Yonsei Med J.
2007 Apr;48(2):337-340. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.2.337.
Chronic Expanding Hematoma of the Thorax
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. wjkoh@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Thoracic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779542
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.2.337
Abstract
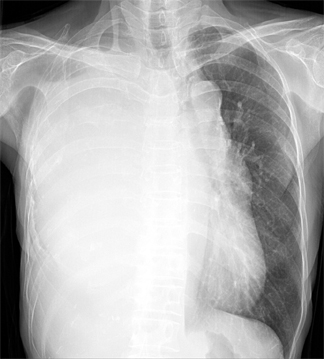
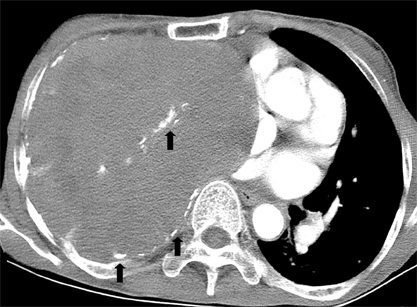
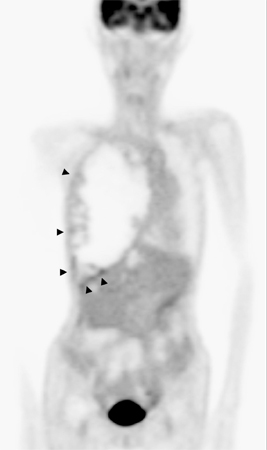
- We report the first case in Korea of a chronic expanding hematoma, which presented as a huge mass in the pleural cavity. A 67-year-old woman exhibiting a slowly-expanding intrathoracic mass, as revealed by a chest radiograph, was admitted to our hospital. The patient had undergone a pneumonectomy 37 years earlier during treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis. Computed tomography revealed a huge mass in her right hemithorax. The differential diagnosis of this mass included chronic empyema combined with a malignancy, such as lymphoma or a soft tissue sarcoma. The tumor, which was classified as an encapsulated chronic hematoma, was removed surgically. Samples sent for histopathological and microbiological analysis revealed no evidence of neoplasia or infection. The patient was finally diagnosed with a chronic expanding hematoma of the thorax. This case is particularly rare due to the patient's development of a very large mass after undergoing treatment for tuberculosis more than 30 years earlier.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hanagiri T, Muranaka H, Hashimoto M, Nishio T, Sakai S, Ono M, et al. Chronic expanding hematoma in the chest. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997. 64:559–561.
Article2. Uramoto H, Nakanishi R, Eifuku R, Muranaka H, Takenoyama M, Yoshino I, et al. Chronic expanding hematoma in the chest. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2000. 41:143–146.3. Iuchi K, Ichimiya A, Akashi A, Mizuta T, Lee YE, Tada H, et al. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the pleural cavity developing from long-standing pyothorax. Cancer. 1987. 60:1771–1775.
Article4. Mentzel T, Goodlad JR, Smith MA, Fletcher CD. Ancient hematoma: a unifying concept for a post-traumatic lesion mimicking an aggressive soft tissue neoplasm. Mod Pathol. 1997. 10:334–340.5. Willen R, Bruce T, Dahlstrom G, Dubiel WT. Squamous epithelial cancer in metaplastic pleura following extrapleural pneumothorax for pulmonary tuberculosis. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1976. 370:225–231.
Article6. Takanami I. Successful treatment of huge chronic expanding hematoma after thoracoplasty. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003. 126:1202–1203.
Article7. Okubo K, Okamoto T, Isobe J, Ueno Y. Rupture of a chronic expanding hematoma of the thorax into lung parenchyma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004. 127:1838–1840.
Article8. Sato M, Kosaka S, Takahashi T. Life threatening chronic expanding hematoma of the thorax. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2004. 45:511–514.9. Roper CL, Cooper JD. Chronic expanding hematoma of the thorax. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2001. 122:1046–1048.
Article10. Hwang GL, Moffatt SD, Mitchell JD, Leung AN. Chronic expanding hematoma of the thorax. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 180:1182–1183.
Article11. Reid JD, Kommareddi S, Lankerani M, Park MC. Chronic expanding hematomas. A clinicopathologic entity. JAMA. 1980. 244:2441–2442.
Article12. Labadie EL, Glover D. Physiopathogenesis of subdural hematomas. Part 1: Histological and biochemical comparisons of subcutaneous hematoma in rats with subdural hematoma in man. J Neurosurg. 1976. 45:382–392.13. Hamada K, Myoui A, Ueda T, Higuchi I, Inoue A, Tamai N, et al. FDG-PET imaging for chronic expanding hematoma in pelvis with massive bone destruction. Skeletal Radiol. 2005. 34:807–811.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Chronic Expanding Hematoma with Initial Presentation as Massive Hemotpysis through Bronchopleural Fistula in the Thorax
- A Case of Spontaneous Chronic Expanding Hematoma in the Thorax
- Four Cases of Successfully Treated Chronic Expanding Soft Tissue Hematoma
- Painful Chronic Expanding Hematoma of the Transtibial Amputation Stump
- Chronic encapsulated expanding hematoma after stereotactic radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformation