Yonsei Med J.
2013 Jan;54(1):225-230. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.1.225.
Cerebral Oxygenation during Laparoscopic Surgery: Jugular Bulb versus Regional Cerebral Oxygen Saturation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Anesthesia and Pain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yjoh@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1776943
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.1.225
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We hypothesized that regional cerebral oxygen saturation (rSO2) could replace jugular bulb oxygen saturation (SjvO2) in the steep Trendelenburg position under pneumoperitoneum. Therefore, we evaluated the relationship between SjvO2 and rSO2 during laparoscopic surgery.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
After induction of anesthesia, mechanical ventilation was controlled to increase PaCO2 from 35 to 45 mm Hg in the supine position, and the changes in SjvO2 and rSO2 were measured. Then, after establishment of pneumoperitoneum and Trendelenburg position, ventilation was controlled to maintain a PaCO2 at 35 mm Hg and the CO2 step and measurements were repeated. The changes in SjvO2 (rSO2) -CO2 reactivity were compared in the supine position and Trendelenburg-pneumoperitoneum condition, respectively.
RESULTS
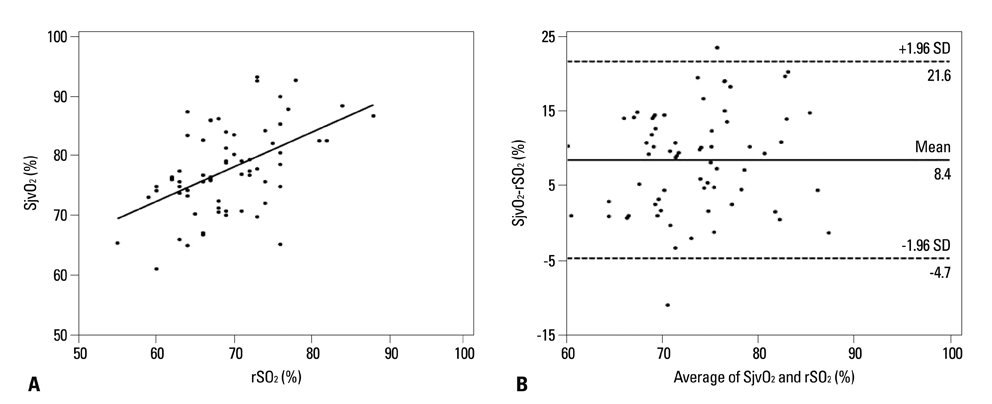
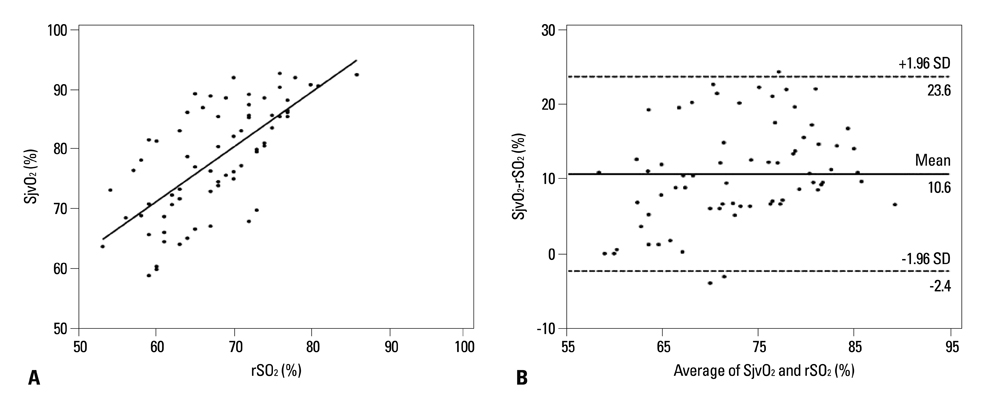
There was little correlation between SjvO2 and rSO2 in the supine position (concordance correlation coefficient=0.2819). Bland-Altman plots showed a mean bias of 8.4% with a limit of agreement of 21.6% and -4.7%. SjvO2 and rSO2 were not correlated during Trendelenburg-pneumoperitoneum condition (concordance correlation coefficient=0.3657). Bland-Altman plots showed a mean bias of 10.6% with a limit of agreement of 23.6% and -2.4%. The SjvO2-CO2 reactivity was higher than rSO2-CO2 reactivity in the supine position and Trendelenburg-pneumoperitoneum condition, respectively (0.9+/-1.1 vs. 0.4+/-1.2% mm Hg-1, p=0.04; 1.7+/-1.3 vs. 0.5+/-1.1% mm Hg-1, p<0.001).
CONCLUSION
There is little correlation between SjvO2 and rSO2 in the supine position and Trendelenburg-pneumoperitoneum condition during laparoscopic surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Anesthetic considerations for robotic surgery
Jeong Rim Lee
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014;66(1):3-11. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2014.66.1.3.
Reference
-
1. Mottrie A, Van Migem P, De Naeyer G, Schatteman P, Carpentier P, Fonteyne E. Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: oncologic and functional results of 184 cases. Eur Urol. 2007. 52:746–750.
Article2. Fujii Y, Tanaka H, Tsuruoka S, Toyooka H, Amaha K. Middle cerebral arterial blood flow velocity increases during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesth Analg. 1994. 78:80–83.
