Yonsei Med J.
2014 Jan;55(1):216-223. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.216.
Effects of Seasonal Differences in Testosterone and Cortisol Levels on Pain Responses Under Resting and Anxiety Conditions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Brain Research Group, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. jaechan@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Life Style Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 3GunSei Biotec Inc., Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779909
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.216
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study investigated whether hormones and pain perception are associated with exam anxiety, and also whether exam anxiety is affected by seasonal differences in testosterone and cortisol levels.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty-six healthy males were recruited from a medical college. Anxiety was induced by having participants perform the Objective Structured Clinical Examination. Pressure was applied to the participants to induce pain. Pain thresholds, pain ratings, anxiety ratings, blood pressure, heart rate, salivary testosterone and cortisol levels were measured under resting and anxiety conditions in the spring and summer. Data were collected from 46 participants during the spring (n=25) and summer (n=21).
RESULTS
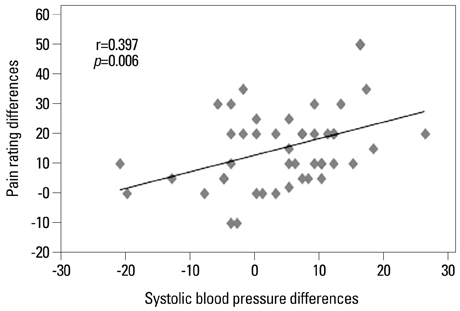
Pain thresholds and testosterone levels were significantly lower under anxiety than at rest for all participants (n=46), while cortisol levels, pain ratings, and anxiety ratings were significantly higher under anxiety than at rest. In the spring (n=25), testosterone levels were significantly higher at rest than under anxiety, while there was no difference in cortisol levels between resting and anxiety conditions. In the summer (n=21), cortisol levels were significantly higher under anxiety than at rest, while there was no difference in testosterone levels between resting and anxiety conditions. There were no significant seasonal differences in pain and anxiety ratings and pain threshold.
CONCLUSION
These results indicate that seasonal differences in testosterone and cortisol levels under anxiety and at rest may affect pain responses. These results also suggest that acute clinical pain may be relieved by managing anxiety that is related to a decrease of testosterone in spring and a large increase of cortisol in summer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brand HS, Schoonheim-Klein M. Is the OSCE more stressful? Examination anxiety and its consequences in different assessment methods in dental education. Eur J Dent Educ. 2009; 13:147–153.
Article2. Ng V, Koh D, Mok BY, Chia SE, Lim LP. Salivary biomarkers associated with academic assessment stress among dental undergraduates. J Dent Educ. 2003; 67:1091–1094.
Article3. Kirschbaum C, Hellhammer DH. Salivary cortisol in psychoneuroendocrine research: recent developments and applications. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1994; 19:313–333.
Article4. Ng V, Koh D, Chia SE. Examination stress, salivary cortisol, and academic performance. Psychol Rep. 2003; 93(3 Pt 2):1133–1134.
Article5. Schulz P, Walker JP, Peyrin L, Soulier V, Curtin F, Steimer T. Lower sex hormones in men during anticipatory stress. Neuroreport. 1996; 7:3101–3104.
Article6. Van den Berghe G. The neuroendocrine response to stress is a dynamic process. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 15:405–419.
Article7. Sternbach H. Age-associated testosterone decline in men: clinical issues for psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry. 1998; 155:1310–1318.
Article8. Edinger KL, Frye CA. Testosterone's anti-anxiety and analgesic effects may be due in part to actions of its 5alpha-reduced metabolites in the hippocampus. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2005; 30:418–430.
Article9. Craft RM, Mogil JS, Aloisi AM. Sex differences in pain and analgesia: the role of gonadal hormones. Eur J Pain. 2004; 8:397–411.
Article10. van Anders SM, Hampson E, Watson NV. Seasonality, waist-to-hip ratio, and salivary testosterone. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2006; 31:895–899.
Article11. Romero LM. Seasonal changes in plasma glucocorticoid concentrations in free-living vertebrates. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2002; 128:1–24.
Article12. Romero LM, Wingfield JC. Alterations in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function associated with captivity in Gambel's white-crowned sparrows (Zonotrichia leucophrys gambelii). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 1999; 122:13–20.
