Yonsei Med J.
2010 Nov;51(6):883-887. 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.6.883.
Discrepancies in Perception of Urinary Incontinence between Patient and Physician after Robotic Radical Prostatectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology and Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jkim@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1779635
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2010.51.6.883
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Reported incidence of urinary incontinence after a radical prostatectomy (RP) varies between studies. This may be due not only to the definition of incontinence applied, but also how the information is acquired. We investigated the differences in perception of post robot-assisted laparoscopic RP (RALP) urinary incontinence acquired through doctor interviews and patient-reported questionnaires.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Of 238 consecutive men who underwent RALP by a single surgeon between July 2005 and February 2008, we evaluated 66 men using the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire (ICIQ) at various time points after surgery. Each patient's ICIQ results were considered to be the patient's perceptions of urinary incontinence. The physician at the same time directly interviewed the patients about the number of pads used and considered complete continence to be equivalent to the use of no pads or safety liners.
RESULTS
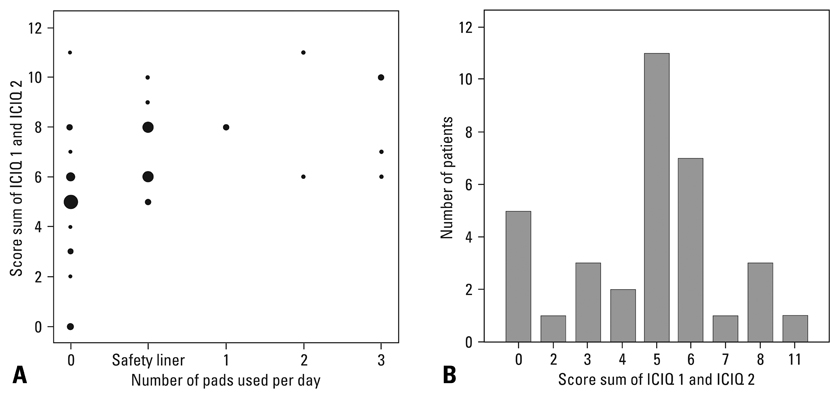
Of the 66 patients, the physician reported that 34 (51.5%) had obtained complete continence. However, analysis of the questionnaires of these 34 patients revealed that only 5 (14.7%) patients reported that they never leaked during the past 4 weeks. Most patients (11 patients, 32.4%) who did not use any pad did in fact reported leakage of a small or moderate amount of urine about once a day.
CONCLUSION
Our results indicate that there are discrepancies in the perception of urinary incontinence between doctor and patient after RALP. Non-use of pads is not equivalent to obtaining complete urinary continence. Therefore, the number of pads used is not a good measure to determine the status of complete urinary continence.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Urinary Incontinence Could Be Controlled by an Inflatable Penile Prosthesis
Hyun Min Choi, Hyung Ki Choi, Hye-Yeon Lee
World J Mens Health. 2016;34(1):34-39. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.2016.34.1.34.
Reference
-
1. Walsh PC, Marschke P, Ricker D, Burnett AL. Patient-reported urinary continence and sexual function after anatomic radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2000. 55:58–61.
Article2. Stolzenburg JU, Do M, Rabenalt R, Pfeiffer H, Horn L, Truss MC, et al. Endoscopic extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy: initial experience after 70 procedures. J Urol. 2003. 169:2066–2071.
Article3. Rassweiler J, Stolzenburg J, Sulser T, Deger S, Zumbé J, Hofmockel G, et al. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy--the experience of the German Laparoscopic Working Group. Eur Urol. 2006. 49:113–119.
Article4. Patel VR, Tully AS, Holmes R, Lindsay J. Robotic radical prostatectomy in the community setting--the learning curve and beyond: initial 200 cases. J Urol. 2005. 174:269–272.
Article5. Sacco E, Prayer-Galetti T, Pinto F, Fracalanza S, Betto G, Pagano F, et al. Urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: incidence by definition, risk factors and temporal trend in a large series with a long-term follow-up. BJU Int. 2006. 97:1234–1241.
Article6. Krupski TL, Saigal CS, Litwin MS. Variation in continence and potency by definition. J Urol. 2003. 170:1291–1294.
Article7. Avery K, Donovan J, Peters TJ, Shaw C, Gotoh M, Abrams P. ICIQ: a brief and robust measure for evaluating the symptoms and impact of urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2004. 23:322–330.
Article8. Eisen SV. Assessment of subjective distress by patients' self-report versus structured interview. Psychol Rep. 1995. 76:35–39.
Article9. Litwin MS, Lubeck DP, Henning JM, Carroll PR. Differences in urologist and patient assessments of health related quality of life in men with prostate cancer: results of the CaPSURE database. J Urol. 1998. 159:1988–1992.
Article10. Dylewski DA, Jamison MG, Borawski KM, Sherman ND, Amundsen CL, Webster GD. A statistical comparison of pad numbers versus pad weights in the quantification of urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2007. 26:3–7.
Article11. Ryhammer AM, Laurberg S, Djurhuus JC, Hermann AP. No relationship between subjective assessment of urinary incontinence and pad test weight gain in a random population sample of menopausal women. J Urol. 1998. 159:800–803.
Article12. Karantanis E, Fynes M, Moore KH, Stanton SL. Comparison of the ICIQ-SF and 24-hour pad test with other measures for evaluating the severity of urodynamic stress incontinence. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2004. 15:111–116.
Article13. Suardi N, Scattoni V, Briganti A, Salonia A, Naspro R, Gallina A, et al. Nerve-sparing radical retropubic prostatectomy in patients previously submitted to holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for bladder outlet obstruction due to benign prostatic enlargement. Eur Urol. 2008. 53:1180–1185.
Article14. Tannenbaum C, Corcos J. Outcomes in urinary incontinence: reconciling clinical relevance with scientific rigour. Eur Urol. 2008. 53:1151–1161.
Article15. Bauer RM, Bastian PJ, Gozzi C, Stief CG. Postprostatectomy incontinence: all about diagnosis and management. Eur Urol. 2009. 55:322–333.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Posterior Urethral Reconstruction (PUR) in Early Recovery of Urinary Continence after Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy
- Improving Urinary Continence after Radical Prostatectomy: Review of Surgical Modifications
- Initial experience with Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy compared to the conventional method: is it a suitable option for robotic prostatectomy beginners?
- Functional recovery after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer
- Case of Fournier’s Gangrene in a Patient with Long-Term Indwelling Catheterization due to Urinary Incontinence after Open Radical Prostatectomy