J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Aug;24(4):695-700. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.4.695.
Association of Plasma Levels of Resistin with Subcutaneous Fat Mass and Markers of Inflammation but not with Metabolic Determinants or Insulin Resistance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Seoul, Korea. cydoctor@chol.com
- 2Department of Family Medicine, Center for Health Promotion, Ilsan-Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Family Medicine, Dongguk University International Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1779206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.4.695
Abstract
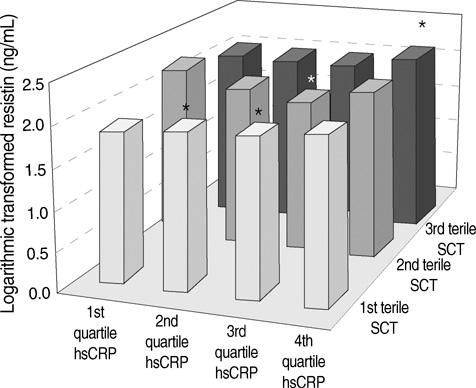
- The aim of the present study was to investigate the relationship of plasma resistin levels with determinants of the metabolic syndrome (MetS) and anthropometric parameters in healthy Korean subjects. Plasma resistin levels were determined in 276 subjects. In subjects with MetS, the plasma resistin levels were not significantly increased compared to those without MetS (8.3+/-4.3 ng/mL vs. 8.5+/-3.6 ng/mL, respectively, P=0.84). In addition, the plasma resistin levels were not correlated with the body mass index, the waist circumference, homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), fasting plasma glucose or insulin levels. However, the plasma resistin levels were positively correlated with the abdominal subcutaneous fat (r=0.18, P<0.01) in all subjects and correlated with TNF alpha(r=-0.16, P<0.05) and hsCRP (r=0.15, P<0.05) in subjects without MetS but not with MetS. With multiple linear regression analysis, these linear associations remained to be significant. The results of this study show that plasma resistin levels in humans were not associated with markers of insulin resistance, obesity or other determinants of the MetS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Anthropometry
Biological Markers/blood
Blood Glucose/analysis
Body Mass Index
C-Reactive Protein/metabolism
Female
Humans
Insulin/blood
*Insulin Resistance
Male
Metabolic Syndrome X/diagnosis/*metabolism
Middle Aged
Obesity/diagnosis/metabolism
Resistin/*blood
Subcutaneous Fat/*chemistry
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/metabolism
Figure
Reference
-
1. Havel PJ. Control of energy homeostasis and insulin action by adipocyte hormones: leptin, acylation stimulating protein, and adiponectin. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2002. 13:51–59.
Article2. Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM, Patel HR, Ahima RS, Lazar MA. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature. 2001. 409:307–312.
Article3. Banerjee RR, Rangwala SM, Shapiro JS, Rich AS, Rhoades B, Qi Y, Wang J, Rajala MW, Pocai A, Scherer PE, Steppan CM, Ahima RS, Obici S, Rossetti L, Lazar MA. Regulation of fasted blood glucose by resistin. Science. 2004. 303:1195–1198.
Article4. Rajala MW, Obici S, Scherer PE, Rossetti L. Adipose-derived resistin and gut-derived resistin-like molecule-beta selectively impair insulin action on glucose production. J Clin Invest. 2003. 111:225–230.5. Muse ED, Obici S, Bhanot S, Monia BP, McKay RA, Rajala MW, Scherer PE, Rossetti L. Role of resistin in diet-induced hepatic insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2004. 114:232–239.
Article6. Fujinami A, Obayashi H, Ohta K, Ichimura T, Nishimura M, Matsui H, Kawahara Y, Yamazaki M, Ogata M, Hasegawa G, Nakamura N, Yoshikawa T, Nakano K, Ohta M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for circulating human resistin: resistin concentrations in normal subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin Chim Acta. 2004. 339:57–63.
Article7. Youn BS, Yu KY, Park HJ, Lee NS, Min SS, Youn MY, Cho YM, Park YJ, Kim SY, Lee HK, Park KS. Plasma resistin concentrations measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a newly developed monoclonal antibody are elevated in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. 89:150–156.
Article8. Degawa-Yamauchi M, Bovenkerk JE, Juliar BE, Watson W, Kerr K, Jones R, Zhu Q, Considine RV. Serum resistin (FIZZ3) protein is increased in obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 88:5452–5455.