Article13. Andersson AM, Carlsen E, Petersen JH, Skakkebaek NE. Variation in levels of serum inhibin B, testosterone, estradiol, luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and sex hormone-binding globulin in monthly samples from healthy men during a 17-month period: possible effects of seasons. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:932–937.
Article14. Dabbs JM Jr. Age and seasonal variation in serum testosterone concentration among men. Chronobiol Int. 1990; 7:245–249.
Article15. Meriggiola MC, Noonan EA, Paulsen CA, Bremner WJ. Annual patterns of luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, testosterone and inhibin in normal men. Hum Reprod. 1996; 11:248–252.
Article16. Nicolau GY, Haus E, Lakatua DJ, Bogdan C, Sackett-Lundeen L, Popescu M, et al. Circadian and circannual variations of FSH, LH, testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (DHEA-S) and 17-hydroxy progesterone (17 OH-Prog) in elderly men and women. Endocrinologie. 1985; 23:223–246.17. Nicolau GY, Lakatua D, Sackett-Lundeen L, Haus E. Circadian and circannual rhythms of hormonal variables in elderly men and women. Chronobiol Int. 1984; 1:301–319.
Article18. Perry HM 3rd, Miller DK, Patrick P, Morley JE. Testosterone and leptin in older African-American men: relationship to age, strength, function, and season. Metabolism. 2000; 49:1085–1091.
Article19. Reinberg A, Lagoguey M, Chauffournier JM, Cesselin F. Circannual and circadian rhythms in plasma testosterone in five healthy young Parisian males. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1975; 80:732–734.
Article20. Reinberg A, Smolensky MH, Hallek M, Smith KD, Steinberger E. Annual variation in semen characteristics and plasma hormone levels in men undergoing vasectomy. Fertil Steril. 1988; 49:309–315.
Article21. Smals AG, Kloppenborg PW, Benraad TJ. Circannual cycle in plasma testosterone levels in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976; 42:979–982.
Article22. Svartberg J, Jorde R, Sundsfjord J, Bønaa KH, Barrett-Connor E. Seasonal variation of testosterone and waist to hip ratio in men: the Tromsø study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:3099–3104.
Article23. Valero-Politi J, Fuentes-Arderiu X. Annual rhythmic variations of follitropin, lutropin, testosterone and sex-hormone-binding globulin in men. Clin Chim Acta. 1998; 271:57–71.
Article24. Baker HW, Burger HG, de Kretser DM, Hudson B, O'Connor S, Wang C, et al. Changes in the pituitary-testicular system with age. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1976; 5:349–372.
Article25. Brambilla DJ, O'Donnell AB, Matsumoto AM, McKinlay JB. Lack of seasonal variation in serum sex hormone levels in middle-aged to older men in the Boston area. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:4224–4229.
Article26. Dai WS, Kuller LH, LaPorte RE, Gutai JP, Falvo-Gerard L, Caggiula A. The epidemiology of plasma testosterone levels in middle-aged men. Am J Epidemiol. 1981; 114:804–816.
Article27. Martikainen H, Tapanainen J, Vakkuri O, Leppäluoto J, Huhtaniemi I. Circannual concentrations of melatonin, gonadotrophins, prolactin and gonadal steroids in males in a geographical area with a large annual variation in daylight. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1985; 109:446–450.
Article28. Svartberg J, Barrett-Connor E. Could seasonal variation in testosterone levels in men be related to sleep? Aging Male. 2004; 7:205–210.
Article29. Vitzthum VJ, Worthman CM, Beall CM, Thornburg J, Vargas E, Villena M, et al. Seasonal and circadian variation in salivary testosterone in rural Bolivian men. Am J Hum Biol. 2009; 21:762–768.
Article30. Matchock RL, Dorn LD, Susman EJ. Diurnal and seasonal cortisol, testosterone, and DHEA rhythms in boys and girls during puberty. Chronobiol Int. 2007; 24:969–990.
Article31. Bellastella A, Criscuolo T, Mango A, Perrone L, Sinisi AA, Faggiano M. Circannual rhythms of plasma luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, testosterone, prolactin and cortisol in prepuberty. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1983; 19:453–459.
