The First Case of Antibiotic-associated Colitis by Clostridium difficile PCR Ribotype 027 in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jassa@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779175
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.3.520
Abstract
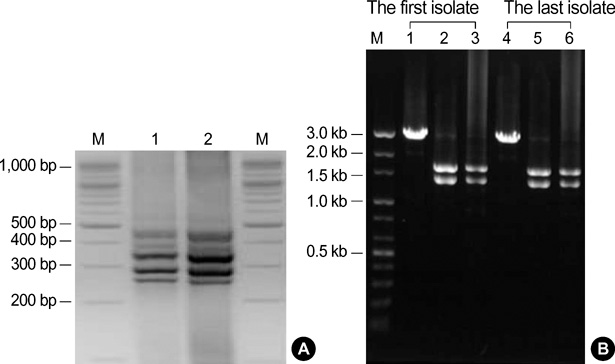
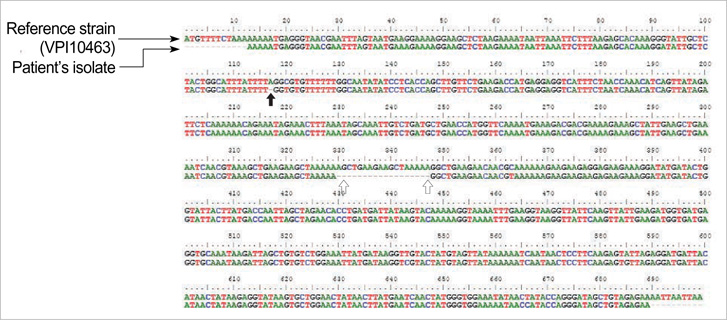
- Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) is a common causative agent of pseudomembranous colitis (PMC). C. difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) ranges from mild diarrhea to life threatening PMC. Recently, a highly virulent strain of C. difficile polymerase chain reaction ribotype 027 was found in North America, Europe, and Japan. A 52-yr-old woman with anti-tuberculosis medication and neurogenic bladder due to traffic accident experienced five episodes of C. difficile PMC after taking antibiotics for pneumonia along with septic shock and acute renal failure. She was readmitted to the intensive care unit and treated with oral vancomycin with refractory of oral metronidazole, inotropics and probiotics for over 60 days. C. difficile isolated both at the first and the last admission was identified as C. difficile ribotype 027 by ribotyping, toxinotyping, and tcdC gene sequencing, which turned out the same pathogen as the epidemic hypervirulent B1/NAP1 strain. This is the first case of C. difficile PCR ribotype 027 in Korea. After discharge, she was maintained on probiotics and rifaximin for 3 weeks. She had no relapse for 6 months.
MeSH Terms
-
Accidents, Traffic
Antitubercular Agents/therapeutic use
Base Sequence
Clostridium difficile/*classification/genetics/isolation & purification
Enterocolitis, Pseudomembranous/*diagnosis/drug therapy/*microbiology
Female
Humans
Kidney Failure, Acute/diagnosis
Korea
Middle Aged
Molecular Sequence Data
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Ribotyping
Shock, Septic/diagnosis
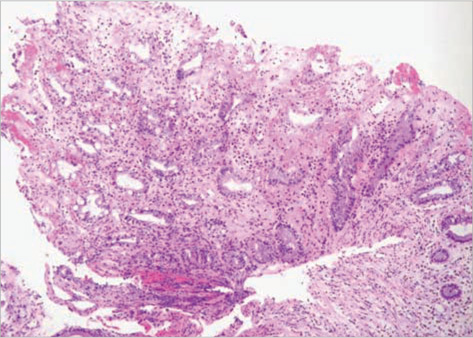
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Clinical and Microbiologic Characteristics of Clostridium difficile Infection Caused by Binary Toxin Producing Strain in Korea
Jieun Kim, Mi-ran Seo, Jung Oak Kang, Tae Yeal Choi, Hyunjoo Pai
Infect Chemother. 2013;45(2):175-183. doi: 10.3947/ic.2013.45.2.175.Rapid and accurate diagnosis of
Clostridium difficile infection by real-time polymerase chain reaction
Pil Hun Song, Jung Hwa Min, You Sun Kim, Soo Yeon Jo, Eun Jin Kim, Kyung Jin Lee, Jeonghun Lee, Hyun Sung, Jeong Seop Moon, Dong Hee Whang
Intest Res. 2018;16(1):109-115. doi: 10.5217/ir.2018.16.1.109.Is
Clostridium difficile infection a real threat in patients with ulcerative colitis? A prospective, multicenter study in Korea
Dae Bum Kim, Kang-Moon Lee, Sang Hyoung Park, You Sun Kim, Eun Soo Kim, Jun Lee, Sung-Ae Jung, Geom Seog Seo, Ji Min Lee
Intest Res. 2018;16(2):267-272. doi: 10.5217/ir.2018.16.2.267.Long-Term Clinical Outcome of
Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized Patients: A Single Center Study
Young Seok Doh, You Sun Kim, Hye Jin Jung, Young Il Park, Jin Won Mo, Hyun Sung, Kyung Jin Lee, Young Ki Seo, Jeong Seop Moon, Seong Woo Hong
Intest Res. 2014;12(4):299-305. doi: 10.5217/ir.2014.12.4.299.
