Application of Calculated Panel Reactive Antibody Using HLA Frequencies in Koreans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. ejoh@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1781440
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2012.32.1.66
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Introduction of the Luminex panel reactive antibody (PRA)-single antigen (SA) assay has increased the detection rates of unacceptable antigens in sensitized patients; the calculated PRA (CPRA) level represents the percentage of actual organ donors that express 1 or more of these unacceptable antigens. We developed a CPRA calculator based on the HLA frequencies in Koreans to measure sensitization levels in Korean patients.
METHODS
To develop the calculator, we obtained the HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-DR phenotypes of 1,622 Koreans, and compared these with previously reported frequencies in Koreans. Sera from patients awaiting kidney transplantation were tested for HLA antibodies by Luminex PRA-screen, PRA-identification (ID), and PRA-SA assays. The measured %PRA from the PRA-screen (N=55) and PRA-ID (N=71) were compared to the %CPRA for the unacceptable antigens obtained from PRA-SA.
RESULTS
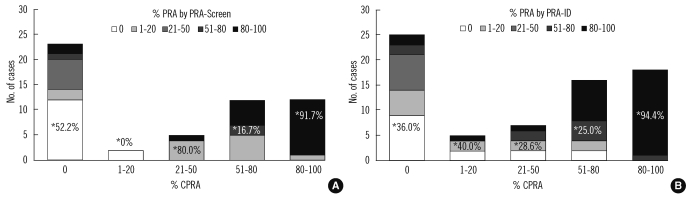
Phenotype frequencies used for the CPRA calculator agreed with previously reported data. The concordance rates among the 3 PRA methods for the detection of class I and class II antibodies were 76.1-81.8% (kappa, 0.519-0.636) and 72.7-83.6% (0.463-0.650), respectively. For the detection of broadly sensitized sera (>50% or >80%), the concordance rates were over 80%. In sera with 80-100% CPRA, 91.7% and 94.4% of the samples had concordant results (80-100% PRA) in the PRA-screen and PRA-ID assay, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Although further clinical studies are required to confirm the benefits of CPRA values, adoption of CPRA analysis based on HLA frequencies in Koreans may be useful for sensitization measurements and organ-allocation algorithms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Investigation of Serum Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antibodies at the Time of Renal Allograft Rejection
Hyeyoung Lee, Ji-Il Kim, In-Sung Moon, Byung Ha Chung, Chul-Woo Yang, Yonggoo Kim, Kyungja Han, Eun-Jee Oh
Ann Lab Med. 2015;35(3):314-320. doi: 10.3343/alm.2015.35.3.314.Kidney Allocation: Present Status and Future Strategy
Yeong Hoon Kim
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2016;30(1):1-5. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2016.30.1.1.Luminex-based Immunoassay for Organ Transplantation
Hyeyoung Lee, Eun-Jee Oh
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2015;29(2):54-60. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2015.29.2.54.Impact of Low-Level Donor-Specific Anti-HLA Antibody on Posttransplant Clinical Outcomes in Kidney Transplant Recipients
Haeun Lee, Hanbi Lee, Sang Hun Eum, Eun Jeong Ko, Ji-Won Min, Eun-Jee Oh, Chul Woo Yang, Byung Ha Chung
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(4):364-374. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.4.364.
Reference
-
1. Cecka JM, Kucheryavaya AY, Reinsmoen NL, Leffell MS. Calculated PRA: initial results show benefits for sensitized patients and a reduction in positive crossmatches. Am J Transplant. 2011; 11:719–724. PMID: 21114658.
Article2. Cecka JM. Calculated PRA (CPRA): the new measure of sensitization for transplant candidates. Am J Transplant. 2010; 10:26–29. PMID: 19958328.
Article3. Jung S, Oh EJ, Yang CW, Ahn WS, Kim Y, Park YJ, et al. Comparative evaluation of ELISA and Luminex panel reactive antibody assays for HLA alloantibody screening. Korean J Lab Med. 2009; 29:473–480. PMID: 19893358.
Article4. Bray RA, Gebel HM. Strategies for human leukocyte antigen antibody detection. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2009; 14:392–397. PMID: 19610172.
