J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Oct;27(10):1202-1207. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.10.1202.
Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication According to the IL-8-251 Polymorphism in Koreans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Healthcare Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital Healthcare System Gangnam Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine and Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. harley1333@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1778827
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.10.1202
Abstract
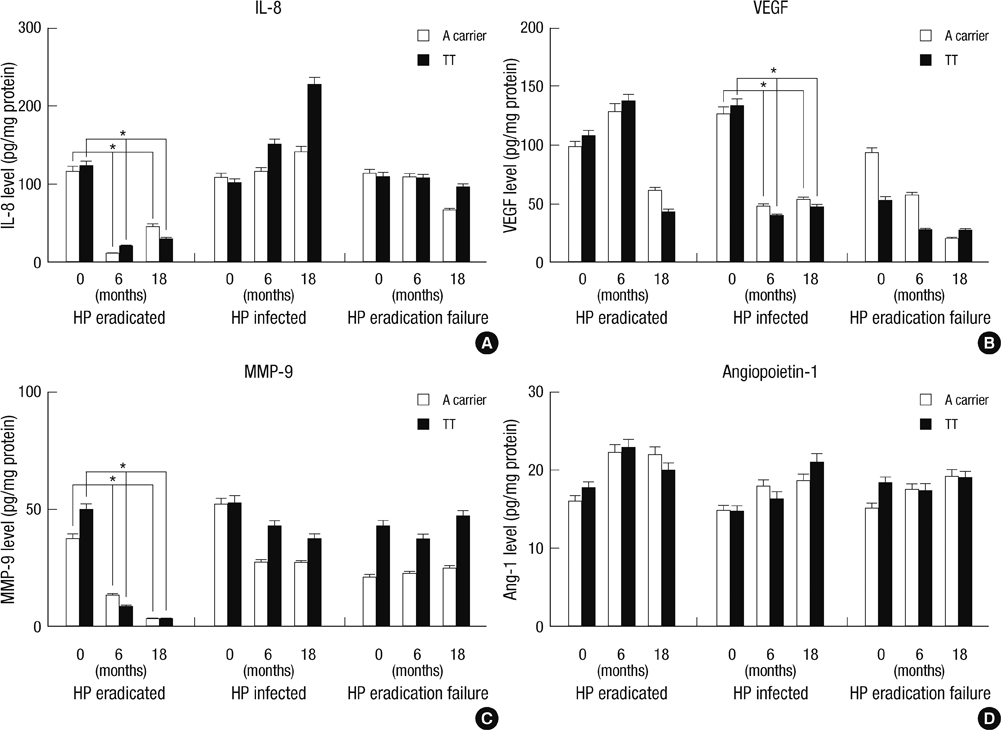
- Previous studies suggested that polymorphisms of proinflammatory cytokine genes are important host genetic factors in Helicobacter pylori infection. The present study evaluated whether IL-8-251 polymorphism affected H. pylori eradication rate and to investigate the effect of H. pylori eradication on angiogenesis and the inflammatory process according to the IL-8-251 polymorphism. A total of 250 H. pylori-positive patients treated by endoscopic resection of the gastric neoplasm were classified into 3 groups (134 H. pylori-eradicated group, 19 H. pylori-eradication failure group, and 97 H. pylori-infected group). H. pylori status, histology, and angiogenic factor levels were evaluated at baseline, 6 months, and 18 months. H. pylori eradication rate was 92.9% in AA genotype, 85.7% in AT genotype and 88.4% in TT genotype (P value = 0.731). Elevated IL-8 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 concentrations in H. pylori-infected gastric mucosa were reversible by successful eradication of H. pylori, independent of the IL-8-251 polymorphism. It is suggested that elevated IL-8 and MMP-9 concentrations in H. pylori-infected gastric mucosa are altered significantly after successful eradication and these conditions continue for 18 months. However, IL-8-251 polymorphism does not affect H. pylori eradication rate and the sequential changes of related angiogenic factors after H. pylori eradication in Koreans.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Alleles
Angiopoietin-1/analysis
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal/therapeutic use
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Female
Gastric Mucosa/metabolism/pathology
Genotype
Helicobacter Infections/*drug therapy
*Helicobacter pylori
Humans
Interleukin-8/analysis/*genetics
Male
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9/analysis
Middle Aged
*Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Proton Pump Inhibitors/therapeutic use
Republic of Korea
Retrospective Studies
Stomach Neoplasms/pathology/surgery
Time Factors
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A/analysis
Angiopoietin-1
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Interleukin-8
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9
Figure
Reference
-
1. Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, Matsumura N, Yamaguchi S, Yamakido M, Taniyama K, Sasaki N, Schlemper RJ. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001. 345:784–789.2. Correa P, Houghton J. Carcinogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology. 2007. 133:659–672.3. Taguchi A, Ohmiya N, Shirai K, Mabuchi N, Itoh A, Hirooka Y, Niwa Y, Goto H. Interleukin-8 promoter polymorphism increases the risk of atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer in Japan. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005. 