J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Jun;21(3):452-456. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.452.
Maternal Serum and Amniotic Fluid Inhibin A Levels in Women who Subsequently Develop Severe Preeclampsia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Medical Genetics, Samsung Cheil Hospital and Women's Healthcare Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hmryu@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Samsung Cheil Hospital and Women's Healthcare Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1778427
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.452
Abstract
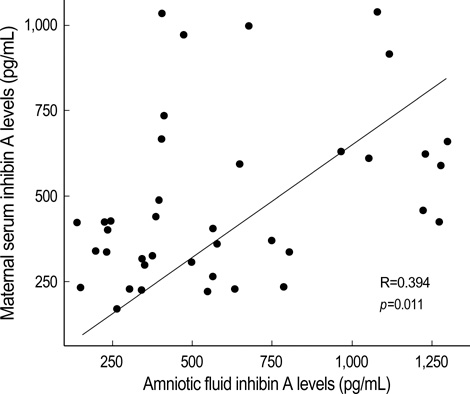
- The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether maternal serum (MS) and amniotic fluid (AF) inhibin A levels are elevated in patients who subsequently develop severe preecalmpsia, and to investigate the correlation between MS and AF inhibin A levels in the second trimester. The study included 40 patients who subsequently developed severe preecalmpsia and 80 normal pregnant women. Inhibin A levels in MS and AF were measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The MS and AF inhibin A levels in patients who developed severe preeclampsia were significantly higher than those in the control group (both for p<0.001). There was a positive correlation between MS and AF inhibin A levels in patients who developed severe preeclampsia (r=0.397, p=0.011), but not in the control group (r=0.185, p=0.126). The best cutoff values of MS and AF inhibin A levels for the prediction of severe preeclampsia were 427 pg/mL and 599 pg/mL, respectively; the estimated ORs that were associated with these cut-off values were 9.95 (95% CI 3.8-25.9, p<0.001) and 6.0 (95% CI 2.3-15.8, p<0.001). An elevated level of inhibin A in MS and AF at the time of second trimester amniocentesis may be a risk factor for the subsequent development of severe preeclampsia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Roberts JM, Cooper DW. Pathogenesis and genetics of pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 2001. 357:53–56.
Article2. Meekins JW, Pijnenborg R, Hanssens M, McFadyen IR, van Asshe A. A study of placental bed spiral arteries and trophoblast invasion in normal and severe pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1994. 101:669–674.
Article3. Muttukrishna S, North RA, Morris J, Schellenberg JC, Taylor RS, Asselin J, Ledger W, Groome N, Redman CW. Serum inhibin A and activin A are elevated prior to the onset of preeclampsia. Hum Reprod. 2000. 15:1640–1645.
Article4. Lambert-Messerlian GM, Silver HM, Petraglia F, Luisi S, Pezzani I, Maybruck WM, Hogge WA, Hanley-Yanez K, Roberts JM, Neveux LM, Canick JA. Second-trimester levels of maternal serum human chorionic gonadotropin and inhibin 6 as predictors of preeclampsia in the third trimester of pregnancy. J Soc Gynecol Invest. 2000. 7:170–174.5. Aquilina J, Barnett A, Thompson O, Harrington K. Second-trimester maternal serum inhibin A concentration as an early marker for preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999. 181:131–136.
Article6. Silver HM, Lambert-Messerlian GM, Star JA, Hogan J, Canick JA. Comparison of maternal serum total activin A and inhibin A in normal, preeclamptic, and nonproteinuric gestationally hypertensive pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999. 180:1131–1137.
Article7. Gratacos E, Casals E, Gomez O, Aibar C, Cararach V, Alonso PL, Fortuny A. Inhibin A serum levels in proteinuric and nonproteinuric pregnancy-induced hypertension: Evidence for placental involvement in gestational hypertension? Hypertens Pregnancy. 2000. 19:315–321.8. Muttukrishna S, Knight PG, Groome NP, Redman CW, Ledger WL. Activin A and inhibin A as possible endocrine markers for preeclampsia. Lancet. 1997. 349:1285–1288.
