J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Jun;21(3):585-587. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.585.
Bucillamine-Induced Pemphigus Vulgaris in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Polymyositis Overlap Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, The Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. dhyoo@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1778451
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.585
Abstract
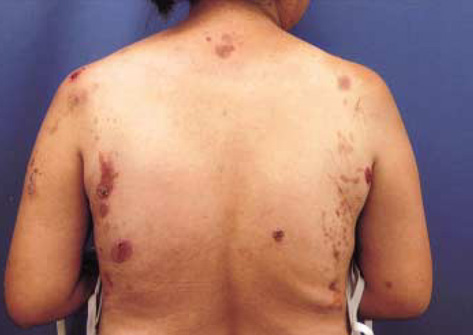
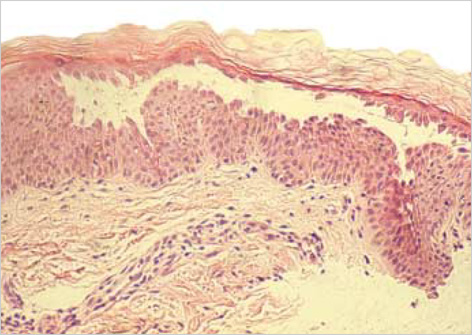
- Bucillamine is a disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug, structurally similar to D-penicillamine. Although D-penicillamine-induced pemphigus has been not infrequently demonstrated, pemphigus associated with bucillamine was rarely reported. We describe a patient complicating pemphigus vulgaris after bucillamine treatment in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and polymyositis (PM) overlap syndrome. PM and RA overlap syndrome was diagnosed three years ago and bucillamine was administrated for 20 months. Skin lesions including erythematous flaccid blisters on her chest, axillae, and back were occurred and were compatible with pemphigus vulgaris by typical pathology. Withdrawal from bucillamine and prednisolone treatment made rapid improvement of pemphigus lesions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Overlap Syndrome of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Polymyositis with the Involvement of Upper Pharyngeal Muscles
Won Seok Jang, So-Mi Kim, Seung-Jae Hong, Sang-Hoon Lee, Ran-Song, Hyung-In Yang, Yeon-Ah Lee
J Rheum Dis. 2013;20(4):251-255. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2013.20.4.251.
Reference
-
1. Yung CW, Hambrick GW Jr. D-Penicillamine--induced pemphigus syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982. 6:317–324.
Article2. Levy RS, Fisher M, Alter JN. Penicillamine: review and cutaneous manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983. 8:548–558.
Article3. Hirohata S, Lipsky PE. Regulation of B cell function by bucillamine, a novel disease-modifying antirheumatic drug. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993. 66:43–51.
Article4. Ciompi ML, Marchetti G, Bazzichi L, Puccetti L, Agelli M. D-penicillamine and gold salt treatments were complicated by myasthenia and pemphigus, respectively, in the same patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1995. 15:95–97.
Article5. Shapiro M, Jimenez S, Werth VP. Pemphigus vulgaris induced by D-penicillamine therapy in a patient with systemic sclerosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000. 42:297–299.
Article6. Jenkins EA, Hull RG, Thomas AL. D-penicillamine and polymyositis: the significance of the anti-Jo-1 antibody. Br J Rheumatol. 1993. 32:1109–1110.
Article7. Negishi M, Kaga S, Kasama T, Hashimoto M, Fukushima T, Yamagata N, Tabata M, Kobayashi K, Ide H, Takahashi T. Lung injury associated with bucillamine therapy. Ryumachi. 1992. 32:135–139.8. Sawa N, Ubara Y, Hara S, Hideyuki K, Tagami T, Yokoyama K, Takemoto F, Yamada A, Mori T, Mikami A, Tachibana S, Nakase K. A case of rheumatoid arthritis with bucillamine-induced myasthenia gravis treated by immunoadsorption therapy. Ryumachi. 1999. 39:33–38.9. Obayashi M, Uzu T, Harada T, Yamato M, Takahara K, Yamauchi A. Clinical course of bucillamine-induced nephropathy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2003. 7:275–278.
Article10. Brenner S, Wolf R, Ruocco V. Drug-induced pemphigus. I. A survey. Clin Dermatol. 1993. 11:501–505.
Article11. Ho VC, Stein HB, Ongley RA, McLeod WA. Penicillamine induced pemphigus. J Rheumatol. 1985. 12:583–586.12. Kishimoto K, Iwatsuki K, Akiba H, Motoki Y, Kaneko F. Subcorneal pustular dermatosis-type IgA pemphigus induced by thiol drugs. Eur J Dermatol. 2001. 11:41–44.13. Bialy-Golan A, Brenner S. Penicillamine-induced bullous dermatoses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996. 35:732–742.
Article14. Ogata K, Nakajima H, Ikeda M, Yamamoto Y, Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Kodama H. Drug-induced pemphigus foliaceus with features of pemphigus vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2001. 144:421–422.
Article15. Kitajima Y. Current and prospective understanding of clinical classification, pathomechanisms and therapy in pemphigus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2003. 295:Suppl 1. 17–23.
Article16. Piamphongsant T, Ophaswongse S. Treatment of pemphigus. Int J Dermatol. 1991. 30:139–146.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Overlap Syndrome with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Polymyositis
- A Case of Overlap Syndrome with Systemic Sclerosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- A Case of Overlap Syndrome of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Polymyositis with the Involvement of Upper Pharyngeal Muscles
- Three Cases of Overlap Syndrome Consisting of Systemic Sclerosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Overlap Syndrome of Antisynthetase Syndrome and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case Report