Yonsei Med J.
2011 Mar;52(2):257-262. 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.2.257.
Delayed Response of Amylin Levels after an Oral Glucose Challenge in Children with Prader-Willi Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jindk@skku.edu
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea.
- 5Clinical Research Center, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779660
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2011.52.2.257
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Amylin secretion is increased parallel to insulin in obese subjects. Despite their marked obesity, a state of relative hypoinsulinemia occurs in children with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS). Based on the hypothesis that amylin levels may be relatively low in PWS children, contributing to their excessive appetite, we studied amylin levels after oral glucose loading in children with PWS and overweight controls.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
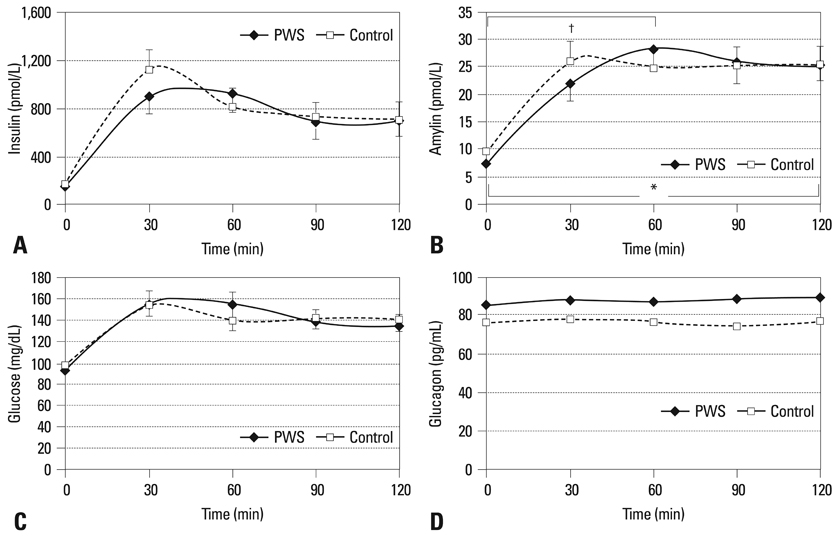
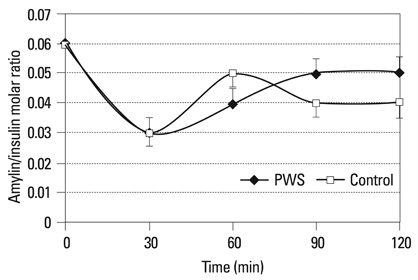
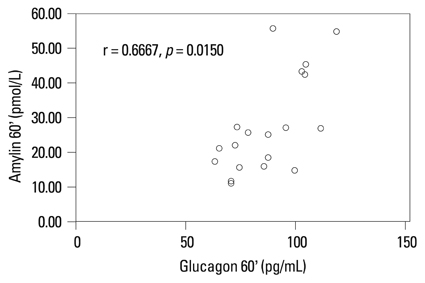
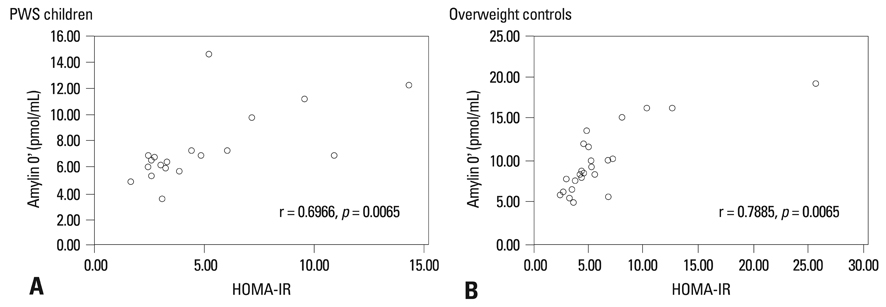
Plasma levels of amylin, glucagon, insulin, and glucose were measured at 0, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min after a glucose challenge in children with PWS (n = 18) and overweight controls (n = 25); the relationships among the variables were investigated in these two groups.
RESULTS
Amylin levels were significantly correlated with insulin during fasting and during the oral glucose tolerance test in both groups. Amylin levels between 0 and 60 min after glucose loading were statistically different between the two groups. They were lower in children with PWS than in the controls between 0 and 30 min after glucose loading.
CONCLUSION
The relatively low levels of amylin, compared to those in overweight controls, during the early phase of glucose loading in patients with PWS, may contribute, in part, to the excessive appetite of PWS patients as compared to the overweight controls.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Holm VA, Cassidy SB, Butler MG, Hanchett JM, Greenswag LR, Whitman BY, et al. Prader-Willi syndrome: consensus diagnostic criteria. Pediatrics. 1993. 91:398–402.
Article2. Cummings DE, Overduin J. Gastrointestinal regulation of food intake. J Clin Invest. 2007. 117:13–23.
Article3. Dham S, Banerji MA. The brain-gut axis in regulation of appetite and obesity. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2006. 3:Suppl 4. 544–554.4. Murphy KG, Bloom SR. Gut hormones and the regulation of energy homeostasis. Nature. 2006. 444:854–859.
Article5. Woods SC, Lutz TA, Geary N, Langhans W. Pancreatic signals controlling food intake; insulin, glucagon and amylin. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2006. 361:1219–1235.
Article6. Rushing PA, Hagan MM, Seeley RJ, Lutz TA, Woods SC. Amylin: a novel action in the brain to reduce body weight. Endocrinology. 2000. 141:850–853.
Article7. Haqq AM, Muehlbauer M, Svetkey LP, Newgard CB, Purnell JQ, Grambow SC, et al. Altered distribution of adiponectin isoforms in children with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS): association with insulin sensitivity and circulating satiety peptide hormones. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007. 67:944–951.
Article8. Krochik AG, Ozuna B, Torrado M, Chertkoff L, Mazza C. Characterization of alterations in carbohydrate metabolism in children with Prader-Willi syndrome. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2006. 19:911–918.
Article9. Ludvik B, Lell B, Hartter E, Schnack C, Prager R. Decrease of stimulated amylin release precedes impairment of insulin secretion in type II diabetes. Diabetes. 1991. 40:1615–1619.
Article10. Dykens EM. Maladaptive and compulsive behavior in Prader-Willi syndrome: new insights from older adults. Am J Ment Retard. 2004. 109:142–153.
Article11. Dykens EM, Roof E. Behavior in Prader-Willi syndrome: relationship to genetic subtypes and age. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2008. 49:1001–1008.
Article12. Hiraiwa R, Maegaki Y, Oka A, Ohno K. Behavioral and psychiatric disorders in Prader-Willi syndrome: a population study in Japan. Brain Dev. 2007. 29:535–542.
Article13. Kim SE, Jin DK, Cho SS, Kim JH, Hong SD, Paik KH, et al. Regional cerebral glucose metabolic abnormality in Prader-Willi syndrome: A 18F-FDG PET study under sedation. J Nucl Med. 2006. 47:1088–1092.14. Martin C. The physiology of amylin and insulin: maintaining the balance between glucose secretion and glucose uptake. Diabetes Educ. 2006. 32:Suppl 3. 101S–104S.
Article15. Lutz TA. Amylinergic control of food intake. Physiol Behav. 2006. 89:465–471.
Article16. Ludvik B, Thomaseth K, Nolan JJ, Clodi M, Prager R, Pacini G. Inverse relation between amylin and glucagon secretion in healthy and diabetic human subjects. Eur J Clin Invest. 2003. 33:316–322.
Article17. Reinehr T, de Sousa G, Niklowitz P, Roth CL. Amylin and its relation to insulin and lipids in obese children before and after weight loss. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007. 15:2006–2011.
Article