Yonsei Med J.
2012 Jan;53(1):213-220. 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.213.
Characteristics of Outpatients with Pandemic H1N1/09 Influenza in a Tertiary Care University Hospital in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leehejo@khmc.or.kr
- 2Biomedical Science, Kyung Hee University Graduate School, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779709
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.213
Abstract
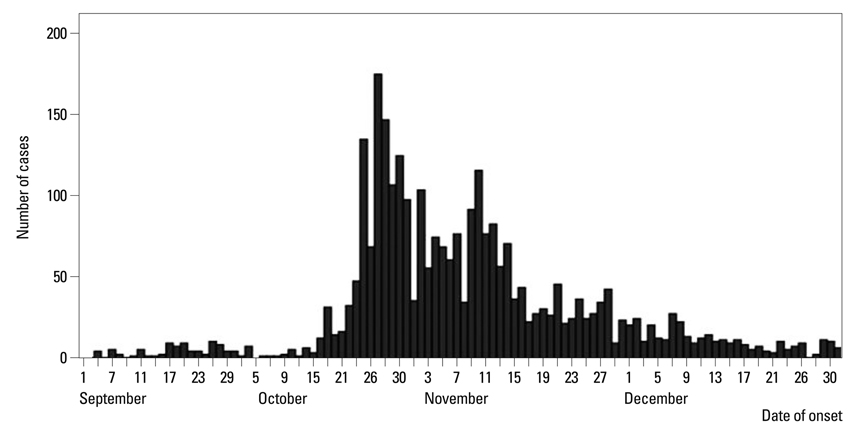
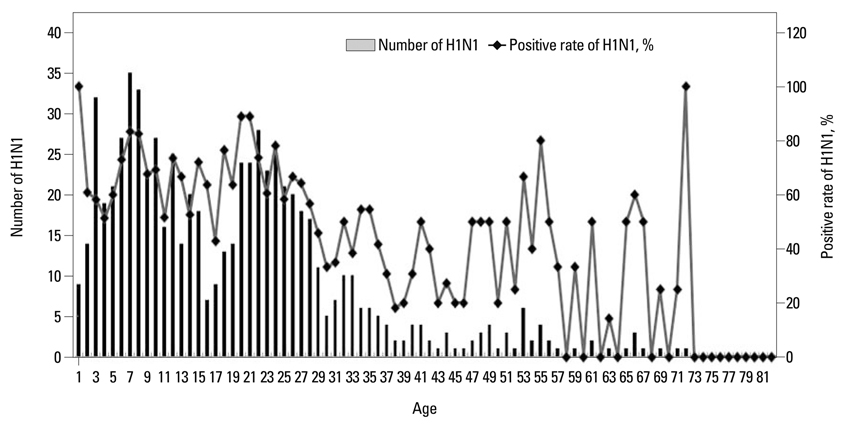
- The pandemic H1N1/09 emerged rapidly in Korea. Here, we describe the clinical characteristics of outpatients in Seoul, Korea who were infected in the 2009 H1N1 pandemic. We reviewed the cases of outpatients with pandemic H1N1/09 who visited a tertiary care teaching hospital between September 1 and December 31, 2009. Infection with pandemic H1N1/09 was confirmed by molecular tests. Of a total of 7,182 tests, 3,020 (42.0%) were positive. Compared with 473 cases of influenza-like illness (ILI), the 586 confirmed cases of pandemic H1N1/09 differed in age [odds ratio (OR) 0.975] and fulfilling at least one of the following factors: age <5 or > or =65 years, history of contact with other pandemic H1N1/09-infected individuals (OR 0.611), fever > or =37.8degrees C (OR 3.567), cough (OR 2.290), and myalgia (OR 1.559). The sensitivity of the best criteria, "fever (> or =37.8degrees C) plus cough" (41.03%) in this study was lower than that of the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC) criteria (47.95%), whereas the positive likelihood ratio (3.55) and positive predictive value (81.6) of this criteria was higher than those of the KCDC criteria (2.98 and 78.7, respectively). The clinical characteristics of pandemic H1N1/09 are, in many regards, indistinguishable from those of ILI. Moreover, the accuracy and predictability of criteria which include only symptoms or signs were not sufficient to diagnose pandemic H1N1/09 infection. Therefore, use of a combination of symptoms with confirmatory laboratory testing is necessary for accurate diagnosis of pandemic H1N1/09.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Child
Comorbidity
Female
Hospitals, University/statistics & numerical data
Humans
*Influenza A Virus, H1N1 Subtype
Influenza, Human/*diagnosis/*epidemiology/physiopathology
Male
Multivariate Analysis
Outpatients/*statistics & numerical data
Pandemics/*statistics & numerical data
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Risk Factors
Young Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. The Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Republic of Korea. Accessed on November 18, 2011. Available at http://www.cdc.go.kr/contents/information/had/b/10144_view.html.2. Lee DH, Shin SS, Jun BY, Lee JK. [National level response to pandemic (H1N1) 2009]. J Prev Med Public Health. 2010. 43:99–104.
Article3. Zarychanski R, Stuart TL, Kumar A, Doucette S, Elliott L, Kettner J, et al. Correlates of severe disease in patients with 2009 pandemic influenza (H1N1) virus infection. CMAJ. 2010. 182:257–264.
Article4. Louie JK, Acosta M, Winter K, Jean C, Gavali S, Schechter R, et al. Factors associated with death or hospitalization due to pandemic 2009 influenza A (H1N1) infection in California. JAMA. 2009. 302:1896–1902.
Article5. Cao B, Li XW, Mao Y, Wang J, Lu HZ, Chen YS, et al. Clinical features of the initial cases of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus infection in China. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:2507–2517.
Article6. ANZIC Influenza Investigators. Webb SA, Pettilä V, Seppelt I, Bellomo R, Bailey M, et al. Critical care services and 2009 H1N1 influenza in Australia and New Zealand. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:1925–1934.
Article7. Novel Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Investigation Team. Dawood FS, Jain S, Finelli L, Shaw MW, Lindstrom S, et al. Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans. N Engl J Med. 2009. 360:2605–2615.
Article8. Ong AK, Chen MI, Lin L, Tan AS, Nwe NW, Barkham T, et al. Improving the clinical diagnosis of influenza--a comparative analysis of new influenza A (H1N1) cases. PLoS One. 2009. 4:e8453.
Article9. Chang YS, van Hal SJ, Spencer PM, Gosbell IB, Collett PW. Comparison of adult patients hospitalised with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 influenza and seasonal influenza during the "PROTECT" phase of the pandemic response. Med J Aust. 2010. 192:90–93.
Article10. Jain S, Kamimoto L, Bramley AM, Schmitz AM, Benoit SR, Louie J, et al. Hospitalized patients with 2009 H1N1 influenza in the United States, April-June 2009. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:1935–1944.
Article11. Perez-Padilla R, de la Rosa-Zamboni D, Ponce de Leon S, Hernandez M, Quiñones-Falconi F, Bautista E, et al. Pneumonia and respiratory failure from swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) in Mexico. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:680–689.
Article12. Nicholson KG. Clinical features of influenza. Semin Respir Infect. 1992. 7:26–37.13. Chen MI, Lee VJ, Lim WY, Barr IG, Lin RT, Koh GC, et al. 2009 influenza A (H1N1) seroconversion rates and risk factors among distinct adult cohorts in Singapore. JAMA. 2010. 303:1383–1391.
Article14. Torres JP, O'Ryan M, Herve B, Espinoza R, Acuña G, Mañalich J, et al. Impact of the novel influenza A (H1N1) during the 2009 autumn-winter season in a large hospital setting in Santiago, Chile. Clin Infect Dis. 2010. 50:860–868.
Article15. Choi WJ, Kim WY, Kim SH, Oh BJ, Kim W, Lim KS, et al. Clinical characteristics of pneumonia in hospitalized patients with novel influenza A (H1N1) in Korea. Scand J Infect Dis. 2010. 42:311–314.
Article16. Jaeschke R, Guyatt GH, Sackett DL. The Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group. Users' guides to the medical literature III How to use an article about a diagnostic test B What are the results and will they help me in caring for my patients? JAMA. 1994. 271:703–707.
Article17. Kim CO, Nam CM, Lee DC, Han SH, Lee JW. Clinical predictors of novel influenza A (H1N1) infection in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2010. 51:895–900.
Article18. Suh M, Lee J, Chi HJ, Kim YK, Kang DY, Hur NW, et al. [Mathematical modeling of the novel influenza A (H1N1) virus and evaluation of the epidemic response strategies in the Republic of Korea]. J Prev Med Public Health. 2010. 43:109–116.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influenza Associated Pneumonia
- The 2009 H1N1 Pandemic Influenza in Korea
- Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and management of pandemic novel Influenza A (H1N1)
- Clinical and Laboratory Finding of the 2009 Pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in Children
- Pandemic Influenza (H1N1) and Mycobacterium tuberculosis Co-infection