Article9. Heilbronn LK, Rood J, Janderova L, Albu JB, Kelley DE, Ravussin E, Smith SR. Relationship between serum resistin concentrations and insulin resistance in nonobese, obese, and obese diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. 89:1844–1848.
Article10. Lee JH, Chan JL, Yiannakouris N, Kontogianni M, Estrada E, Seip R, Orlova C, Mantzoros CS. Circulating resistin levels are not associated with obesity or insulin resistance in humans and are not regulated by fasting or leptin administration: cross-sectional and interventional studies in normal, insulin-resistant, and diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 88:4848–4856.
Article11. Shetty GK, Economides PA, Horton ES, Mantzoros CS, Veves A. Circulating adiponectin and resistin levels in relation to metabolic factors, inflammatory markers, and vascular reactivity in diabetic patients and subjects at risk for diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:2450–2457.
Article12. Sjostrom L, Kvist H, Cederblad A, Tylen U. Determination of total adipose tissue and body fat in women by computed tomography, 40K, and tritium. Am J Physiol. 1986. 250:E736–E745.
Article13. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985. 28:412–419.14. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ, Krauss RM, Savage PJ, Smith SC Jr, Spertus JA, Costa F. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation. 2005. 112:2735–2752.15. Moore GB, Chapman H, Holder JC, Lister CA, Piercy V, Smith SA, Clapham JC. Differential regulation of adipocytokine mRNAs by rosiglitazone in db/db mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. 286:735–741.
Article16. Way JM, Gorgun CZ, Tong Q, Uysal KT, Brown KK, Harrington WW, Oliver WR Jr, Willson TM, Kliewer SA, Hotamisligil GS. Adipose tissue resistin expression is severely suppressed in obesity and stimulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:25651–25653.17. Fukui Y, Motojima K. Expression of resistin in the adipose tissue is modulated by various factors including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2002. 4:342–345.18. Rajala MW, Lin Y, Ranalletta M, Yang XM, Qian H, Gingerich R, Barzilai N, Scherer PE. Cell type-specific expression and coregulation of murine resistin and resistin-like molecule-alpha in adipose tissue. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. 16:1920–1930.19. Fasshauer M, Klein J, Neumann S, Eszlinger M, Paschke R. Tumor necrosis factor alpha is a negative regulator of resistin gene expression and secretion in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. 288:1027–1031.20. Savage DB, Sewter CP, Klenk ES, Segal DG, Vidal-Puig A, Considine RV, O'Rahilly S. Resistin/Fizz3 expression in relation to obesity and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma action in humans. Diabetes. 2001. 50:2199–2202.21. Patel L, Buckels AC, Kinghorn IJ, Murdock PR, Holbrook JD, Plumpton C, Macphee CH, Smith SA. Resistin is expressed in human macrophages and directly regulated by PPAR gamma activators. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. 300:472–476.22. McTernan CL, McTernan PG, Harte AL, Levick PL, Barnett AH, Kumar S. Resistin, central obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2002. 359:46–47.
Article23. Hotamisligil GS. The irresistible biology of resistin. J Clin Invest. 2003. 111:173–174.
Article24. Smith SR, Bai F, Charbonneau C, Janderova L, Argyropoulos G. A promoter genotype and oxidative stress potentially link resistin to human insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2003. 52:1611–1618.
Article25. Felipe F, Bonet ML, Ribot J, Palou A. Modulation of resistin expression by retinoic acid and vitamin A status. Diabetes. 2004. 53:882–889.
Article26. Bo S, Gambino R, Pagani A, Guidi S, Gentile L, Cassader M, Pagano GF. Relationships between human serum resistin, inflammatory markers and insulin resistance. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005. 29:1315–1320.
Article27. Lu SC, Shieh WY, Chen CY, Hsu SC, Chen HL. Lipopolysaccharide increases resistin gene expression in vivo and in vitro. FEBS lett. 2003. 530:158–162.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Relation of Serum Adiponectin and Resistin Concentrations with Metabolic Risk Factors
- Common Genetic Polymorphisms in the Promoter of Resistin Gene are Major Determinants of Plasma Resistin Concentrations in Humans
- Serum Resistin Levels are Associated with Obesity but not with Insulin Resistance in Children and Adolescents
- Resistin in Rodents and Humans
- Resistin Inhibits Insulin Secretion Through Inhibition of Insulin Granule Docking Via Downregulation of Rab3A in Pancreatic Beta-cells