Korean J Gastroenterol.
2010 Mar;55(3):194-197. 10.4166/kjg.2010.55.3.194.
A Case of Non-occulsive Mesentery Ischemia with Pulmonary Embolism due to Protein C Deficiency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. donghyuk.sinn@samsung.com
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1775902
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2010.55.3.194
Abstract
- Protein C is an important physiological anticoagulant factor. Protein C deficiency has been linked to venous thrombosis at unusual sites, including the cerebral and mesenteric veins. Hereditary protein C deficiency is inherited primarily as an autosomal dominant trait with incomplete penetrance. Protein C and S deficiencies are known to increase the risk of venous thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism. Testing for protein C levels and function is necessary for the detection of both type I and type II protein C deficiency. In this article, we report a case of pulmonary embolism and mesentery ischemia due to type 1 protein C deficiency.
MeSH Terms
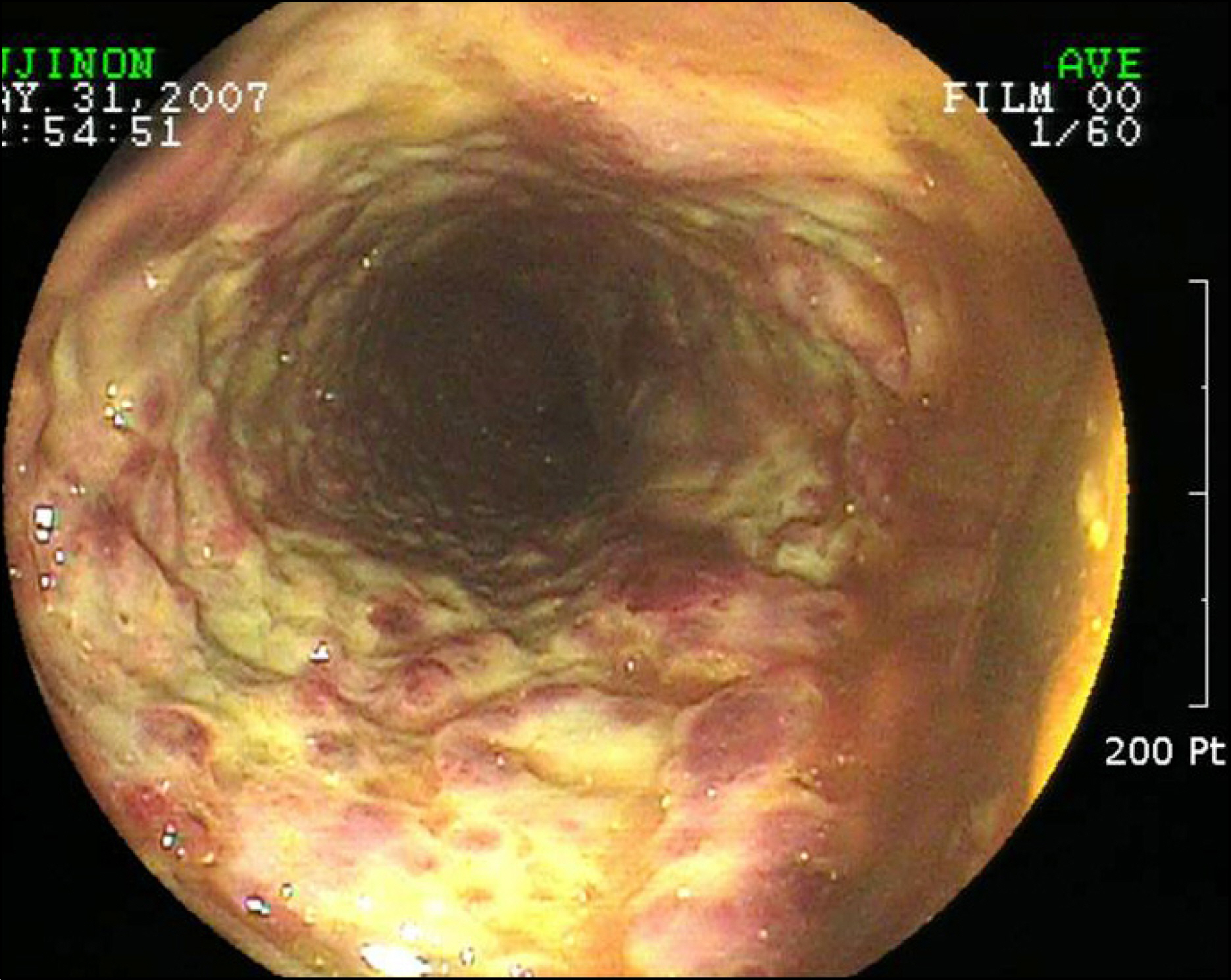
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jin PP, Wang XF, Dai J, Ding QL, Wang HL. Hereditary protein C deficiency: a case report. Pathology. 2007; 39:290–291.
Article2. Kim HJ, Kim DK, Koh KC, Kim JY, Kim SH. Severe protein C deficiency from compound heterozygous mutations in the PROC gene in two Korean adult patients. Thromb Res. 2008; 123:412–417.
Article3. Yoshida M, Mukohara N, Obo H, Ozaki N, Shida T, Okita Y. Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy for chronic pulmonary thromboembolism in protein C deficiency. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006; 54:70–74.
Article4. Rackoff A, Shores N, Willner I. Mesenteric venous thrombosis in a patient with pancreatitis and protein C deficiency. South Med J. 2005; 98:232–234.
Article5. Vrabec JP, Levin LA. Type II protein C deficiency in a 16-year-old girl with central retinal vein occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 143:341–342.
Article6. Cho JH, Park CW, Cho BR, et al. A case of pulmonary thromboembolism associated with protein C deficiency. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2003; 14:125–128.7. Cho YP, Lee DH, Jung SM, Jang HJ, Kim JS, Han MS. Vascular diseases associated with protein C and/or deficiencies. J Korean Surg Soc. 2002; 62:181–186.8. Demir T, Celkan T, Ahunbay G, Babaoglu A, Besikci R. Venous and intrapericardial thrombosis: secondary to transient protein C deficiency. Pediatr Cardiol. 2006; 27:497–499.9. Hoshi S, Hijikata M, Togashi Y, et al. Protein C deficiency in a family with thromboembolism and identified gene mutations. Intern Med. 2007; 46:997–1003.
Article10. Paç FA, Cağdaş DN. Treatment of massive cardiac thrombi in a patient with protein C and protein S deficiency. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2007; 18:699–702.
Article11. Imberti D, Pierfranceschi MG. Successful protein C concen10. Paç FA, Cağdaş DN. Treatment of massive cardiac thrombi in a patient with protein C and protein S deficiency. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2007; 18:699–702.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pulmonary Embolism with Protein C, S Deficiency in Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Recurrent Acute Pulmonary Embolism Associated With Protein S Deficiency
- Hereditary protein S deficiency presenting acute pulmonary embolism
- Pulmonary Thromboembolism Caused by PROS1 Gene Mutation
- Concurrent Isolated Cortical Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Thromboembolism as An Initial Presentation of Protein S Deficiency