Korean J Gastroenterol.
2009 Dec;54(6):349-354. 10.4166/kjg.2009.54.6.349.
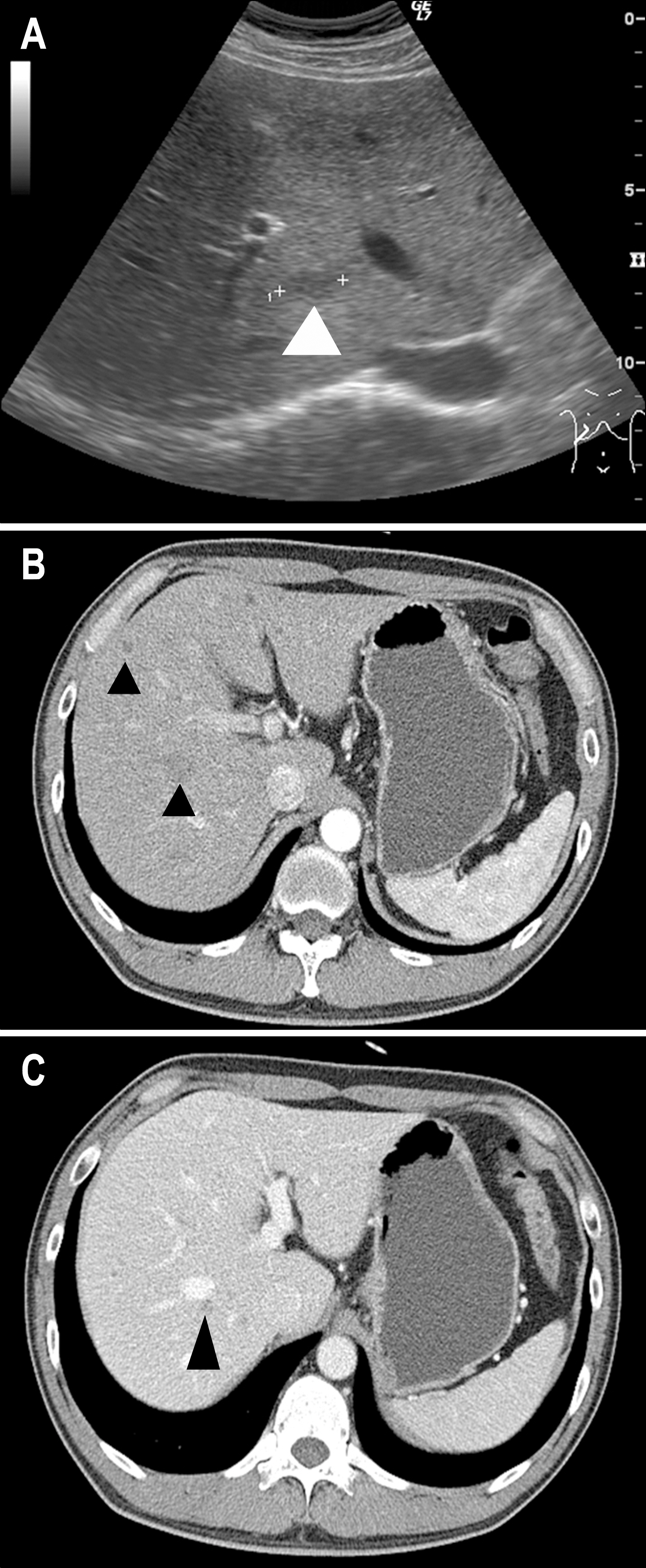
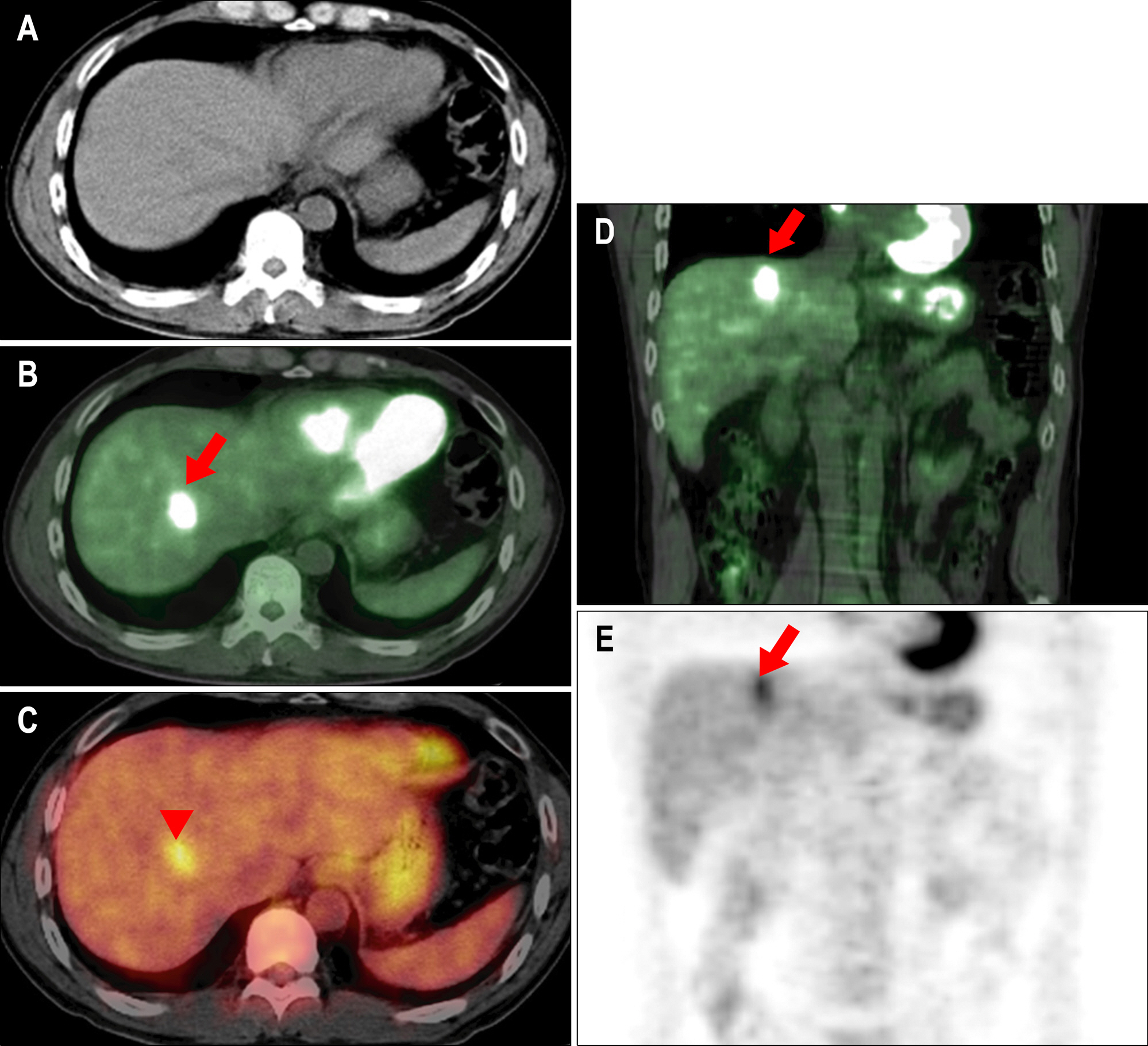
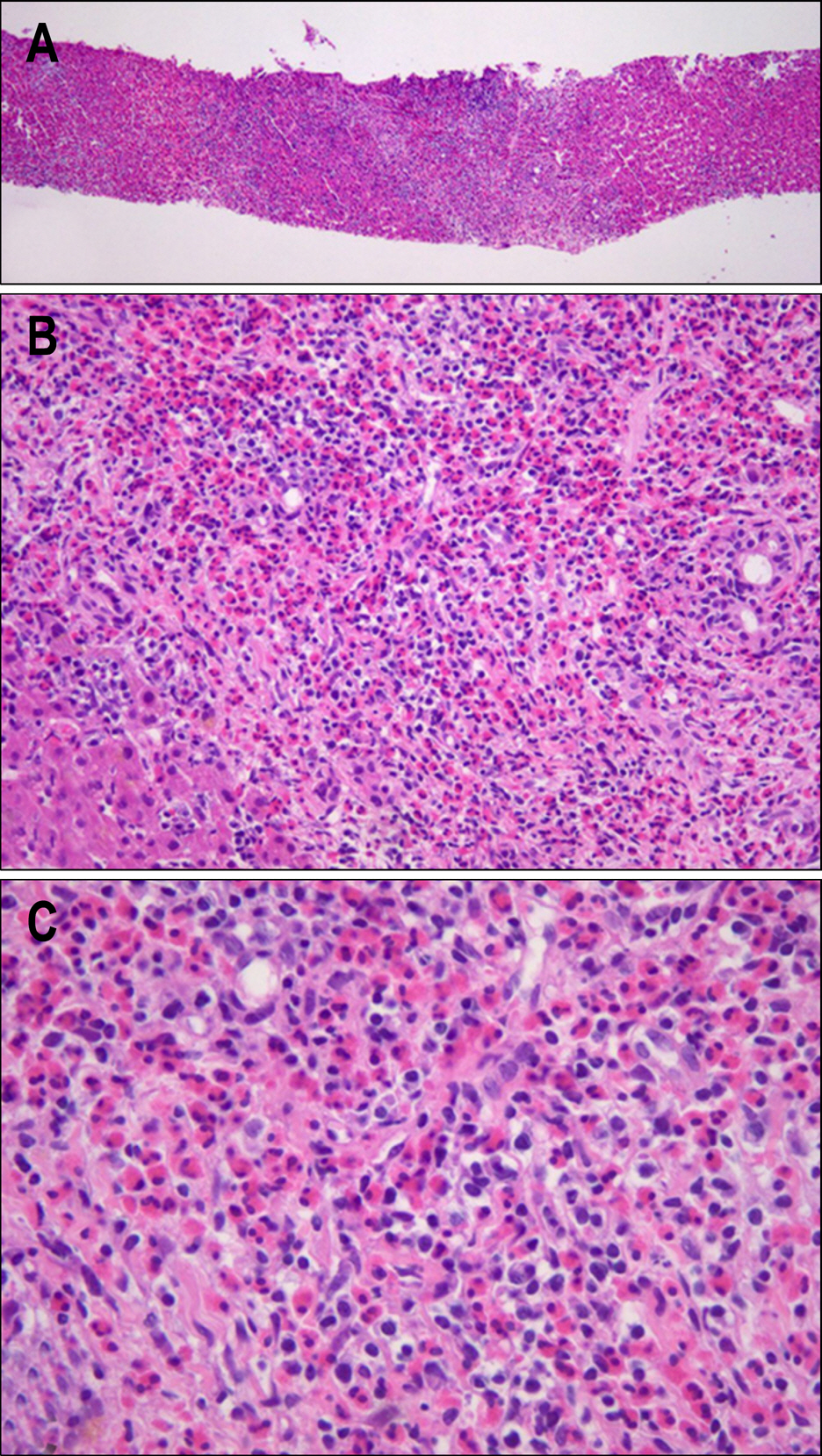
A Case of Eosinophilic Abscess Mistaken for Metastasis due to FDG Uptake in PET-CT
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Soon Chun Hyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. liverkys@schbc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Soon Chun Hyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Soon Chun Hyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Nuclear Medicine, Soon Chun Hyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1775933
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2009.54.6.349
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Enhanced Resolution of Eosinophilic Liver Abscess Associated with Toxocariasis by Albendazole Treatment
Eun Young Jang, Moon Seok Choi, Geum Youn Gwak, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik, Joon Hyeok Lee, Yong Han Paik, Byung Chul Yoo
