Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2016 Jan;8(1):49-54. 10.4168/aair.2016.8.1.49.
Relationship Between Allergic Rhinitis and Mental Health in the General Korean Adult Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. kshent@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biostatistics, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2166649
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2016.8.1.49
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was conducted to evaluate the association between AR and mental health status in the general Korean adult population and to investigate the relative burden of AR on mental health using the Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) classification.
METHODS
A cross-sectional study was performed by using data from 11,154 individuals, 19 years old or older in the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2012. Univariate analysis was conducted in the healthy AR groups with weighted prevalence of demographic characteristics, socioeconomic status, and comorbid diseases. Subanalysis that classified AR severity according to the ARIA classification was carried out to evaluate the relationship of AR severity with mental health. The odds ratios (ORs) for each component representing mental health status were estimated by multiple logistic regression analysis with confounder adjustment.
RESULTS
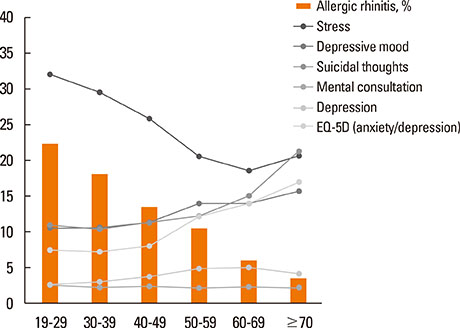
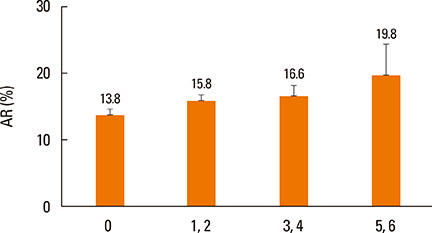
Univariate analysis with the chi-square test after adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, smoking status, alcohol use status, and exercise status, components representing mental health status showed a linear relationship with the severity of AR according to the ARIA classification. Stress, depressive mood, suicidal thoughts, and psychological consultation factors were correlated with AR after adjustment for demographic characteristics and socioeconomic status. Even after adjustment for comorbid allergic diseases, the correlation remained significant with stress, depressive mood, and psychological consultation factors (OR [95% CI]; 1.227 [1.042, 1.445], 1.368 [1.095, 1.71], 1.804 [1.096, 2.969], respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
Patients with AR appear to be at higher risk of mental disorders in the general Korean adult population. Moreover, persistent or severe AR was correlated with poor mental health. Therefore, better control of AR may be conducive to better mental health, and more attention should be paid to the psychological status of AR patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Unmet Primary Physicians' Needs for Allergic Rhinitis Care in Korea
Hyeon-Jong Yang, Young Hyo Kim, Bora Lee, Do Youn Kong, Dong-Kyu Kim, Mi-Ae Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Won-young Kim, Jeong Hee Kim, Yang Park, So Yeon Park, Woo Yong Bae, Keejae Song, Min Suk Yang, Sang Min Lee, Young-Mok Lee, Hyun Jong Lee, Jae-Hong Cho, Hye Mi Jee, Jeong-Hee Choi, Young Yoo, Young-Il Koh,
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(3):265-271. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.3.265.Prevalence of Self-reported Allergic Diseases and IgE Levels: A 2010 KNHANES Analysis
Hye Jung Park, Eun-Jin Kim, Dankyu Yoon, Jeom Kyu Lee, Woo-Sung Chang, Yoen-Mi Lim, Jung-Won Park, Joo-Shil Lee
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(4):329-339. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.4.329.
