Korean J Lab Med.
2008 Dec;28(6):449-456. 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.6.449.
Production and Characterization of Anti-Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 Monoclonal Antibody
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. euichong@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Aerospace Medical Center, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 1781580
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.6.449
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
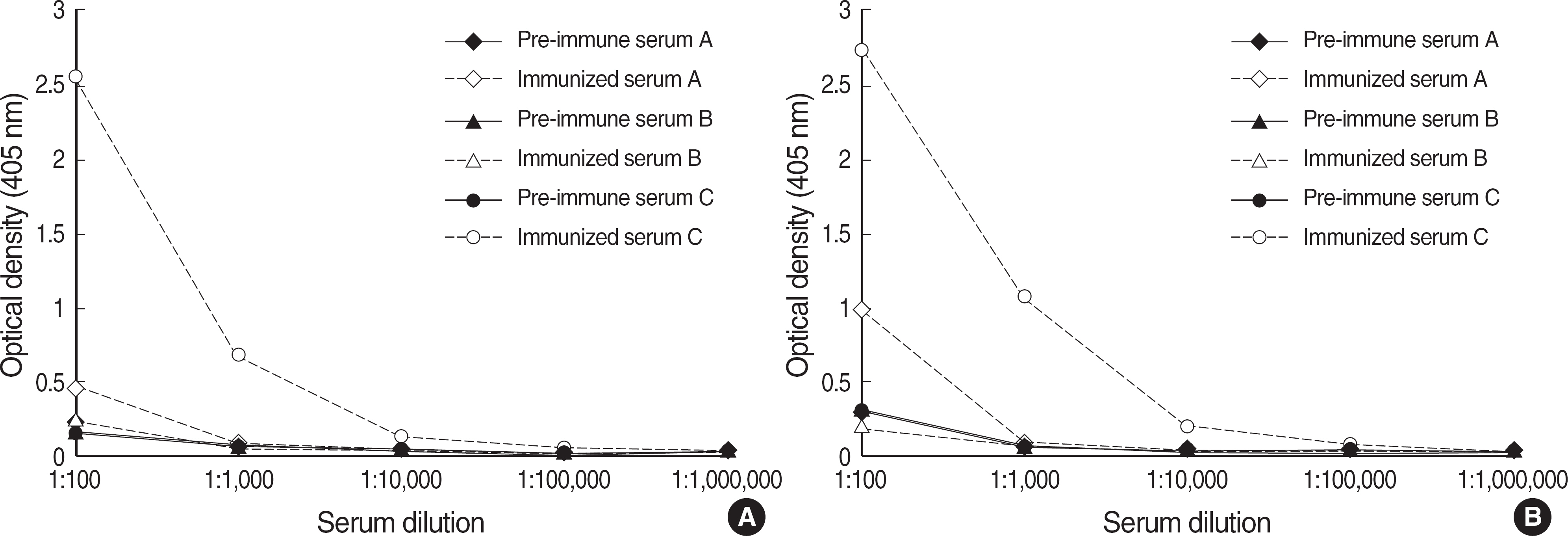
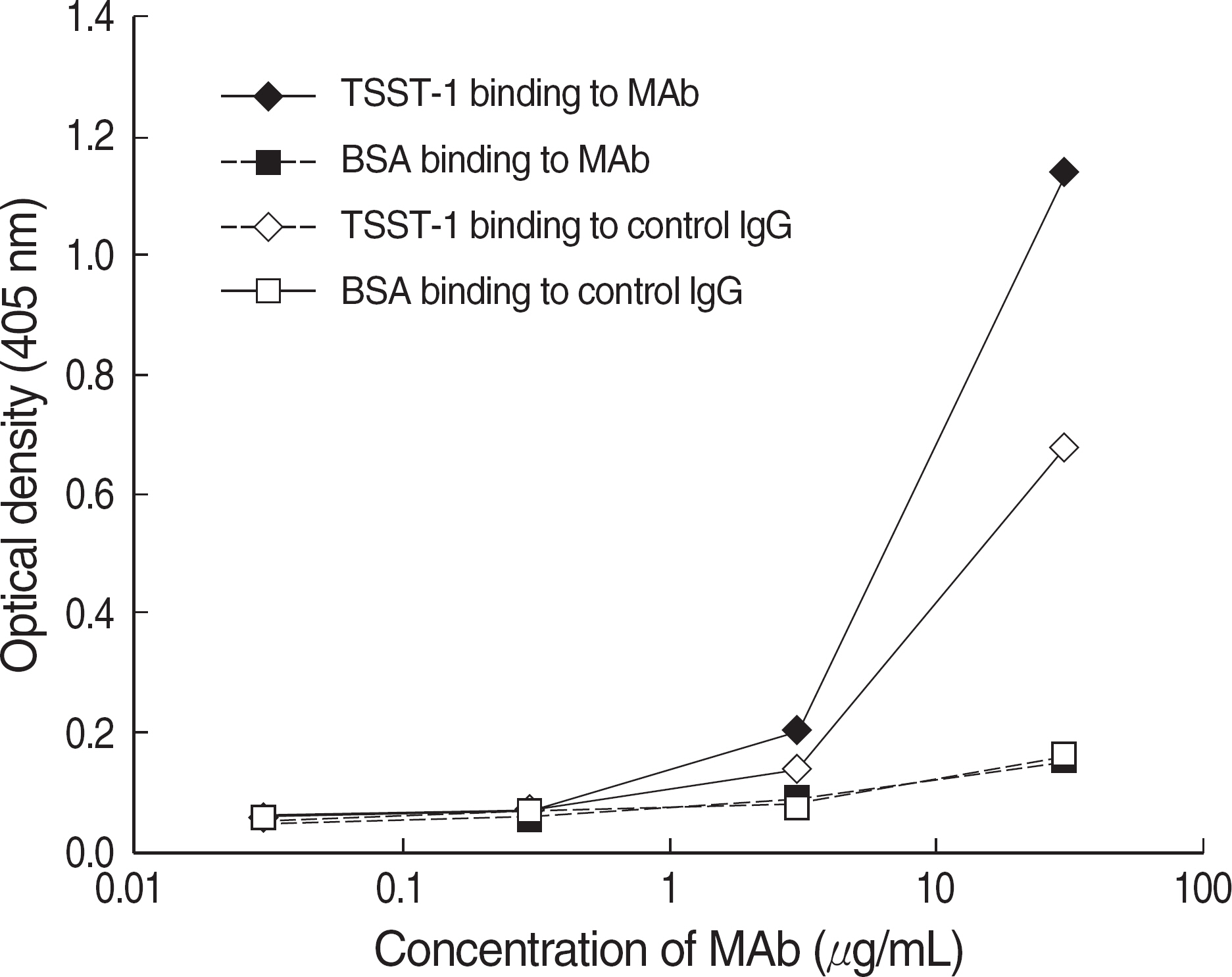
Recently the association between the virulence factors of Staphylococcus aureus and the outcome of the patients infected with the organism appears to be the subject of active investigation. Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) is thought to be a clinically more significant virulence factor than other staphylococcal toxins. We attempted to produce and characterize monoclonal antibodies to staphylococcal TSST-1. METHODS: An important epitope of TSST-1, amino acids 1-15 region, was synthesized into a peptide antigen, and Balb/c mice were immunized by intraperitoneal injection of the synthetic antigen. Hybridomas were produced by fusing immunized murine splenocytes with immortal myeloma cells. Hybridomas were cloned through a limiting dilution method. Stable cultured hybridoma was injected into the peritoneal cavity of Balb/c mice, and peritoneal fluid containing the monoclonal antibody was produced. RESULTS: One IgG2b type monoclonal antibody and two IgM type monoclonal antibodies were obtained. The IgG2b type monoclonal antibody was able to detect 5 microgram of TSST-1 with Western blot analysis and showed a strong reactivity to TSST-1 with ELISA. CONCLUSIONS: Highly immunoreactive anti-TSST-1 monoclonal antibody was produced by the use of synthesized peptide antigen. Diagnostic and protective capacity of this monoclonal antibody should be evaluated in the future.
