J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Jan;24(Suppl 1):S210-S214. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S210.
Two Korean Infants with Genetically Confirmed Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome of Finnish Type
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. cheonghi@snu.ac.kr
- 2East West Kidney Diseases Research Institute, Department of Pediatrics, Kyung-Hee University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Kidney Research Institute, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1778164
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S210
Abstract
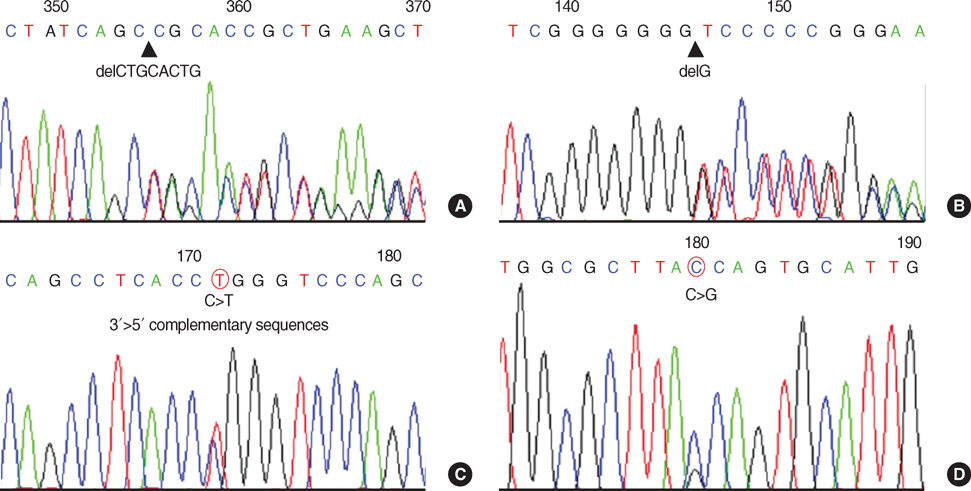
- Congenital nephrotic syndrome is defined as nephrotic syndrome which manifests in utero or during the first 3 months of life. The prototype of congenital nephrotic syndrome is congenital nephrotic syndrome of Finnish type (CNF, OMIM #602716), which is caused by loss-of-function mutations of the nephrin gene (NPHS1). There have been few clinical case reports of CNF in Korea, but none of which was confirmed by genetic study. Here, we report two children with congenital nephrotic syndrome. Genetic analysis of the NPHS1 gene revealed compound heterozygous frame-shifting mutations (c.2156_2163 delTGCACTGC causing p.L719DfsX4 and c.3250_3251insG causing p.V1084GfsX12) in one patient and a missense mutation (c.1381G>A causing p.R460Q) and a nonsense mutation (c.2442C>G causing p.Y814X) in the other patient. The nonsense mutation was novel. The clinical courses of the patients were typical of CNF. This is the first report of genetically confirmed CNF in Korea to date. The early genetic diagnosis of CNF is important for proper clinical management of the patients and precise genetic counseling of the families.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Habib R. Nephrotic syndrome in the 1st year of life. Pediatr Nephrol. 1993. 7:347–353.
Article2. Hinkes BG, Mucha B, Vlangos CN, Gbadegesin R, Liu J, Hasselbacher K, Hangan D, Ozaltin F, Zenker M, Hildebrandt F. Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Paediatrische Nephrologie Study Group. Nephrotic syndrome in the first year of life: two thirds of cases are caused by mutations in 4 genes (NPHS1, NPHS2, WT1, and LAMB2). Pediatrics. 2007. 119:e907–e919.
Article3. Kestilä M, Lenkkeri U, Mannikkö M, Lamerdin J, McCready P, Putaala H, Ruotsalainen V, Morita T, Nissinen M, Herva R, Kashtan CE, Peltonen L, Holmberg C, Olsen A, Tryggvason K. Positionally cloned gene for a novel glomerular protein-nephrin-is mutated in congenital nephrotic syndrome. Mol Cell. 1998. 1:575–582.
Article4. Beltcheva O, Martin P, Lenkkeri U, Tryggvason K. Mutation spectrum in the nephrin gene (NPHS1) in congenital nephrotic syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2001. 17:368–373.
Article5. Jalanko H. Congenital nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007. 10. 30. [Epub ahead of print].
Article6. Lee YK, Cha ES, Kwon MJ, Lee JS, Kim PK, Jeong HJ. Congenital nephrotic syndrome. Korean J Nephrol. 1997. 16:136–141.7. Min JS, Shon YK, Lee SW, Kang SC, Park YK, Yang MH. A case of Finnish type of congenital nephrotic syndrome. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1982. 25:175–182.8. Boute N, Gribouval O, Roselli S, Benessy F, Lee H, Fuchshuber A, Dahan K, Gubler MC, Niaudet P, Antignac C. NPHS2, encoding the glomerular protein podocin, is mutated in autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Nat Genet. 2000. 4:349–354.
Article9. Mucha B, Ozaltin F, Hinkes BG, Hasselbacher K, Ruf RG, Schultheiss M, Hangan D, Hoskins BE, Everding AS, Bogdanovic R, Seeman T, Hoppe B, Hildebrandt F. Members of the APN study group. Mutations in the Wilms' tumor 1 gene cause isolated steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome and occur in exons 8 and 9. Pediatr Res. 2006. 59:325–331.
