Ann Lab Med.
2013 Mar;33(2):145-149. 10.3343/alm.2013.33.2.145.
Rothia mucilaginosa Pneumonia Diagnosed by Quantitative Cultures and Intracellular Organisms of Bronchoalveolar Lavage in a Lymphoma Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. mnkim@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781316
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2013.33.2.145
Abstract
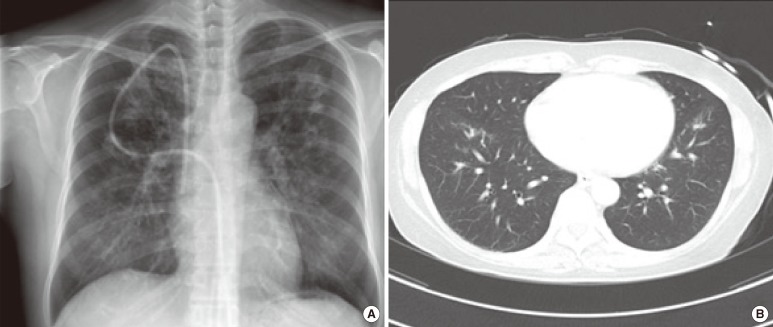
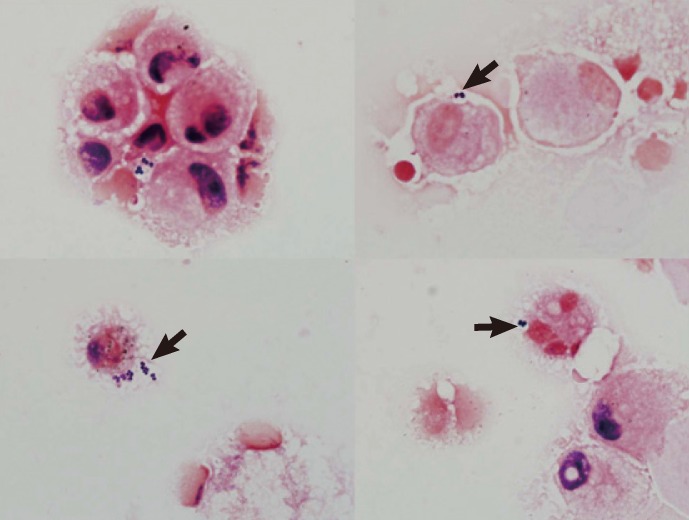
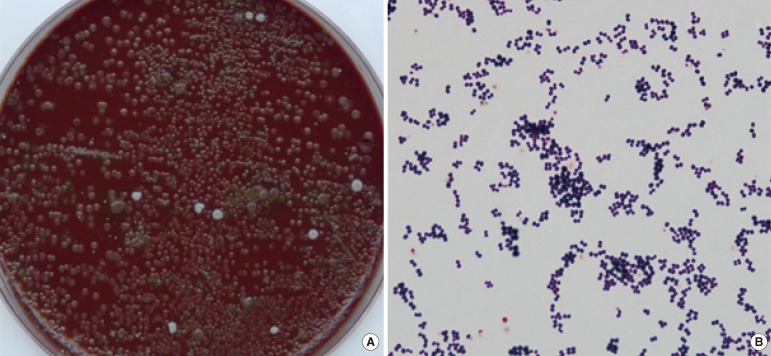
- Rothia mucilaginosa is a gram-positive coccus of the family Micrococcaceae. R. mucilaginosa is considered a part of the normal flora of the human oropharynx and upper respiratory tract and lower respiratory tract infections attributable to R. mucilaginosa are not frequent. We present a case of pneumonia, in which the R. mucilaginosa infection was diagnosed by quantitative cultures of a bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) specimen. A 46-yr-old woman with B lymphoblastic lymphoma was admitted to the hospital for scheduled chemotherapy. Her chest computed tomography (CT) scan revealed bilateral multifocal nodular and patchy consolidation in both lungs. Investigation of the BAL specimen revealed that 7% of leukocytes had intracellular gram-positive cocci. The quantitative cultures of the BAL specimen grew mucoid, non-hemolytic, and grayish convex colonies on blood agar at a count of approximately 200,000 colony-forming units/mL. The colonies were identified as R. mucilaginosa. The patient was empirically treated with levofloxacin for 7 days, after which findings on the chest radiograph and CT scan improved. She was discharged with improvement on hospital day 46. To our knowledge, this is the first report of R. mucilaginosa pneumonia diagnosed in Korea. Quantitative culture of BAL specimen and examination of intracellular organisms are crucial for assessing the clinical significance of R. mucilaginosa recovered from the lower respiratory tract.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Becker K, von Eiff C. Becker K, Christof von EIFF, Bernard KA, Carroll KC, Versalovic J, editors. Staphylococcus, Micrococcus and other catalase-positive cocci. Manual of clinical microbiology. 2011. 10th ed. Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology;p. 308–330.2. Rubin SJ, Lyons RW, Murcia AJ. Endocarditis associated with cardiac catheterization due to a Gram-positive coccus designated Micrococcus mucilaginosus incertae sedis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978; 7:546–549. PMID: 670378.3. Faiad G, Singh M, Narasimhan A, Mendez M, Shama S, Nassar N. Rothia mucilaginosa life threatening infections in non-neutropenic hosts. Open J Intern Med. 2011; 1:68–71.4. Ascher DP, Zbick C, White C, Fischer GW. Infections due to Stomatococcus mucilaginosus: 10 cases and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1991; 13:1048–1052. PMID: 1775836.5. Treviño M, García-Zabarte A, Quintás A, Varela E, López-Paz JM, Jato A, et al. Stomatococcus mucilaginosus septicemia in a patient with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998; 17:505–507. PMID: 9764554.6. Korsholm TL, Haahr V, Prag J. Eight cases of lower respiratory tract infection caused by Stomatococcus mucilaginosus. Scand J Infect Dis. 2007; 39:913–917. PMID: 17886126.7. Lambotte O, Debord T, Soler C, Roué R. Pneumonia due to Stomatococcus mucilaginosus in an AIDS patient: case report and literature review. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1999; 5:112–114. PMID: 11856231.8. Sánchez-Carrillo C, Cercenado E, Cibrián F, Bouza E. Stomatococcus mucilaginosus pneumonia in a liver-transplant patient. Clin Microbiol Newsl. 1995; 16:150–151.9. Cunniffe JG, Mallia C, Alcock PA. Stomatococcus mucilaginosus lower respiratory tract infection in a patient with AIDS. J Infect. 1994; 29:327–330. PMID: 7884227.10. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for antimicrobial dilution and disk susceptibility testing of infrequently isolated or fastidious bacteria; Approved guideline 2nd ed, M45-A2. 2010. Wayne, PA: Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute;p. 18–19.11. Cantral DE, Tape TG, Reed EC, Spurzem JR, Rennard SI, Thompson AB. Quantitative culture of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for the diagnosis of bacterial pneumonia. Am J Med. 1993; 95:601–607. PMID: 8259777.
Article12. Allaouchiche B, Jaumain H, Dumontet C, Motin J. Early diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Is it possible to define a cutoff value of infected cells in BAL fluid? Chest. 1996; 110:1558–1565. PMID: 8989077.13. Torres A, El-Ebiary M, Fábregas N, Gonzáilez J, de la Bellacasa JP, Hernández C, et al. Value of intracellular bacteria detection in the diagnosis of ventilator associated pneumonia. Thorax. 1996; 51:378–384. PMID: 8733489.
Article14. Solé-Violán J, Rodríguez de Castro F, Rey A, Martín-González JC, Cabrera-Navarro P. Usefulness of microscopic examination of intracellular organisms in lavage fluid in ventilator-associated pneumonia. Chest. 1994; 106:889–894. PMID: 8082373.
Article15. Horan TC, Andrus M, Dudeck MA. CDC/NHSN surveillance definition of health care-associated infection and criteria for specific types of infections in the acute care setting. Am J Infect Control. 2008; 36:309–332. PMID: 18538699.
Article16. Garcia LS, Isenberg HD, editors. Clinical microbiology procedures handbook. 2010. 1:3rd ed. Washington DC: ASM Press;3.11.2.173.11.2.20-7.17. von Eiff C, Herrmann M, Peters G. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Stomatococcus mucilaginosus and of Micrococcus spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995; 39:268–270. PMID: 7695321.18. von Eiff C, Peters G. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, and levofloxacin against Micrococcus species and Stomatococcus mucilaginosus isolated from healthy subjects and neutropenic patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998; 17:890–892. PMID: 10052561.19. Skogen PG, Kolmannskog S, Bergh K. Bactericidal activity in cerebrospinal fluid by treating meningitis caused by Stomatococcus mucilaginosus with rifampicin, cefotaxime and vancomycin in a neutropenic child. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2001; 7:39–42. PMID: 11284946.20. McWhinney PH, Kibbler CC, Gillespie SH, Patel S, Morrison D, Hoffbrand AV, et al. Stomatococcus mucilaginosus: an emerging pathogen in neutropenic patients. Clin Infect Dis. 1992; 14:641–646. PMID: 1562654.21. Chomarat M, Vital MG, Flandrois JP. Susceptibility to aminoglycosides of 63 strains of Stomatococcus mucilaginosus isolated from sputum. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1991; 276:63–67. PMID: 1789902.22. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Twenty-Second Informational supplement,M100-S22. 2012. Wayne, PA: Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute;p. 70–79.23. Capitano B, Mattoes HM, Shore E, O'Brien A, Braman S, Sutherland C, et al. Steady-state intrapulmonary concentrations of moxifloxacin, levofloxacin, and azithromycin in older adults. Chest. 2004; 125:965–973. PMID: 15006955.
Article24. Zhanel GG, Ennis K, Vercaigne L, Walkty A, Gin AS, Embil J, et al. A critical review of the fluoroquinolones: focus on respiratory infections. Drugs. 2002; 62:13–59. PMID: 11790155.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis with Cerebral Hemorrhage Caused by Rothia mucilaginosa
- A case of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis by Rothia mucilaginosa
- Implication of quantitative culture of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in the diagnosis of ventilator assocaited pneumonia in patients with antimicrobial therapy
- Reasons for Low Bacterial Yields from Quantitative Cultures of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid
- Bronchoalveolar Lavage of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia: Cytological and Ultrastructural Features