J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Jan;26(1):108-115. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.1.108.
Relationships of Mental Disorders and Weight Status in the Korean Adult Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. jnbae@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Science, Institute of Human Behavioral Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Psychiatry, Kangwon National University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Psychiatry, Gachon Medical School, Incheon, Korea.
- 6Department of Psychiatry, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Neuropsychiatry, DongGuk International Hospital, DongGuk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 8Department of Psychiatry, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 9Department of Psychiatry, Depression center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1777984
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.1.108
Abstract
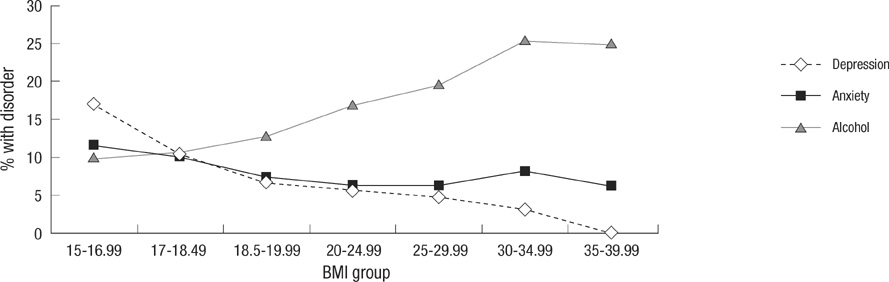
- The purpose of this study was to evaluate the associations between weight status and mental disorders, including depressive disorder, anxiety disorder and alcohol use disorder. A total of nationally representative 6,510 subjects aged 18-64 yr was interviewed in face-to-face household survey. Response rate was 81.7%. Mental disorders were diagnosed using the Korean version of the Composite International Diagnostic Interview (K-CIDI). The subjects reported their heights and weights. After adjusting for age and gender, the lifetime diagnosis of depressive disorder had a significant association with only the underweight group (odds ratio [OR], 1.68, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.19-2.38). The association between underweight and depressive disorder was the strongest for subjects with a high education level (OR, 1.75, 95% CI, 1.2-2.56), subjects with a married/cohabiting status (OR, 1.94, 95% CI, 1.17-3.22) and smokers (OR, 2.58, 95% CI, 1.33-4.98). There was no significant association between obesity and depressive disorder in Korea. But there was a significant association between the underweight group and depressive disorder. The relationship between obesity and mental disorder in a Korean population was different from that in a Western population. These results suggest that the differences of traditional cultures and races might have an important effect on the associations between the weight status and mental disorders.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Relationships between obesity, blood and urinary compositions, and dietary habits and depressed mood in Koreans at the age of 40, a life transition period
*
Ji Eun Chu, Ji Min Lee, Han-Ik Cho, Jung Yoon Park
J Nutr Health. 2012;46(3):261-275. doi: 10.4163/jnh.2012.46.3.261.
Reference
-
1. Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korean health and nutrition examination survey. 2005. Seoul: 38–39.2. Crisp AH, McGuiness B. Jolly fat: relation between obesity and psychoneurosis in general population. Br Med J. 1976. 1:7–9.3. Palinkas LA, Wingard DL, Barrett-Connor E. Depressive symptoms in overweight and obese older adults: a test of the "jolly fat" hypothesis. J Psychosom Res. 1996. 40:59–66.4. Roberts RE, Kaplan GA, Shema SJ, Strawbridge WJ. Are the obese at greater risk for depression? Am J Epidemiol. 2000. 152:163–170.5. Simon GE, Von Korff M, Saunders K, Miglioretti DL, Crane PK, van Belle G, Kessler RC. Association between obesity and psychiatric disorders in the US adult population. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006. 63:824–830.6. Scott KM, McGee MA, Wells JE, Oakley Browne MA. Obesity and mental disorders in the adult general population. J Psychosom Res. 2008. 64:97–105.7. Li ZB, Ho SY, Chan WM, Ho KS, Li MP, Leung GM, Lam TH. Obesity and depressive symptoms in Chinese elderly. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2004. 19:68–74.8. Kuriyama S, Koizumi Y, Matsuda-Ohmori K, Seki T, Shimazu T, Hozawa A, Awata S, Tsuji I. Obesity and depressive symptoms in elderly Japanese: the Tsurugaya project. J Psychosom Res. 2006. 60:229–235.9. Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. The Epidemiological survey of psychiatric illnesses in Korea. 2006. Seoul: 27–31.10. Cho MJ, Hahm BJ, Suh DW, Hong JP, Bae JN, Kim JK, Lee DW, Cho SJ. Development of a Korean version of the Composite International Diagnostic Interview (K-CIDI). J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2002. 41:123–137.11. World Health Organization. CIDI, Core version 2.1 Trainer's manual. 