Reference
-
1. Dykewicz MS, Hamilos DL. Rhinitis and sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:S103–S115.2. Radon K, Gerhardinger U, Schulze A, Zock JP, Norback D, Toren K, et al. Occupation and adult onset of rhinitis in the general population. Occup Environ Med. 2008; 65:38–43.3. Salo PM, Calatroni A, Gergen PJ, Hoppin JA, Sever ML, Jaramillo R, et al. Allergy-related outcomes in relation to serum IgE: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:1226–1235.e7.4. Katelaris CH, Lai CK, Rhee CS, Lee SH, Yun WD, Lim-Varona L, et al. Nasal allergies in the Asian-Pacific population: results from the Allergies in Asia-Pacific Survey. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011; 25:S3–S15.5. Arnedo-Pena A, García-Marcos L, Blanco-Quirós A, Martínez Gimeno A, Aguinaga Ontoso I, González Díaz C, et al. Time trends in prevalence of symptoms of allergic rhinitis in 13-14 year-old schoolchildren in 8 areas of Spain between 1993-1994 and 2001-2002 according to the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC). Med Clin (Barc). 2004; 123:490–495.6. Lee SL, Wong W, Lau YL. Increasing prevalence of allergic rhinitis but not asthma among children in Hong Kong from 1995 to 2001 (Phase 3 International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood). Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004; 15:72–78.7. Lee H, Kim GS. Geographical and sociodemographic risk factors for allergic diseases in korean children. Asian Nurs Res. 2011; 5:1–10.8. Bousquet J, Bullinger M, Fayol C, Marquis P, Valentin B, Burtin B. Assessment of quality of life in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis with the French version of the SF-36 Health Status Questionnaire. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994; 94:182–188.9. Juniper EF. Quality of life in adults and children with asthma and rhinitis. Allergy. 1997; 52:971–977.10. Juniper EF. Measuring health-related quality of life in rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 99:S742–S749.11. Meltzer EO, Nathan RA, Seiner JC, Storms W. Quality of life and rhinitic symptoms: results of a nationwide survey with the SF-36 and RQLQ questionnaires. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 99:S815–S819.12. Spector SL. Overview of comorbid associations of allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 99:S773–S780.13. Leynaert B, Neukirch C, Liard R, Bousquet J, Neukirch F. Quality of life in allergic rhinitis and asthma. A population-based study of young adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 162:1391–1396.14. Postolache TT, Komarow H, Tonelli LH. Allergy: a risk factor for suicide? Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2008; 10:363–376.15. Sansone RA, Sansone LA. Allergic rhinitis: relationships with anxiety and mood syndromes. Innov Clin Neurosci. 2011; 8:12–17.16. Park JE, Lee JY, Jeon HJ, Han KH, Sohn JH, Sung SJ, et al. Age-related differences in the influence of major mental disorders on suicidality: a Korean nationwide community sample. J Affect Disord. 2014; 162:96–101.17. Johnston R, Brady HE. The rolling cross-section design. Elect Stud. 2002; 21:283–295.18. Choi JY, Ha HS, Kwon HS, Lee SH, Cho HH, Yim HW, et al. Characteristics of metabolically obese, normal-weight women differ by menopause status: the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Menopause. 2013; 20:85–93.19. Cheng HM, Kim S, Park GH, Chang SE, Bang S, Won CH, et al. Low vitamin D levels are associated with atopic dermatitis, but not allergic rhinitis, asthma, or IgE sensitization, in the adult Korean population. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 133:1048–1055.20. Nathan RA, Meltzer EO, Seiner JC, Storms W. Prevalence of allergic rhinitis in the United States. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 99:S808–S814.21. Choi CJ, Seo M, Choi WS, Kim KS, Youn SA, Lindsey T, et al. Relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and lung function among Korean adults in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2008-2010. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:1703–1710.22. Cuffel B, Wamboldt M, Borish L, Kennedy S, Crystal-Peters J. Economic consequences of comorbid depression, anxiety, and allergic rhinitis. Psychosomatics. 1999; 40:491–496.23. Tonelli LH, Holmes A, Postolache TT. Intranasal immune challenge induces sex-dependent depressive-like behavior and cytokine expression in the brain. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008; 33:1038–1048.24. Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Heffner KL, Glaser R, Malarkey WB, Porter K, Atkinson C, et al. How stress and anxiety can alter immediate and late phase skin test responses in allergic rhinitis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2009; 34:670–680.25. Tonelli LH, Katz M, Kovacsics CE, Gould TD, Joppy B, Hoshino A, et al. Allergic rhinitis induces anxiety-like behavior and altered social interaction in rodents. Brain Behav Immun. 2009; 23:784–793.26. Fang BJ, Tonelli LH, Soriano JJ, Postolache TT. Disturbed sleep: linking allergic rhinitis, mood and suicidal behavior. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2010; 2:30–46.27. Léger D, Annesi-Maesano I, Carat F, Rugina M, Chanal I, Pribil C, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its consequences on quality of sleep: an unexplored area. Arch Intern Med. 2006; 166:1744–1748.28. Kremer B, den Hartog HM, Jolles J. Relationship between allergic rhinitis, disturbed cognitive functions and psychological well-being. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:1310–1315.29. Wilken JA, Berkowitz R, Kane R. Decrements in vigilance and cognitive functioning associated with ragweed-induced allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002; 89:372–380.30. Wamboldt MZ, Hewitt JK, Schmitz S, Wamboldt FS, Räsänen M, Koskenvuo M, et al. Familial association between allergic disorders and depression in adult Finnish twins. Am J Med Genet. 2000; 96:146–153.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dermographism ( IV ): The Prevalence in Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Rhinitis
- Relationship Between Atopy and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness
- Allergic Rhinitis and Sleep-disordered Breathing
- Association between Allergic Rhinitis and Osteoarthritis in the Korean Adult Population-Based on the 3rd to 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Genetic Role in Allergic Rhinitis