Article10. Schumacher V, Scharer K, Wuhl E, Altrogge H, Bonzel KE, Guschmann M, Neuhaus TJ, Pollastro RM, Kuwertz-Bröking E, Bulla M, Tondera AM, Mundel P, Helmchen U, Waldherr R, Weirich A, Royer-Pokora B. Spectrum of early onset nephrotic syndrome associated with WT1 missense mutations. Kidney Int. 1998. 53:1594–1600.
Article11. Zenker M, Aigner T, Wendler O, Tralau T, Müntefering H, Fenski R, Pitz S, Schumacher V, Royer-Pokora B, Wühl E, Cochat P, Bouvier R, Kraus C, Mark K, Madlon H, Dötsch J, Rascher W, Maruniak-Chudek I, Lennert T, Neumann LM, Reis A. Human laminin beta 2 deficiency causes congenital nephrosis with mesangial sclerosis and distinct eye abnormalities. Hum Mol Genet. 2004. 13:2625–2632.12. Hasselbacher K, Wiggins RC, Matejas V, Hinkes BG, Mucha B, Hoskins BE, Ozaltin F, Nürnberg G, Becker C, Hangan D, Pohl M, Kuwertz-Bröking E, Griebel M, Schumacher V, Royer-Pokora B, Bakkaloglu A, Nürnberg P, Zenker M, Hildebrandt F. Recessive missense mutations in LAMB2 expand the clinical spectrum of LAMB2-associated disorders. Kidney Int. 2006. 70:1008–1012.
Article13. Choi HJ, Lee BH, Kang JH, Jeong HJ, Moon KC, Ha IS, Yu YS, Matejas V, Zenker M, Choi Y, Cheong HI. Variable phenotype of Pierson syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2008. 23:995–1000.
Article14. Hinkes B, Wiggins RC, Gbadegesin R, Vlangos CN, Seelow D, Nürnberg G, Garg P, Verma R, Chaib H, Hoskins BE, Ashraf S, Becker C, Hennies HC, Goyal M, Wharram BL, Schachter AD, Mudumana S, Drummond I, Kerjaschki D, Waldherr R, Dietrich A, Ozaltin F, Bakkaloglu A, Cleper R, Basel-Vanagaite L, Pohl M, Griebel M, Tsygin AN, Soylu A, Müller D, Sorli CS, Bunney TD, Katan M, Liu J, Attanasio M, O'toole JF, Hasselbacher K, Mucha B, Otto EA, Airik R, Kispert A, Kelley GG, Smrcka AV, Gudermann T, Holzman LB, Nurnberg P, Hildebrandt F. Positional cloning uncovers mutations in PLCE1 responsible for a nephrotic syndrome variant that may be reversible. Nat Genet. 2006. 38:1397–1405.
Article15. Kaplan JM, Kim SH, North KN, Rennke H, Correia LA, Tong HQ, Mathis BJ, Rodríguez-Pérez JC, Allen PG, Beggs AH, Pollak MR. Mutations in ACTN4, encoding alpha-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet. 2000. 24:251–256.16. Winn MP, Conlon PJ, Lynn KL, Farrington MK, Creazzo T, Hawkins AF, Daskalakis N, Kwan SY, Ebersviller S, Burchette JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Howell DN, Vance JM, Rosenberg PB. A mutation in the TRPC6 cation channel causes focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Science. 2005. 308:1801–1804.17. Kim JM, Wu H, Green G, Winkler CA, Kopp JB, Miner JH, Unanue ER, Shaw AS. CD2-associated protein haploinsufficiency is linked to glomerular disease susceptibility. Science. 2003. 300:1298–1300.
Article18. Cho HY, Lee JH, Choi HJ, Lee BH, Ha IS, Choi Y, Cheong HI. WT1 and NPHS2 mutations in Korean children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2008. 23:63–70.
Article19. Gigante M, Monno F, Roberto R, Laforgia N, Assael MB, Livolti S, Caringella A, La Manna A, Masella L, Iolascon A. Congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type in Italy: a molecular approach. J Nephrol. 2002. 15:696–702.20. Sako M, Nakanishi K, Obana M, Yata N, Hoshii S, Takahashi S, Wada N, Takahashi Y, Kaku Y, Satomura K, Ikeda M, Honda M, Iijima K, Yoshikawa N. Analysis of NPHS1, NPHS2, ACTN4, and WT1 in Japanese patients with congenital nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2005. 67:1248–1255.
Article21. Patrakka J, Kestilä M, Wartiovaara J, Ruotsalainen V, Tissari P, Lenkkeri U, Männikkö M, Visapää I, Holmberg C, Rapola J, Tryggvason K, Jalanko H. Congenital nephrotic syndrome (NPHS1): features resulting from different mutations in Finnish patients. Kidney Int. 2000. 58:972–980.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of Finnish Type of Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome
- Clinical Evaluation of Nephrotic Syndrome Manifesting in the First Year of Life
- HLA Type in Minimal Lesion Nephrotic Syndrome (MLNS) in Childhood
- A Case of Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome due to Diffuse Mesangial Sclerosis
- A case of Congenital Syphilitic Nephrotic Syndrome