14:2487–2493.4. Ohyauchi M, Imatani A, Yonechi M, Asano N, Miura A, Iijima K, Koike T, Sekine H, Ohara S, Shimosegawa T. The polymorphism interleukin 8-251 A/T influences the susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori related gastric diseases in the Japanese population. Gut. 2005. 54:330–335.5. Lu W, Pan K, Zhang L, Lin D, Miao X, You W. Genetic polymorphisms of interleukin (IL)-1B, IL-1RN, IL-8, IL-10 and tumor necrosis factor {alpha} and risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Carcinogenesis. 2005. 26:631–636.6. Machado JC, Figueiredo C, Canedo P, Pharoah P, Carvalho R, Nabais S, Castro Alves C, Campos ML, Van Doorn LJ, Caldas C, et al. A proinflammatory genetic profile increases the risk for chronic atrophic gastritis and gastric carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2003. 125:364–371.7. El-Omar EM, Rabkin CS, Gammon MD, Vaughan TL, Risch HA, Schoenberg JB, Stanford JL, Mayne ST, Goedert J, Blot WJ, et al. Increased risk of noncardia gastric cancer associated with proinflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms. Gastroenterology. 2003. 124:1193–1201.8. Figueiredo C, Machado JC, Pharoah P, Seruca R, Sousa S, Carvalho R, Capelinha AF, Quint W, Caldas C, van Doorn LJ, et al. Helicobacter pylori and interleukin 1 genotyping: an opportunity to identify high-risk individuals for gastric carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002. 94:1680–1687.9. Zhang QB, Dawodu JB, Husain A, Etolhi G, Gemmell CG, Russell RI. Association of antral mucosal levels of interleukin 8 and reactive oxygen radicals in patients infected with Helicobacter pylori. Clin Sci (Lond). 1997. 92:69–73.10. Craig PM, Territo MC, Karnes WE, Walsh JH. Helicobacter pylori secretes a chemotactic factor for monocytes and neutrophils. Gut. 1992. 33:1020–1023.11. Kitadai Y, Sasaki A, Ito M, Tanaka S, Oue N, Yasui W, Aihara M, Imagawa K, Haruma K, Chayama K. Helicobacter pylori infection influences expression of genes related to angiogenesis and invasion in human gastric carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. 311:809–814.12. Kitadai Y, Haruma K, Sumii K, Yamamoto S, Ue T, Yokozaki H, Yasui W, Ohmoto Y, Kajiyama G, Fidler IJ, et al. Expression of interleukin-8 correlates with vascularity in human gastric carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1998. 152:93–100.13. Ye BD, Kim SG, Park JH, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS. The Interleukin-8-251 A allele is associated with increased risk of noncardia gastric adenocarcinoma in Helicobacter pylori-infected Koreans. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009. 43:233–239.14. Song JH, Kim SG, Jung SA, Lee MK, Jung HC, Song IS. The interleukin-8-251 AA genotype is associated with angiogenesis in gastric carcinogenesis in Helicobacter pylori-infected Koreans. Cytokine. 2010. 51:158–165.15. Cox JM, Clayton CL, Tomita T, Wallace DM, Robinson PA, Crabtree JE. cDNA array analysis of cag pathogenicity island-associated Helicobacter pylori epithelial cell response genes. Infect Immun. 2001. 69:6970–6980.16. Arinir U, Klein W, Rohde G, Stemmler S, Epplen JT, Schultze-Werninghaus G. Polymorphisms in the interleukin-8 gene in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Electrophoresis. 2005. 26:2888–2891.17. Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, Correa P. Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney System. International Workshop on the Histopathology of Gastritis, Houston 1994. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996. 20:1161–1181.18. Nasu J, Doi T, Endo H, Nishina T, Hirasaki S, Hyodo I. Characteristics of metachronous multiple early gastric cancers after endoscopic mucosal resection. Endoscopy. 