Article32. Butler RK, Finn DP. Stress-induced analgesia. Prog Neurobiol. 2009; 88:184–202.
Article33. Meagher MW, Arnau RC, Rhudy JL. Pain and emotion: effects of affective picture modulation. Psychosom Med. 2001; 63:79–90.
Article34. Rhudy JL, Meagher MW. Fear and anxiety: divergent effects on human pain thresholds. Pain. 2000; 84:65–75.
Article35. Rhudy JL, Meagher MW. Noise stress and human pain thresholds: divergent effects in men and women. J Pain. 2001; 2:57–64.
Article36. Choi JC, Chung MI, Lee YD. Modulation of pain sensation by stress-related testosterone and cortisol. Anaesthesia. 2012; 67:1146–1151.
Article37. Kanegane K, Penha SS, Munhoz CD, Rocha RG. Dental anxiety and salivary cortisol levels before urgent dental care. J Oral Sci. 2009; 51:515–520.
Article38. King SL, Hegadoren KM. Stress hormones: how do they measure up? Biol Res Nurs. 2002; 4:92–103.
Article39. Liening SH, Stanton SJ, Saini EK, Schultheiss OC. Salivary testosterone, cortisol, and progesterone: two-week stability, interhormone correlations, and effects of time of day, menstrual cycle, and oral contraceptive use on steroid hormone levels. Physiol Behav. 2010; 99:8–16.
Article40. Zartman RR, McWhorter AG, Seale NS, Boone WJ. Using OSCE-based evaluation: curricular impact over time. J Dent Educ. 2002; 66:1323–1330.
Article41. Zhang Z, Su H, Peng Q, Yang Q, Cheng X. Exam anxiety induces significant blood pressure and heart rate increase in college students. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2011; 33:281–286.
Article42. Grillon C, Duncko R, Covington MF, Kopperman L, Kling MA. Acute stress potentiates anxiety in humans. Biol Psychiatry. 2007; 62:1183–1186.
Article43. Choi JC, Park SK, Kim YH, Shin YW, Kwon JS, Kim JS, et al. Different brain activation patterns to pain and pain-related unpleasantness during the menstrual cycle. Anesthesiology. 2006; 105:120–127.
Article44. Choi JC, Yi DJ, Han BS, Lee PH, Kim JH, Kim BH. Placebo effects on analgesia related to testosterone and premotor activation. Neuroreport. 2011; 22:419–423.
Article45. Martin JH. Neuroanatomy: Text and Atlas. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies;2003. p. 125–126.46. Choi JC, Min S, Kim YK, Choi JH, Seo SM, Chang SJ. Changes in pain perception and hormones pre- and post-kumdo competition. Horm Behav. 2013; 64:618–623.
Article47. Terburg D, Morgan B, van Honk J. The testosterone-cortisol ratio: a hormonal marker for proneness to social aggression. Int J Law Psychiatry. 2009; 32:216–223.
Article48. Glenn AL, Raine A, Schug RA, Gao Y, Granger DA. Increased testosterone-to-cortisol ratio in psychopathy. J Abnorm Psychol. 2011; 120:389–399.
Article49. Daitzman R, Zuckerman M. Disinhibitory sensation seeking, personality and gonadal hormones. Pers Individ Differ. 1980; 1:103–110.
Article50. Schulkin J, Gold PW, McEwen BS. Induction of corticotropin-releasing hormone gene expression by glucocorticoids: implication for understanding the states of fear and anxiety and allostatic load. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1998; 23:219–243.
Article51. Stanton SJ, Mullette-Gillman OA, Huettel SA. Seasonal variation of salivary testosterone in men, normally cycling women, and women using hormonal contraceptives. Physiol Behav. 2011; 104:804–808.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neurosteroid Levels in Patients with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- Seasonal Variations and Correlations between Vitamin D and Total Testosterone Levels
- Comparison of Serum Cortisol and Testosterone Levels in Acute and Chronic Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
- Evaluation of Salivary Cortisol and Anxiety Levels in Myofascial Pain Dysfunction Syndrome
- An Exploratory Study on Occupational Stress and Anxiety Through Salivary Cortisol and Self-Report Scale in Korean Nurses on Shift and Regular Work