Article3. Huettemann E, Terborg C, Sakka SG, Petrat G, Schier F, Reinhart K. Preserved CO(2) reactivity and increase in middle cerebral arterial blood flow velocity during laparoscopic surgery in children. Anesth Analg. 2002. 94:255–258.
Article4. Smythe PR, Samra SK. Monitors of cerebral oxygenation. Anesthesiol Clin North America. 2002. 20:293–313.
Article5. Macmillan CS, Andrews PJ. Cerebrovenous oxygen saturation monitoring: practical considerations and clinical relevance. Intensive Care Med. 2000. 26:1028–1036.
Article6. Tobias JD. Cerebral oxygenation monitoring: near-infrared spectroscopy. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2006. 3:235–243.
Article7. Casati A, Spreafico E, Putzu M, Fanelli G. New technology for noninvasive brain monitoring: continuous cerebral oximetry. Minerva Anestesiol. 2006. 72:605–625.8. Yao FS, Tseng CC, Ho CY, Levin SK, Illner P. Cerebral oxygen desaturation is associated with early postoperative neuropsychological dysfunction in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2004. 18:552–558.
Article9. Nagdyman N, Ewert P, Peters B, Miera O, Fleck T, Berger F. Comparison of different near-infrared spectroscopic cerebral oxygenation indices with central venous and jugular venous oxygenation saturation in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2008. 18:160–166.
Article10. Leyvi G, Bello R, Wasnick JD, Plestis K. Assessment of cerebral oxygen balance during deep hypothermic circulatory arrest by continuous jugular bulb venous saturation and near-infrared spectroscopy. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2006. 20:826–833.
Article11. Nagdyman N, Fleck T, Schubert S, Ewert P, Peters B, Lange PE, et al. Comparison between cerebral tissue oxygenation index measured by near-infrared spectroscopy and venous jugular bulb saturation in children. Intensive Care Med. 2005. 31:846–850.
Article12. Barnhart HX, Haber M, Song J. Overall concordance correlation coefficient for evaluating agreement among multiple observers. Biometrics. 2002. 58:1020–1027.
Article13. Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986. 1:307–310.
Article14. Kim MB, Ward DS, Cartwright CR, Kolano J, Chlebowski S, Henson LC. Estimation of jugular venous O2 saturation from cerebral oximetry or arterial O2 saturation during isocapnic hypoxia. J Clin Monit Comput. 2000. 16:191–199.15. Brown R, Wright G, Royston D. A comparison of two systems for assessing cerebral venous oxyhaemoglobin saturation during cardiopulmonary bypass in humans. Anaesthesia. 1993. 48:697–700.
Article16. Fearn SJ, Chant HJ, Picton AJ, Mortimer AJ, McCollum CN. The contribution of extracranial blood oxygenation on near-infrared spectroscopy during carotid endarterectomy. Anaesthesia. 1997. 52:704–705.17. Knirsch W, Stutz K, Kretschmar O, Tomaske M, Balmer C, Schmitz A, et al. Regional cerebral oxygenation by NIRS does not correlate with central or jugular venous oxygen saturation during interventional catheterisation in children. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008. 52:1370–1374.
Article18. Dullenkopf A, Frey B, Baenziger O, Gerber A, Weiss M. Measurement of cerebral oxygenation state in anaesthetized children using the INVOS 5100 cerebral oximeter. Paediatr Anaesth. 2003. 13:384–391.
Article19. Yoshitani K, Kawaguchi M, Tatsumi K, Kitaguchi K, Furuya H. A comparison of the INVOS 4100 and the NIRO 300 near-infrared spectrophotometers. Anesth Analg. 2002. 94:586–590.
Article20. Lee JR, Lee PB, Do SH, Jeon YT, Lee JM, Hwang JY, et al. The effect of gynaecological laparoscopic surgery on cerebral oxygenation. J Int Med Res. 2006. 34:531–536.
Article21. Park EY, Koo BN, Min KT, Nam SH. The effect of pneumoperitoneum in the steep Trendelenburg position on cerebral oxygenation. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009. 53:895–899.
Article22. Pollard V, Prough DS, DeMelo AE, Deyo DJ, Uchida T, Widman R. The influence of carbon dioxide and body position on near-infrared spectroscopic assessment of cerebral hemoglobin oxygen saturation. Anesth Analg. 1996. 82:278–287.
Article23. Choi SH, Lee SJ, Rha KH, Shin SK, Oh YJ. The effect of pneumoperitoneum and Trendelenburg position on acute cerebral blood flow-carbon dioxide reactivity under sevoflurane anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2008. 63:1314–1318.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison between Regional Cerebral Oxygen Saturation and Jugular Bulb Venous Oxygen Saturation in Patients Undergoing OPCAB Surgery
- Comparison of Analytical Methods of Cerebral Oxygenation during CPB: Hypothermia versus Normothermia
- The Effects of CO2 Insufflation on Jugular Bulb Venous Blood Oxygen Saturation during Thoracoscopy
- Jugular Bulb Venous Oxygen Saturation Monitoring in Brain Surgery
- Cerebral Oxygen Saturation Monitoring during Carotid Endarterectomy: A case report