MeSH Terms
-
Amino Acid Sequence
Animals
Antibodies, Monoclonal/biosynthesis/*immunology/isolation & purification
Bacterial Toxins/*immunology
Blotting, Western
Enterotoxins/*immunology
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Hybridomas/metabolism
Mice
Molecular Sequence Data
Peptides/chemical synthesis/pharmacology
Superantigens/*immunology
Figure
Reference
-
1.Hong SG., Lee JW., Yong DE., Kim EC., Jeong SH., Park YJ, et al. Antimicrobial resistance of clinically important bacteria isolated from 12 hospitals in Korea. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 7:171–7. (홍성근, 이종욱, 용동은, 김의종, 정석훈, 박연준 등. 국내 12개 병원의 임상검체에서 분리된 주요 세균의 항균제 내성율. 대한임상미생물학회지 2004;7: 171-7.).2.Lee HM., Yong DE., Lee KW., Hong SG., Kim EC., Jeong SH, et al. Antimicrobial resistance of clinically important bacteria isolated from 12 hospitals in Korea in 2004. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 8:66–73. (이혁민, 용동은, 이경원, 홍성근, 김의종, 정석훈등. 2004년도국내12개병원에서분리된주요세균의항균제내성율. 대한임상미생물학회지 2005;8: 66-73.).3.Kim JS., Kim HS., Song WK., Cho HC., Lee KM., Kim EC. Antimicrobial resistance profiles of Staphylococcus aureus isolated in 13 Korean hospitals. Korean J Lab Med. 2004. 24:223–9. (김재석, 김한성, 송원근, 조현찬, 이규만, 김의종. 국내 13개 의료기관에서 수집된 Staphylococcus aureus의 항균제 감수성 양상. 대한진단검사의학회지 2004;24: 223-9.).4.Deresinski S. Antistaphylococcal vaccines and immunoglobulins: current status and future prospects. Drugs. 2006. 66:1797–806.5.Shurland S., Zhan M., Bradham DD., Roghmann MC. Comparison of mortality risk associated with bacteremia due to methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2007. 28:273–9.6.Reed SD., Friedman JY., Engemann JJ., Griffiths RI., Anstrom KJ., Kaye KS, et al. Costs and outcomes among hemodialysis-dependent patients with methicillin-resistant or methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2005. 26:175–83.7.Cosgrove SE., Qi Y., Kaye KS., Harbarth S., Karchmer AW., Carmeli Y. The impact of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia on patient outcomes: mortality, length of stay, and hospital charges. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2005. 26:166–74.8.Kim JS., Kim HS., Song W., Cho HC., Lee KM., Kim EC. Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates with toxic shock syndrome toxin and Staphylococcal enterotoxin C genes. Korean J Lab Med. 2007. 27:118–23. (김재석, 김한성, 송원근, 조현찬, 이규만, 김의종. Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin과 Staphylococcal Enterotoxin C 유전자양성인메티실린내성Staphylococcus aureus 의분자생물학적유형분석. 대한진단검사의학회지 2007;27: 118-23.).9.Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990. 248:1066.
Article10.Acharya KR., Passalacqua EF., Jones EY., Harlos K., Stuart DI., Brehm RD, et al. Structural basis of superantigen action inferred from crystal structure of toxic-shock syndrome toxin-1. Nature. 1994. 367:94–7.
Article11.Prasad GS., Earhart CA., Murray DL., Novick RP., Schlievert PM., Ohlendorf DH. Structure of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. Biochemistry. 1993. 32:13761–6.
Article12.Jupin C., Anderson S., Damais C., Alouf JE., Parant M. Toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 as an inducer of human tumor necrosis factors and gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1988. 167:752–61.
Article13.Kum WW., Laupland KB., See RH., Chow AW. Improved purification and biologic activities of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1993. 31:2654–60.
Article14.Parsonnet J., Gillis ZA., Richter AG., Pier GB. A rabbit model of toxic shock syndrome that uses a constant, subcutaneous infusion of toxic shock syndrome that toxin 1. Infect Immun. 1987. 55:1070–6.15.Blanco L., Choi EM., Connolly K., Thompson MR., Bonventre PF. Mutants of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1: mitogenicity and recognition by a neutralizing monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1990. 58:3020–8.
Article16.Bonventre PF., Heeg H., Cullen C., Lian CJ. Toxicity of recombinant toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and mutant toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus in a rabbit infection model of toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1993. 61:793–9.17.Cullen CM., Blanco LR., Bonventre PF., Choi E. A toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 mutant that defines a functional site critical for T-cell activation. Infect Immun. 1995. 63:2141–6.
Article18.Deresiewicz RL., Woo J., Chan M., Finberg RW., Kasper DL. Mutations affecting the activity of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. Biochemistry. 1994. 33:12844–51.
Article19.Earhart CA., Mitchell DT., Murray DL., Pinheiro DM., Matsumura M., Schlievert PM, et al. Structures of five mutants of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 with reduced biological activity. Biochemistry. 1998. 37:7194–202.