Article9. Sebire NJ, Roberts L, Noble P, Wallace E, Nicolaides KH. Raised maternal serum inhibin A concentration at 10 to 14 weeks of gestation is associated with pre-eclampsia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 2000. 107:795–797.
Article10. Fraser RF, McAsey ME, Coney P. Inhibin A and pro-alpha C are elevated in preeclamptic pregnancy and correlate with human chorionic gonadotropin. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1998. 40:37–42.11. Wallace EM, Riley SC, Crossley JA, Ritoe SC, Horne A, Shade M, Ellis PM, Aitken DA, Groome NP. Dimeric inhibins in amniotic fluid, maternal serum, and fetal serum in human pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997. 82:218–222.
Article12. Wallace EM, Crossley JA, Groome NP, Aitken DA. Amniotic fluid inhibin A in chromosomally normal and Down's syndrome pregnancies. J Endocrinol. 1997. 152:109–112.13. Wallace EM, D'Antona D, Shearing C, Evans LW, Thirunavukarasu P, Ashby JP, Shade M, Groome NP. Amniotic fluid levels of dimeric inhibins, pro-alpha C inhibin, activin A and follistatin in Down's syndrome. Clin Endocrinol. 1999. 50:669–673.14. Cuningham FG, Gant NF, Leveno KJ, Gilstrap LC III, Hauth JC, Wenstrom KD. Williams Obstetrics. 2001. 21st Ed. McGraw-Hill;568–569.15. Cuckle H, Sehmi I, Jones R. Maternal serum inhibin A can predict pre-eclampsia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998. 105:1101–1103.
Article16. Aquilina J, Thompson O, Thilaganathan B, Harrington K. Improved early prediction of pre-eclampsia by combining second-trimester maternal serum inhibin A and uterine artery Doppler. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001. 17:477–484.17. King IB, Williams MA, Sorensen TK, Luthy DA. Inhibin A and activin A levels in the second trimester as predictors of preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998. 178:S115.18. Grobman WA, Wang EY. Serum levels of activin A and inhibin A and the subsequent development of preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 2000. 96:390–394.
Article19. D'Anna R, Baviera G, Corrado F, Leonardi I, Buemi M, Jasonni VM. Is mid-trimester maternal serum inhibin A a marker of preeclampsia or intrauterine growth restriction? Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2002. 81:540–543.20. Pijnenborg R, Dixon G, Robertson WB, Brosens I. Trophoblastic invasion of human decidua from 8 to 18 weeks of pregnancy. Placenta. 1980. 1:3–19.
Article21. Arnholdt H, Meisel F, Fandrey K, Lohrs U. Proliferation of villous trophoblast of the human placenta in normal and abnormal pregnancies. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1991. 60:365–372.
Article22. Redman CW. Current topic: pre-eclampsia and the placenta. Placenta. 1991. 12:301–308.23. Keelan JA, Marvin KW, Sato TA, McCowan LM, Coleman M, Evans LW, Groome NP, Mitchell MD. Concentrations of activin A, inhibin A and follistatin in human amnion, choriodecidual and placental tissues at term and preterm. J Endocrinol. 1999. 163:99–106.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of midtrimester amniotic fluid 8-isoprostane measurement in the prediction of severe preeclampsia
- Uric Acid Concentrations of Serum , Amniotic Fluid , and Fetal Serum in Pregnant Woman with Preeclampsia
- Midtrimester Amniotic Fluid Levels and Each Ratio of Activn A, Inhibin A and B in Down's Syndrome and Other Complicated Pregnancies
- Amniotic fluid human chorionic gonadotropin and alpha-fetoprotein in severe preeclampsia
- The Differences in Second Trimester Quad Test Markers in Patients with Severe Preeclampsia Depending on the Disease Onset Time and the Presence of Fetal Growth Restriction