J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2019 Sep;21(3):152-157. 10.7461/jcen.2019.21.3.152.
Chronic encapsulated expanding hematoma after stereotactic radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, Ilsan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Ilsan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Korea. cychoi@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2465245
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2019.21.3.152
Abstract
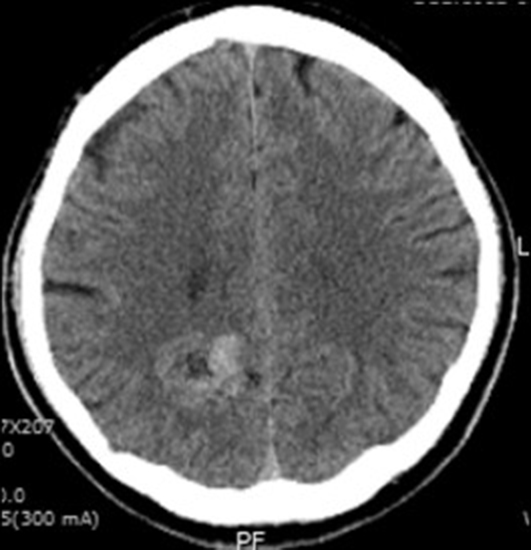
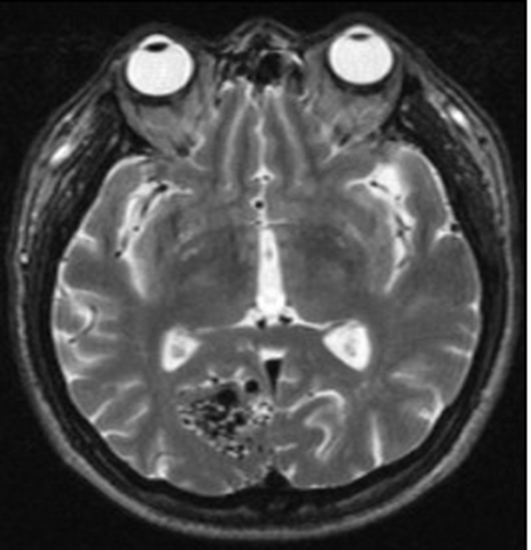
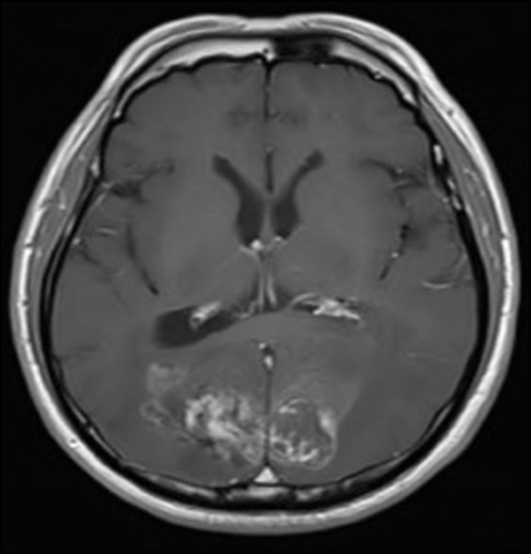
- Stereotactic radiosurgery has become excellent alternative treatment for cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVM). This technique has expanded to treatment of larger AVM which is not amenable to surgical management. However, its variable adverse effects should be also taken into considerations sincerely because of radiobiological characteristics such as delayed onset and progressive neurological deteriorations. Herein, we report a case in which progressively expanding hemorrhagic cyst with repeated bleedings so called chronic encapsulated expanding hematoma was developed on several years after radiosurgery treatment. Neurological and radiological findings were improved by surgical removal.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ferrara N, Davis-Smyth T. The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev. 1997; 18(1):4–25.
Article2. Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003; 9(6):669–676.
Article3. Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Pollock BE, Maitz AH, Lunsford LD. Complications from arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery: multivariate analysis and risk modeling. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997; 38(3):485–490.