Article20.Hurley JM., Shimonkevitz R., Hanagan A., Enney K., Boen E., Malmstrom S, et al. Identification of class II major histocompatibility complex and T cell receptor binding sites in the superantigen toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Exp Med. 1995. 181:2229–35.
Article21.Kum WW., Laupland KB., Chow AW. Defining a novel domain of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 critical for major histocompatibility complex class II binding, superantigenic activity and lethality. Can J Microbiol. 1999. 46:171–9.22.Gampfer JM., Samstag A., Waclavicek M., Wolf HM., Eibl MM., Gulle H. Epitope mapping of neutralizing TSST-1 specific antibodies induced by immunization with toxin or toxoids. Vaccine. 2002. 20:3675–84.
Article23.Yokoyama WM., Christensen M., Santos GD., Miller D. Production of monoclonal antibodies. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2006. ;Chapter 2: Unit 2.5.
Article24.Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975. 256:495–7.
Article25.Littlefield JW. Selection of hybrids from matings of fibroblasts in vitro and their presumed recombinants. Science. 1964. 145:709–10.
Article26.McKearn TJ. Cloning of hybridoma cells by limiting dilution in fluid phase. Kennett RH, McKearn TJ, editors. , eds.Monoclonal antibodies, Hybridomas: A new dimension in biological analysis. New York: Plenum Press;1980. p. 370.27.Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970. 227:680–5.
Article28.Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of protein from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some application. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1976. 76:4350–4.29.Lokker NA., Strittmatter U., Steiner C., Fagg B., Graff P., Kocher HP, et al. Mapping the epitopes of neutralizing anti-human IL-3 monoclonal antibodies. Implications for structure-activity relationship. J Immunol. 1991. 146:893–8.30.Wells DE., Reeves MW., McKinney RM., Graves LM., Olsvik O., Bergan T, et al. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and use of a monoclonal antibody in a rapid, one-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of picogram quantities of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1987. 25:516–21.
Article31.Best GK., Scott DF., Kling JM., Thompson MR., Adinolfi LE., Bonventre PF. Protection of rabbits in an infection model of toxic shock syndrome (TSS) by a TSS toxin-1-specific monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1988. 56:998–9.
Article32.Scott DF., Best GK., Kling JM., Thompson MR., Adinolfi LE., Bonventre PF. Passive protection of rabbits infected with toxic shock syndrome-associated strains of Staphylococcus aureus by monoclonal antibody to toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. Rev Infect Dis. 1989. 11(S):S214–8.33.Pang LT., Kum WW., Chow AW. Inhibition of staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced lymphocyte proliferation and tumor necrosis factor alpha secretion by MAb5, an anti-toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 2000. 68:3261–8.
Article34.Kum WW., Chow AW. Inhibition of staphylococcal enterotoxin A-induced superantigenic and lethal activities by a monoclonal antibody to toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. J Infect Dis. 2001. 183:1739–48.
Article35.Gilleland HE Jr., Hughes EE., Gilleland LB., Matthews-Greer JM., Staczek J. Use of synthetic peptides to identify surface-exposed, linear B-cell epitopes within outer membrane protein F of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Curr Microbiol. 1995. 31:279–86.36.Loh DY., Bothwell AL., White-Scharf ME., Imanishi-Kari T., Baltimore D. Molecular basis of a mouse strain-specific anti-hapten response. Cell. 1983. 33:85–93.
Article37.Solin ML., Kaartinen M., Mäkelä O. The same few V genes account for a majority of oxazolone antibodies in most mouse strains. Mol Immunol. 1992. 29:1357–62.
Article38.Mernaugh RL., Kaspar CW., Durand DP., Hill JH., Jones FE. A simple, efficient, standard-dilution method for cloning hybridomas. Biotechnol Tech. 1987. 1:31–3.
Article39.Miyazawa H., Bannai H., Yanase T., Morita C., Satoh S., Sugiyama J, et al. A reverse-sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for verocytotoxin 1 and 2 antibodies in human and bovine sera. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999. 6:701–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Group G Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome
- Prevalence of Antibody to Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 in Burn Patients
- A Case of Streptococcal Toxic Shock Like Syndrome with Pleural Effusion
- Correlation Between the Prevalence of Superantigenic Toxin Genes and Coagulase Serotypes of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates
- Toxic Shock Syndrome after Mastopexy and Augmentation Mammoplasty with Saline-Filled Mammary Implant