2005. 37:990–993.19. Arima N, Adachi K, Katsube T, Amano K, Ishihara S, Watanabe M, Kinoshita Y. Predictive factors for metachronous recurrence of early gastric cancer after endoscopic treatment. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999. 29:44–47.20. Wong BC, Lam SK, Wong WM, Chen JS, Zheng TT, Feng RE, Lai KC, Hu WH, Yuen ST, Leung SY, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication to prevent gastric cancer in a high-risk region of China: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004. 291:187–194.21. Leung WK, Lin SR, Ching JY, To KF, Ng EK, Chan FK, Lau JY, Sung JJ. Factors predicting progression of gastric intestinal metaplasia: results of a randomised trial on Helicobacter pylori eradication. Gut. 2004. 53:1244–1249.22. Ito M, Haruma K, Kamada T, Mihara M, Kim S, Kitadai Y, Sumii M, Tanaka S, Yoshihara M, Chayama K. Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy improves atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia: a 5-year prospective study of patients with atrophic gastritis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002. 16:1449–1456.23. Yeo M, Kim DK, Han SU, Lee JE, Kim YB, Cho YK, Kim JH, Cho SW, Hahm KB. Novel action of gastric proton pump inhibitor on suppression of Helicobacter pylori induced angiogenesis. Gut. 2006. 55:26–33.24. Mera R, Fontham ET, Bravo LE, Bravo JC, Piazuelo MB, Camargo MC, Correa P. Long term follow up of patients treated for Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut. 2005. 54:1536–1540.25. Kamada T, Haruma K, Hata J, Kusunoki H, Sasaki A, Ito M, Tanaka S, Yoshihara M. The long-term effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy on symptoms in dyspeptic patients with fundic atrophic gastritis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003. 18:245–252.26. Sung JJ, Lin SR, Ching JY, Zhou LY, To KF, Wang RT, Leung WK, Ng EK, Lau JY, Lee YT, et al. Atrophy and intestinal metaplasia one year after cure of H. pylori infection: a prospective, randomized study. Gastroenterology. 2000. 119:7–14.27. Bergin PJ, Anders E, Sicheng W, Erik J, Jennie A, Hans L, Pierre M, Qiang PH, Marianne QJ. Increased production of matrix metalloproteinases in Helicobacter pylori-associated human gastritis. Helicobacter. 2004. 9:201–210.28. Kim JS, Kim JM, Jung HC, Song IS. Helicobacter pylori down-regulates the receptors of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin in vascular endothelial cells: implications in the impairment of gastric ulcer healing. Dig Dis Sci. 2004. 49:778–786.29. Savage SA, Hou L, Lissowska J, Chow WH, Zatonski W, Chanock SJ, Teager M. Interleukin-8 polymorphisms are not associated with gastric cancer risk in a Polish population. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006. 15:589–591.30. Kamangar F, Abnet CC, Hutchinson AA, Newschaffer CJ, Helzlsouer K, Shugart YY, Pietinen P, Dawsey SM, Albanes D, Virtamo J, et al. Polymorphisms in inflammation-related genes and risk of gastric cancer (Finland). Cancer Causes Control. 2006. 17:117–125.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in functional dyspepsia
- Approach to Patients after Successful Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
- What is the Most Important Factor for Gastric Carcinogenesis in Koreans: Helicobacter pylori, Host Factor or Environmental Factor?
- Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: Report of 3 cases
- Effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori Eradication before Endoscopic Resection