Article5. Howell WM, Carter V, Clark B. The HLA system: immunobiology, HLA typing, antibody screening and crossmatching techniques. J Clin Pathol. 2010; 63:387–390. PMID: 20418230.
Article6. Roh EY, Kim HS, Kim SM, Lim YM, Han BY, Park MH. HLA-A, -B, -DR allele frequencies and haplotypic associations in Koreans defined by generic-level DNA typing. Korean J Lab Med. 2003; 23:420–430.7. Whang DH, Yang YS, Hong HK. Allele and haplotype frequencies of human leukocyte antigen-A, -B, and -DR loci in Koreans: DNA typing of 1,500 cord blood units. Korean J Lab Med. 2008; 28:465–474. PMID: 19127112.
Article8. Raymond M, Rousset F. GENEPOP (version 1.2): population genetics software for exact tests and ecumenicism. J Hered. 1995; 86:248–249.
Article9. Rousset F. Genepop'007: a complete re-implementation of the genepop software for Windows and Linux. Mol Ecol Resour. 2008; 8:103–106. PMID: 21585727.
Article10. Zachary AA, Montgomery RA, Leffell MS. Defining unacceptable HLA antigens. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2008; 13:405–410. PMID: 18685337.
Article11. Lee KW, Kim YS. Serologic ambiguity and allelic frequency of the HLA-B40 family in the Korean population. Tissue Antigens. 1997; 49:383–388. PMID: 9151390.
Article12. Lee KW, Oh DH, Lee C, Yang SY. Allelic and haplotypic diversity of HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1, and -DQB1 genes in the Korean population. Tissue Antigens. 2005; 65:437–447. PMID: 15853898.
Article13. Kerman R, Lappin J, Kahan B, Katz S, McKissick E, Hosek K, et al. The crossmatch may still be the most clinically relevant histocompatibility test performed. Clin Transpl. 2007; 227–229. PMID: 18642454.14. Kerman RH. Understanding the sensitized patient. Heart Fail Clin. 2007; 3:1–9. PMID: 17545004.
Article15. Phelan D, Mohanakumar T, Ramachandran S, Jendrisak MD. Living donor renal transplantation in the presence of donor-specific human leukocyte antigen antibody detected by solid-phase assay. Hum Immunol. 2009; 70:584–588. PMID: 19477211.
Article16. Aubert V, Venetz JP, Pantaleo G, Pascual M. Low levels of human leukocyte antigen donor-specific antibodies detected by solid phase assay before transplantation are frequently clinically irrelevant. Hum Immunol. 2009; 70:580–583. PMID: 19375474.
Article17. Ho EK, Vasilescu ER, Colovai AI, Stokes MB, Hallar M, Markowitz GS, et al. Sensitivity, specificity and clinical relevance of different cross-matching assays in deceased-donor renal transplantation. Transpl Immunol. 2008; 20:61–67. PMID: 18929659.
Article18. Bray RA, Murphey C, Schaub S. Calculated PRA: a process whose time has come or 'Déjà vu' all over again? Am J Transplant. 2011; 11:650–651. PMID: 21401870.
Article19. Vaidya S, Hilson B, Sheldon S, Cano P, Fernandez-Vina M. DP reactive antibody in a zero mismatch renal transplant pair. Hum Immunol. 2007; 68:947–949. PMID: 18191721.
Article20. Goral S, Prak EL, Kearns J, Bloom RD, Pierce E, Doyle A, et al. Preformed donor-directed anti-HLA-DP antibodies may be an impediment to successful kidney transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008; 23:390–392. PMID: 17956891.
Article21. Bray RA, Nolen JD, Larsen C, Pearson T, Newell KA, Kokko K, et al. Transplanting the highly sensitized patient: The emory algorithm. Am J Transplant. 2006; 6:2307–2315. PMID: 16939516.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of NIH-CDC and AHG-CDC methods for the Detection of Panel Reactive Antibodies
- HLA-A, B Antibodies in Korean Pregnant Women
- Evaluation of In-house Lymphocyte Panel of 72 Wells for the Identification of HLA Antibody Specificity
- HLA-DR Antigens and HLA-B: DR Haplotypes in Koreans
- Performance Analysis of Panel Reactive Antibody Test by Lambda Antigen Tray Kit using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay