Ann Lab Med.
2013 Mar;33(2):130-135. 10.3343/alm.2013.33.2.130.
A Rare Case of Transformation of Childhood Myelodysplastic Syndrome to Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine and Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Greencross Reference Laboratory, Yongin, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. yaong97@paran.com
- 5Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 1781313
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2013.33.2.130
Abstract
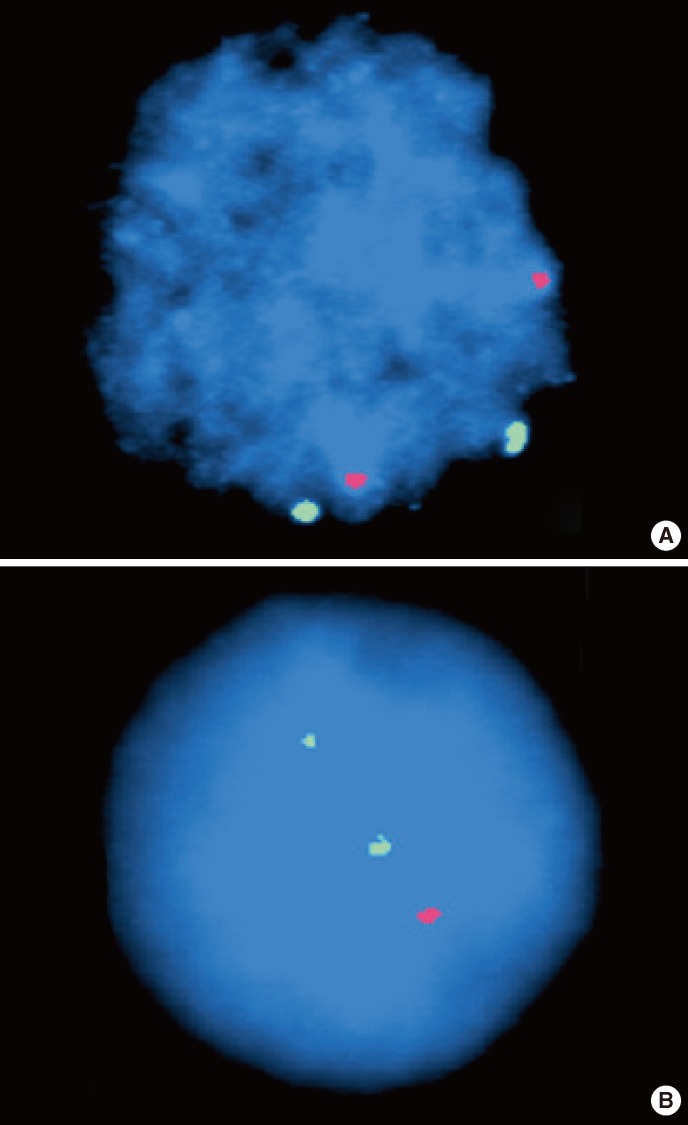
- Transformation of MDS into ALL during childhood is extremely rare. We report a rare case of an 8-yr-old girl who presented with refractory cytopenia of childhood (RCC) that transformed into ALL only 3 months after the diagnosis of childhood MDS. Although no cytogenetic abnormalities were observed in conventional karyotype and FISH analysis, we found several deletions on chromosomes 5q, 12q, 13q, and 22q. Partial homozygous deletion of the RB1 gene was observed on microarray analysis, with the bone marrow specimen diagnosed as ALL. This is the first case report of transformation of ALL from childhood MDS in Korea. We also compared the clinical, cytological, and cytogenetic features of 4 previously reported childhood MDS cases that transformed into ALL.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Bone Marrow Cells/pathology
*Cell Transformation, Neoplastic/genetics
Child
Chromosome Aberrations
Female
Gene Deletion
Humans
In Situ Hybridization, Fluorescence
Karyotyping
Myelodysplastic Syndromes/*diagnosis/genetics
Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma/*diagnosis/genetics
Retinoblastoma Protein/genetics
Retinoblastoma Protein
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kouides PA, Bennett JM. Understanding the myelodysplastic syndromes. Oncologist. 1997; 2:389–401. PMID: 10388074.
Article2. Malcovati L, Nimer SD. Myelodysplastic syndromes: diagnosis and staging. Cancer Control. 2008; 15:4–13. PMID: 18813205.
Article3. Ma X, Does M, Raza A, Mayne ST. Myelodysplastic syndromes: incidence and survival in the United States. Cancer. 2007; 109:1536–1542. PMID: 17345612.4. Niemeyer CM, Kratz CP, Hasle H. Pediatric myelodysplastic syndromes. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2005; 6:209–214. PMID: 15869732.
Article5. Hasle H, Niemeyer CM, Chessells JM, Baumann I, Bennett JM, Kerndrup G, et al. A pediatric approach to the WHO classification of myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative diseases. Leukemia. 2003; 17:277–282. PMID: 12592323.
Article6. Germing U, Aul C, Niemeyer CM, Haas R, Bennett JM. Epidemiology, classification and prognosis of adults and children with myelodysplastic syndromes. Ann Hematol. 2008; 87:691–699. PMID: 18575866.
Article7. Disperati P, Ichim CV, Tkachuk D, Chun K, Schuh AC, Wells RA. Progression of myelodysplasia to acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Implications for disease biology. Leuk Res. 2006; 30:233–239. PMID: 16046234.
Article8. Bader-Meunier B, Miélot F, Tchernia G, Buisine J, Delsol G, Duchayne E, et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes in childhood: report of 49 patients from a French multicentre study. French Society of Paediatric Haematology and Immunology. Br J Haematol. 1996; 92:344–350. PMID: 8602998.9. Goel R, Kumar R, Bakhshi S. Transformation of childhood MDS-refractory anemia to acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2007; 29:725–727. PMID: 17921857.
Article10. Gupta V, Bhatia B. Transformation of myelodysplastic syndrome to acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a child. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2010; 26:111–113. PMID: 21886397.
Article11. Janssen JW, Buschle M, Layton M, Drexler HG, Lyons J, Berghe H, et al. Clonal analysis of myelodysplastic syndromes: evidence of multipotent stem cell origin. Blood. 1989; 73:248–254. PMID: 2562924.
Article12. San Miguel JF, Hernández JM, González-Sarmiento R, González M, Sánchez I, Orfao A, et al. Acute leukemia after a primary myelodysplastic syndrome: immunophenotypic, genotypic, and clinical characteristics. Blood. 1991; 78:768–774. PMID: 1859889.13. Orfao A, Ortuño F, Santiago M, Lopez A, San Miguel J. Immunophenotyping of acute leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes. Cytometry A. 2004; 58:62–71. PMID: 14994223.
Article14. Fujii S, Shimizu K, Klimek V, Geller MD, Nimer SD, Dhodapkar MV. Severe and selective deficiency of interferon-gamma-producing invariant natural killer T cells in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 2003; 122:617–622. PMID: 12899717.15. Amin HM, Jilani I, Estey EH, Keating MJ, Dey AL, Manshouri T. Increased apoptosis in bone marrow B lymphocytes but not T lymphocytes in myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood. 2003; 102:1866–1868. PMID: 12730116.
Article16. Span LFR, Vierwinden G, Pennings AH, Boezeman JB, Raymakers RA, de Witte T. Programmed cell death is an intrinsic feature of MDS progenitors, predominantly found in the cluster-forming cells. Exp Hematol. 2005; 33:435–442. PMID: 15781334.
Article17. Abruzzese E, Buss D, Rainer R, Pettenati MJ, Rao PN. Progression of a myelodysplastic syndrome to pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case report and cell lineage study. Ann Hematol. 1996; 73:35–38. PMID: 8695722.
Article18. Kohno T, Amenomori T, Atogami S, Sasagawa I, Nakamura H, Kuriyama K, et al. Progression from myelodysplastic syndrome to acute lymphoblastic leukemia with Philadelphia chromosome and p190 BCR-ABL transcript. Br J Haematol. 1996; 93:389–391. PMID: 8639433.19. Lima CS, de Souza CA, Cardinalli IA, Lorand-Metze I. Lymphoblastic transformation of myelodysplastic syndrome. Sao Paulo Med J. 1997; 115:1508–1512. PMID: 9595816.
Article20. Sato N, Nakazato T, Kizaki M, Ikeda Y, Okamoto S. Transformation of myelodysplastic syndrome to acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Hematol. 2004; 79:147–151. PMID: 15005342.
Article21. Zainina S, Cheong SK. Myelodysplastic syndrome transformed into Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (FAB:L3). Clin Lab Haematol. 2006; 28:282–283. PMID: 16898972.22. Serefhanoglu S, Goker H, Buyukasik Y, Sayinalp N, Ozcebe OI. Transformation of adult myelodysplastic syndrome-refractory anemia to acute T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. J Natl Med Assoc. 2009; 101:370–372. PMID: 19397230.
Article23. Niemeyer CM, Baumann I. Classification of childhood aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011; 2011:84–89. PMID: 22160017.
Article24. Bejar R, Levine R, Ebert BL. Unraveling the molecular pathophysiology of myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:504–515. PMID: 21220588.
Article25. Teachey DT. Lanzkowsky P, editor. Lymphoproliferative disorders, myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative disorders. Manual of pediatric hematology and oncology. 2010. 5th ed. London: Academic Press;p. 494–503.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sweet's Syndrome with Myelodysplastic Syndrome Progressing to Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
- A case of gastric granulocytic sarcoma in a patient with transformed acute leukemia from myelodysplastic syndrome
- Meeting Report: 2009 Symposium on Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia - Update on the Diagnosis and Treatment for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Childhood & Adolescence; Seoul; Korea; June 27, 2009
- Pancreatitis Induced by 6-mercaptopurine and 6-thioguanine in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- A Case of Erythema Nodosum-like Leukemia Cutis in a Patient with Myelodysplastic Syndrome