Article4. Gökçil Z, Odabaşi Z, Atilla S, Kütükçü Y, Vural O, Yardim M. Radiological follow-up in encapsulated intracerebral hematoma mimicking intratumoural bleeding. Acta Neurol Belg. 1998; 98(1):27–31.5. Greiner-Perth R, Neubauer U, Schenke H. Chronic encapsulated intracerebral hematoma—a well-defined disease. Report on two cases and review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev. 1997; 20(4):231–238.6. Jain R, Robertson PL, Gandhi D, Gujar SK, Muraszko KM, Gebarski S. Radiation-induced cavernomas of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26(5):1158–1162.7. Kaido T, Hoshida T, Uranishi R, Akita N, Kotani A, Nishi N, et al. Radiosurgery-induced brain tumor: case report. J Neurosurg. 2001; 95(4):710–713.8. Kim M, Lee S, Sim J. A case of very large cyst formation with Gamma Knife radiosurgery for an arteriovenous malformation. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1999; 72:168–174.
Article9. Kodama K, Goto T, Sato A, Sakai K, Tanaka Y, Hongo K. Standard and limitation of intraoperative monitoring of the visual evoked potential. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010; 152(4):643–648.
Article10. Kurita H, Sasaki T, Kawamoto S, Taniguchi M, Kitanaka C, Nakaguchi H, et al. Chronic encapsulated expanding hematoma in association with gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery for a cerebral arteriovenous malformation: case report. J Neurosurg. 1996; 84(5):874–878.11. Marti HH, Risau W. Systemic hypoxia changes the organ-specific distribution of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95(26):15809–15814.
Article12. Marti HJ, Bernaudin M, Bellail A, Schoch H, Euler M, Petit E, et al. Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression precedes neovascularization after cerebral ischemia. Am J Pathol. 2000; 156(3):965–976.
Article13. Nagy G, Grainger A, Hodgson TJ, Rowe JG, Coley SC, Kemeny AA, et al. Staged-Volume Radiosurgery of Large Arteriovenous Malformations Improves Outcome by Reducing the Rate of Adverse Radiation Effects. Neurosurgery. 2017; 80(2):180–192.
Article14. Nakamizo A, Suzuki SO, Saito N, Shono T, Matsumoto K, Onaka S, et al. Clinicopathological study on chronic encapsulated expanding hematoma associated with incompletely obliterated AVM after stereotactic radiosurgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011; 153(4):883–893.
Article15. Pollock BE, Brown RD Jr. Management of cysts arising after radiosurgery to treat intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery. 2001; 49(2):259–265.
Article16. Sasaki T, Itakura T, Suzuki K, Kasuya H, Munakata R, Muramatsu H, et al. Intraoperative monitoring of visual evoked potential: introduction of a clinically useful method. J Neurosurg. 2010; 112(2):273–284.
Article17. Shuto T, Ohtake M, Matsunaga S. Proposed mechanism for cyst formation and enlargement following Gamma Knife Surgery for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg. 2012; 117 Suppl:135–143.
Article18. Takeuchi S, Takasato Y, Masaoka H, Hayakawa T, Otani N, Yoshino Y, et al. Development of chronic encapsulated intracerebral hematoma after radiosurgery for a cerebral arteriovenous malformation. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009; 151(11):1513–1515.
Article19. Wang H-C, Chang RJ, Xiao F. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for large arteriovenous malformations. Surg Neurol Int. 2012; 3(Suppl 2):S105–S105.
Article20. Yamamoto M, Hara M, Ide M, Ono Y, Jimbo M, Saito I. Radiation-related adverse effects observed on neuro-imaging several years after radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Surg Neurol. 1998; 49(4):385–398.
Article21. Yamamoto M, Jimbo M, Hara M, Saito I, Mori K. Gamma knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: long-term follow-up results focusing on complications occurring more than 5 years after irradiation. Neurosurgery. 1996; 38(5):906–914.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Complications after Radiosurgery of the Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
- Stereotactic radiosurgery as an alternative treatment for dural arteriovenous fistula
- Recurrence of pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformation after obliteration by radiosurgery: a case report
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for dural arteriovenous fistula
- Radiosurgery for Cerebrovascular Disease