1997. Geneva: World Health Organization;1–244.12. World Health Organization. The world health report 2002: reducing risks, promoting healthy life. 2002. Geneva: World Health Organization;59.13. Cho MJ, Kim JK, Jeon HJ, Suh T, Chung IW, Hong JP, Bae JN, Lee DW, Park JI, Cho SJ, Lee CK, Hahm BJ. Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of DSM-IV psychiatric disorders among Korean adults. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2007. 195:203–210.14. WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004. 363:157–163.15. Korean society for the study of obesity. Clinical obesity. 2008. Seoul: Korean medical book publisher;179–180.16. Crandall CS, D'Anello S, Sakalli N, Lazarus E, Wieczorkowska G, Feather NT. An attribution-value model prejudice: anti-fat attitudes in six nations. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 2001. 27:30–37.17. Foster GD, Wadden TA. Blackburn GL, Kander BS, editors. The psychology of obesity, weight loss, and weight regain: research and clinical findings. Obesity: psychophysiology, psychology, and treatment. 1994. New York: Chapman & Hall;140–166.18. Mussell MP, Mitchell JE, Weller CL, Raymond NC, Crow SJ, Crosby RD. Onset of binge eating, dieting, obesity, and mood disorder among subjects seeking treatment for binge eating disorder. Int J Eat Disord. 1995. 17:395–401.19. Pickering RP, Grant BF, Chou SP, Compton WM. Are overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity associated with psychopathology? Results form the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007. 68:998–1009.20. Yanovski SZ. Binge eating disorder and obesity in 2003: could treating an eating disorder have a positive effect on the obesity epidemic? Int J Eat Disord. 2003. 34:Suppl. S117–S120.21. Ganley RM. Emotion and eating in obesity: a review of the literature. Int J Eat Disord. 1989. 8:343–361.22. Godart NT, Flament MF, Perdereau F, Jeammet P. Comorbidity between eating disorders and anxiety disorders: a review. Int J Eat Disord. 2002. 32:253–270.23. John U, Meyer C, Rumpf HJ, Hapke U. Relationships of psychiatric disorders with overweight and obesity in an adult general population. Obes Res. 2005. 13:101–109.24. Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG. Alcohol, body weight, and weight gain in middle-aged men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003. 77:1312–1317.25. Helzer JE, Canino GJ, Yeh EK, Bland RC, Lee CK, Hwu HG. Alcoholism--North America and Asia. A comparison of population surveys with the Diagnostic Interview Schedule. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1990. 47:313–319.26. Demyttenaere K, Bruffaerts R, Posada-Villa J, Gasquet I, Kovess V, Lepine JP, Angermeyer MC, Bernert S, de Girolamo G, Morosini P, Polidori G, Kikkawa T, Kawakami N, Ono Y, Takeshima T, Uda H, Karam EG, Fayyad JA, Karam AN, Mneimneh ZN, Medina-Mora ME, Borges G, Lara C, de Graaf R, Ormel J, Gureje O, Shen Y, Huang Y, Zhang M, Alonso J, Haro JM, Vilagut G, Bromet EJ, Gluzman S, Webb C, Kessler RC, Merikangas KR, Anthony JC, Von Korff MR, Wang PS, Brugha TS, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Lee S, Heeringa S, Pennell BE, Zaslavsky AM, Ustun TB, Chatterji S. WHO World Mental Health Survey Consortium. Prevalence, severity and unmet need for treatment of mental disorders in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. JAMA. 2004. 291:2581–2590.27. Kuczmarski MF, Kuczmarski RJ, Najjar M. Effect of age on validity of self-reported height, weight, and body mass index: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. 1988-1994. J Am Diet Assoc. 2001. 101:28–34.28. Steering Committee of the Western Pacific Region of the World Health Organization. The International Association for the Study of Obesity, and the International Obesity Task Force. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. 2000. Melbourne, Australia: Health Communications Australia Pty Ltd;18.29. Kanazawa M, Yoshiike N, Osaka T, Numba Y, Zimmet P, Inoue S. Criteria and classification of obesity in Japan and Asia-Oceania. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2002. 11:Suppl 8. S732–S737.30. McNeely MJ, Boyko EJ, Shofer JB, Newell-Morris L, Leonetti DL, Fujimoto WY. Standard definition of overweight and central adiposity for determining diabetes risk in Japanese Americans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001. 74:101–107.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Patterns of mental disorders among the elderly in a Korean rural community
- Mental Health Literacy for Diabetic Patients
- Social Distance Attitudes of Nursing Students towards Adults with Mental Disorders
- Common Mental Disorders in Primary Care
- Relationship Between Allergic Rhinitis and Mental Health in the General Korean Adult Population