Reference
-
1. Mylonakis E, Ryan ET, Calderwood SB. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. Arch Intern Med. 2001. 161:525–533.2. Aslam S, Hamill RJ, Musher DM. Treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated disease: old therapies and new strategies. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005. 5:549–557.3. Bartlett JG. Narrative review: the new epidemic of Clostridium difficile-associated enteric disease. Ann Intern Med. 2006. 145:758–764.4. Warny M, Pepin J, Fang A, Killgore G, Thompson A, Brazier J, Frost E, McDonald LC. Toxin production by an emerging strain of Clostridium difficile associated with outbreaks of severe disease in North America and Europe. Lancet. 2005. 366:1079–1084.5. Jung SW, Jeon SW, Do BH, Kim SG, Ha SS, Cho CM, Tak WY, Kweon YO, Kim SK, Choi YH, Cha SI. Clinical aspects of rifampicin-associated pseudomembranous colitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007. 41:38–40.
Article6. Kato H, Ito Y, van den Berg RJ, Kuijper EJ, Arakawa Y. First isolation of Clostridium difficile 027 in Japan. Euro Surveill. 2007. 12:E070111.3.7. Stubbs SL, Brazier JS, O'Neill GL, Duerden BI. PCR targeted to the 16S-23S rRNA gene intergenic spacer region of Clostridium difficile and construction of a library consisting of 116 different PCR ribotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:461–463.8. Rupnik M, Avesani V, Janc M, von Eichel-Streiber C, Delmée M. A novel toxinotyping scheme and correlation of toxinotypes with serogroups of Clostridium difficile isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1998. 36:2240–2247.9. Spigaglia P, Mastrantonio P. Comparative analysis of Clostridium difficile clinical isolates belonging to different genetic lineages and time periods. J Med Microbiol. 2004. 53:1129–1136.10. Curry SR, Marsh JW, Muto CA, O'Leary MM, Pasculle AW, Harrison LH. tcdC genotypes associated with Severe TcdC truncation in an epidemic clone and other strains of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. 45:215–221.11. Bartlett JG, Chang TW, Gurwith M, Gorbach SL, Onderdonk AB. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to toxin-producing clostridia. N Engl J Med. 1978. 298:531–534.
Article12. Bartlett JG. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis. 1992. 15:573–581.
Article13. Mandelll GL, Petri WA Jr. Hardman JG, Limbird LE, editors. Antimicrobial agents (continued). Goldman and Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 1996. 9th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill;1155–1174.14. Fekety R, McFarland LV, Surawicz CM, Greenberg RN, Elmer GW, Mulligan ME. Recurrent Clostridium difficile diarrhea: characteristics of risk factors for patients in a prospective, randomized, double-blinded trial. Clin Infect Dis. 1997. 24:324–333.15. Do AN, Fridkin SK, Yechouron A, Banerjee SN, Killgore GE, Bourgault AM, Jolivet M, Jarvis WR. Risk factors for early recurrent Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis. 1998. 26:954–959.16. Pepin J, Routhier S, Gagnon S, Brazeau I. Management and outcomes of a first recurrence of Clostridium difficile-associated disease in Quebec, Canada. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. 42:758–764.17. You DM, Franzos MA, Holman RP. Successful treatment of fulminant Clostridium difficile infection with fecal bacteriotherapy. Ann Intern Med. 2008. 148:632–633.18. Pepin J, Valiquette L, Cossette B. Mortality attributable to nosocomial Clostridium difficile-associated disease during an epidemic caused by a hypervirulent strain in Quebec. CMAJ. 2005. 173:1037–1042.19. Gerding DN, Muto CA, Owens RC Jr. Treatment of Clostridium difficile infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:Suppl 1. S32–S42.20. Hermsen JL, Dobrescu C, Kudsk KA. Clostridium difficile infection: a surgical disease in evolution. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008. 12:1512–1517.21. Kato N, Ou CY, Kato H, Bartley SL, Luo CC, Killgore GE, Ueno K. Detection of toxigenic Clostridium difficile in stool specimens by the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1993. 167:455–458.22. Karasawa T, Nojiri T, Hayashi Y, Maegawa T, Yamakawa K, Wang XM, Nakamura S. Laboratory diagnosis of toxigenic Clostridium difficile by polymerase chain reaction: presence of toxin genes and their stable expression in toxigenic isolates from Japanese individuals. J Gastroenterol. 1999. 34:41–45.23. Bidet P, Lalande V, Salauze B, Burghoffer B, Avesani V, Delmee M, Rossier A, Barbut F, Petit JC. Comparison of PCR-ribotyping, arbitrary primed PCR, and pulsed-filed gel electrophoresis for typing Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:2484–2487.24. Gerding DN, Muto CA, Owens RC Jr. Measures to control and prevent Clostridium difficile infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:Suppl 1. S43–S49.25. Bartlett JG, Gerding DN. Clinical recognition and diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:Suppl 1. S12–S18.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Emergence of Clostridium difficile Ribotype 027 in Korea
- Characteristics of Clostridium difficile colitis
- A Case of Pseudomembranous Colitis due to Clostridium difficile
- Evaluation of the Xpert Clostridium difficile Assay for the Diagnosis of Clostridium difficile Infection
- A Case of Cytomegalovirus and Pseudomembranous Colitis in an Immunocompetent Adult