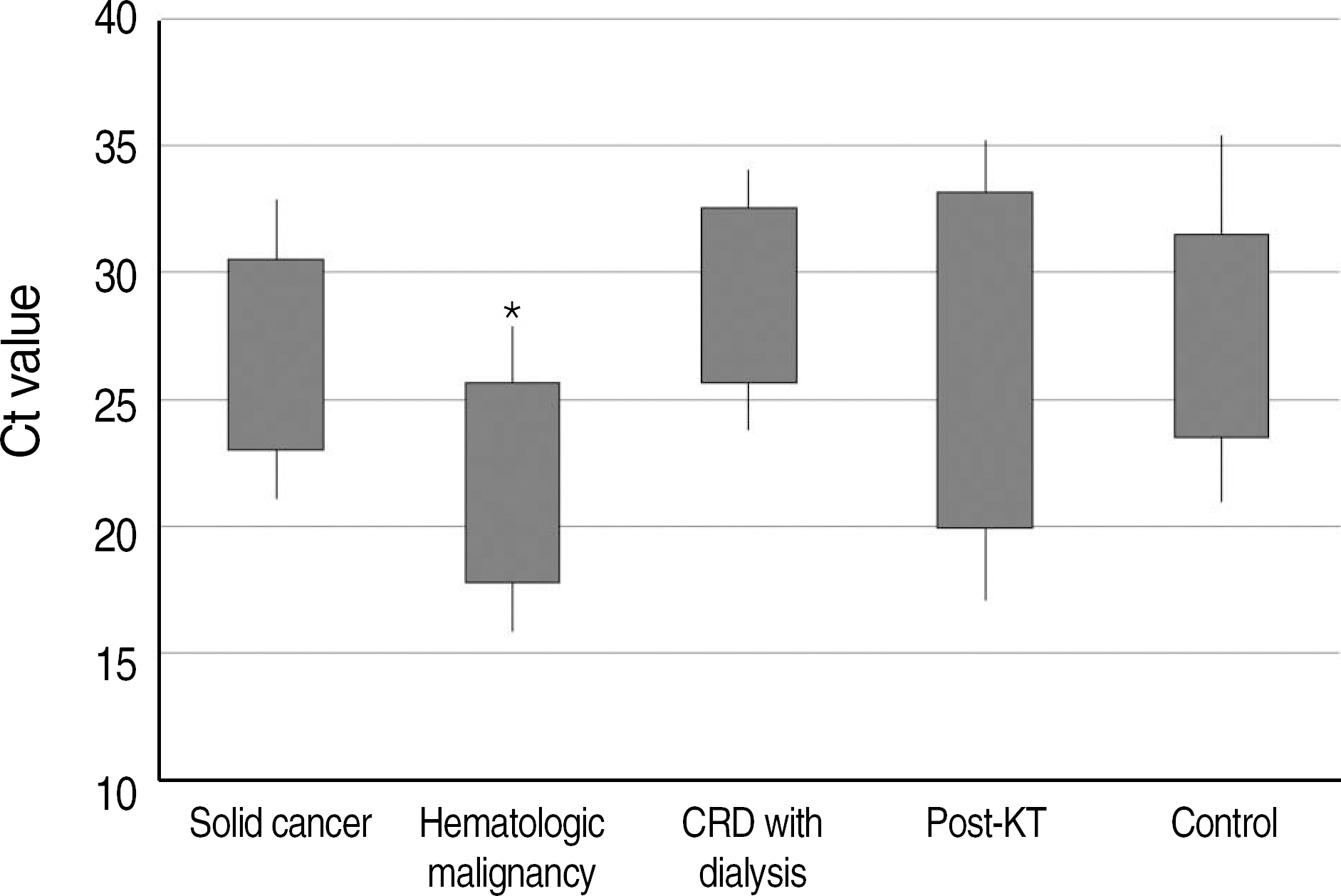
Positive results were obtained in 2,953/8,112 (36.4%) subjects and 46/390 (11.8%) immunocompromised patients. H1N1 was identified in 8.7% patients with solid cancer, 12.9% patients with hematologic malignancy, 16.7% patients with chronic renal disease, and 14.5% patients with kidney transplantation. The mean cycle threshold (Ct) value of PCR was significantly lower (P<0.05) in patients with hematologic malignancy as compared to that in patients with chronic renal disease and control subjects. Four patients died due to respiratory complications.
CONCLUSIONS
The detection rate of H1N1 was significantly lower in immunocompromised patients than in other patients. The Ct value of patients with hematologic malignancy was significantly lower than that of other immunocompromised patients and control subjects.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Child
Child, Preschool
Female
Humans
*Immunocompromised Host
Infant
Influenza A Virus, H1N1 Subtype/genetics/*isolation & purification
Influenza, Human/complications/*diagnosis/epidemiology
Kidney Failure, Chronic/complications
Leukemia/complications
Male
Middle Aged
Neoplasms/complications
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Prevalence of Seasonal Influenza Viruses and Pandemic H1N1 Virus in Beijing from 2008 to 2012
Shujuan Cui, Lili Tian, Xiaomin Peng, Guilan Lu, Weixian Shi, Dongmei Meng, Quanyi Wang
Ann Lab Med. 2012;32(6):455-456. doi: 10.3343/alm.2012.32.6.455.
Reference
-
1.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus infection - Mexico, March-April 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009. 58:467–70.2.Chan M. World now at the start of 2009 influenza pandemic. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/statements/2009/h1n1_pandemic_phase6_20090611/en. (Updated on Jun. 2009.3.Jain S., Kamimoto L., Bramley AM., Schmitz AM., Benoit SR., Louie J, et al. Hospitalized patients with 2009 H1N1 influenza in the United States, April-June 2009. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:1935–44.
Article4.Dawood FS., Jain S., Finelli L., Shaw MW., Lindstrom S., Garten RJ, et al. Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans. N Engl J Med. 2009. 360:2605–15.
Article5.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Surveillance for pediatric deaths associated with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus infection - United States, April-August 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009. 58:941–7.6.Kunisaki KM., Janoff EN. Influenza in immunosuppressed populations: a review of infection frequency, morbidity, mortality, and vaccine responses. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009. 9:493–504.
Article7.Lapinsky SE. H1N1 novel influenza A in pregnant and immuno-compromised patients. Crit Care Med. 2010. 38:e52–7.
Article8.Couch RB., Englund JA., Whimbey E. Respiratory viral infections in immunocompetent and immunocompromised persons. Am J Med. 1997. 102:2–9.9.Clements ML., Betts RF., Tierney EL., Murphy BR. Serum and nasal wash antibodies associated with resistance to experimental challenge with influenza A wild-type virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1986. 24:157–60.
Article10.Gooskens J., Jonges M., Claas EC., Meijer A., Kroes AC. Prolonged influenza virus infection during lymphocytopenia and frequent detection of drug-resistant viruses. J Infect Dis. 2009. 199:1435–41.
Article11.Chemaly RF., Ghosh S., Bodey GP., Rohatgi N., Safdar A., Keating MJ, et al. Respiratory viral infections in adults with hematologic malignancies and human stem cell transplantation recipients: a retrospective study at a major cancer center. Medicine (Baltimore). 2006. 85:278–87.12.Nichols WG., Guthrie KA., Corey L., Boeckh M. Influenza infections after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: risk factors, mortality, and the effect of antiviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 39:1300–6.
Article13.Redelman-Sidi G., Sepkowitz KA., Huang CK., Park S., Stiles J., Eagan J, et al. 2009 H1N1 influenza infection in cancer patients and hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. J Infect. 2010. 60:257–63.
Article14.Seiter K., Nadelman RB., Liu D., Ahmed T., Montecalvo MA. Novel influenza A (H1N1) in patients with hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2010. 28:e27–9.
Article15.Kharfan-Dabaja MA., Velez A., Richards K., Greene JN., Field T., Sandin R. Influenza A/pandemic 2009/H1N1 in the setting of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a potentially catastrophic problem in a vulnerable population. Int J Hematol. 2010. 91:124–7.
Article16.Watcharananan SP., Suwatanapongched T., Wacharawanichkul P., Chantratitaya W., Mavichak V., Mossad SB. Influenza A/H1N1 2009 pneumonia in kidney transplant recipients: characteristics and outcomes following high-dose oseltamivir exposure. Transpl Infect Dis. 2010. 12:127–31.
Article17.Kumar A., Zarychanski R., Pinto R., Cook DJ., Marshall J., Lacroix J, et al. Critically ill patients with 2009 influenza A(H1N1) infection in Canada. JAMA. 2009. 302:1872–9.
Article18.Gordon SM. Update on 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus. Cleve Clin J Med. 2009. 76:577–82.
Article19.Ginocchio CC., Zhang F., Manji R., Arora S., Bornfreund M., Falk L, et al. Evaluation of multiple test methods for the detection of the novel 2009 influenza A (H1N1) during the New York City outbreak. J Clin Virol. 2009. 45:191–5.
Article20.Kapelusznik L., Patel R., Jao J., Patel G., Daefler S., Labombardi V, et al. Severe pandemic (H1N1) 2009 influenza with false negative direct fluorescent antibody assay: case series. J Clin Virol. 2009. 46:279–81.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of High Dose Oseltamivir Treatment in an Influenza A (H1N1) Infected Patient with Severe Graft Versus Host Disease
- Influenza Associated Pneumonia
- Encephalitis Induced by 2009 H1N1 Influenza A
- Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and management of pandemic novel Influenza A (H1N1)
- Pandemic Influenza (H1N1) and Mycobacterium tuberculosis Co-infection