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2015;65(4):222-228. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2015.65.4.222.
Reference
-
1. Fantone JC, Ward PA. Role of oxygen-derived free radicals and metabolites in leukocyte-dependent inflammatory reactions. Am J Pathol. 1982; 107:395–418.2. Kim WH, Kim SH, Kim YH, et al. Fluorine-18-FDG PET findings of focal eosinophilic liver disease: correlation with CT and/or MRI, laboratory, and pathologic findings. Abdom Imaging. 2009; 11:[Epub ahead of print].
Article3. Hong SW, Kim H, Park C, Lee SI. Eosinophilic liver abscess in patients with gastric carcinoma. Korean J Pathol. 1993; 27:27–33.4. Kang HR, Kwon HS, Song WJ, et al. Analysis of 54 cases of eosinophilic liver abscess-underlying diseases and clinical characteristics. Korean J Asthma, Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 24:229–235.5. Lim JH, Lee KS. Eosinophilic infiltration in Korea: idiopathic? Korean J Radiol. 2006; 7:4–6.
Article6. Fauci AS, Harley JB, Roberts WC, Ferrans VJ, Gralnick HR, Bjornson BH: NIH conference. The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Clinical pathologic and therapeutic consideration. Ann Intern Med. 1982; 97:78–92.7. Kim GB, Kwon JH, Kang DS. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: imaging findings in patients with hepatic involvement. AJR. 1993; 161:577–580.
Article8. Jang HJ, Lee WJ, Lee SJ, Kim SH, Lim HK, Lim JH. Focal eosinophilic necrosis of the liver in patients with underlying gastric or colorectal cancer: CT differentiation from metastasis. Korean J Radiol. 2002; 3:240–244.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- F-18 FDG Uptake in an Eosinophilic Liver Abscess Mimicking Hepatic Metastasis on PET/CT Images
- Value of Bone Scan in Addition to F-18 FDG PET/CT and Characteristics of Discordant Lesions between F-18 FDG PET/CT and Bone Scan in the Spinal Bony Metastasis
- Case Report of Prostate Cancer Patient with Only Lymph Node Involvement on F-18 FDG PET/CT
- Discordant Molecular Imaging Findings with 2‑[18F]FDG and [68Ga] Ga‑PSMA PET/CT in a Patient with Both Bladder and Prostate Cancer
- Significant Mismatch between FDG Uptake and Size after Chemotherapy in a Patient with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer