Efficacy of Peginterferon and Ribavirin Combination Therapy of Chronic Hepatitis C: A Pooled Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea. 93cool@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1775796
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2012.60.5.306
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
A combination of peginterferon and ribavirin is the standard therapy for chronic hepatitis C (CHC). However, the respective study has not been carried out in a large scale in Korea. The purpose of this study was to collect the studies that have been reported in Korea in order to analyze the therapeutic effect of combination therapy and compare to find racial difference.
METHODS
Twenty-eight papers related to the therapeutic effect of combination therapy in CHC patients were analyzed based on pooled analysis.
RESULTS
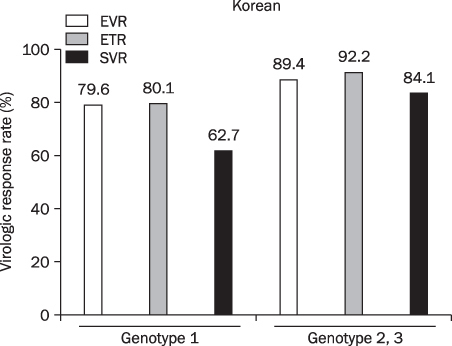
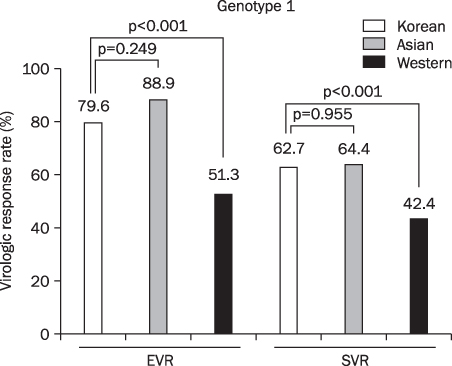
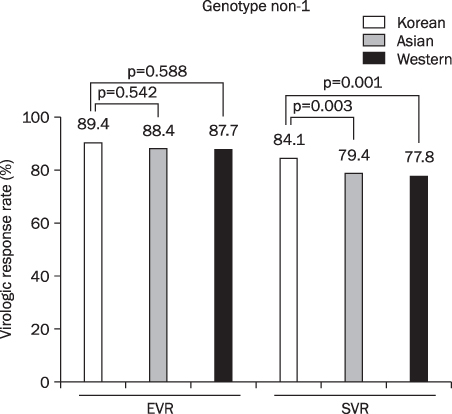
Based on the analysis for genotype 1 in Korea, early virologic response (EVR), end of treatment response (ETR), and sustained virologic response (SVR) were 79.6% (125/157), 80.1% (166/207), and 62.7% (341/543). The EVR, ETR, and SVR for genotype 2 and 3 were 89.4% (119/133), 92.2% (203/220), and 84.1% (434/516). Data from other Asians showed that EVR and SVR for genotype 1 were 88.9% (290/326) and 64.4% (491/762) respectively and 88.8% (135/152), and 79.4% (151/190) for genotype 2 and 3 respectively. In Western, EVR and SVR for genotype 1 were 51.3% (1,981/3,860) and 42.4% (1,798/4,231) respectively, and for genotype 2 and 3 were 87.7% (350/399) and 77.8% (533/685) respectively. Based on the comparative analysis, no statistical difference in SVR between Koreans and other Asians (p=0.955) was observed; However, the SVR of Koreans was higher with significance than that of Westerns (p<0.001) On the other hand, there was no difference what so ever, in SVR for genotype 2 amongst the different races.
CONCLUSIONS
The SVR of combination therapy for the Korean chronic hepatitis C patients was similar to other Asians but higher than Westerns.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Antiviral Agents/*therapeutic use
Databases, Factual
Drug Therapy, Combination
Genotype
Hepacivirus/genetics
Hepatitis C, Chronic/*drug therapy/ethnology
Humans
Interferon-alpha/*therapeutic use
Polyethylene Glycols/*therapeutic use
Recombinant Proteins/therapeutic use
Ribavirin/*therapeutic use
Treatment Outcome
Antiviral Agents
Interferon-alpha
Polyethylene Glycols
Recombinant Proteins
Ribavirin
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Efficacy of Sofosbuvir Combination Therapy for Hepatitis C Genotype 2 or 3 That Are Difficult to Manage with Standard Treatment
Young Kul Jung, Ju Hyun Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2013;62(3):185-187. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2013.62.3.185.Prevalence, Risk Factors and Clinical Characteristics in Patients with Genotype 6 Chronic Hepatitis C: A Single Institute Experience
Seung Kak Shin, Soo Yong Park, Young Kul Jung, Eui Joo Kim, Heon Nam Lee, Jong Joon Lee, Oh Sang Kwon, Duck Joo Choi, Yun Soo Kim, Ju Hyun Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2015;65(2):105-111. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2015.65.2.105.Hope for Cirrhosis Patients with Genotype 1 Hepatitis C Virus Who Failed the Previous Treatment
Jung Hyun Kwon
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2015;66(2):131-133. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2015.66.2.131.Renewed 2015 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Hepatitis C by Korean Association for the Study of the Liver; What Has Been Changed? - Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C Genotype 1
Sang Hoon Park
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2016;67(3):127-131. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2016.67.3.127.Role of Th17 and Treg during the Chronic Infection of Hepatitis C Virus
Hyun Mu Shin, Jae-Won Lee, Nam-Hyuk Cho
J Bacteriol Virol. 2015;45(4):389-393. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2015.45.4.389.
Reference
-
1. Alter MJ, Kruszon-Moran D, Nainan OV, et al. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1988 through 1994. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:556–562.2. McHutchison JG. Understanding hepatitis C. Am J Manag Care. 2004. 10:2 Suppl. S21–S29.3. Suh DJ, Jeong SH. Current status of hepatitis C virus infection in Korea. Intervirology. 2006. 49:70–75.4. Lauer GM, Walker BD. Hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2001. 345:41–52.5. Hu KQ, Tong MJ. The long-term outcomes of patients with compensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis and history of parenteral exposure in the United States. Hepatology. 1999. 29:1311–1316.6. Fattovich G, Giustina G, Degos F, et al. Morbidity and mortality in compensated cirrhosis type C: a retrospective follow-up study of 384 patients. Gastroenterology. 1997. 112:463–472.7. Zeuzem S, Feinman SV, Rasenack J, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2000. 343:1666–1672.8. Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001. 358:958–965.9. Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:975–982.10. Yoon BC, Kim HJ, Kim KS, Yoo HD, Lee SU, Han BH. Therapeutic Efficacy of Combination Therapy with Alpha Interferon and Ribavirin in Chronic Hepatitis C. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2001. 37:203–209.11. Lee H, Choi MS, Paik SW, et al. Peginterferon Alfa-2a plus Ribavirin for Initial Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2006. 12:31–40.12. McHutchison JG, Lawitz EJ, Shiffman ML, et al. IDEAL Study Team. Peginterferon alfa-2b or alfa-2a with ribavirin for treatment of hepatitis C infection. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:580–593.13. Goh PG, Kim MJ, Kim HJ, et al. Importance of medication adherence to peginterferon-ribavirin combination therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011. 57:294–301.14. Jeong SW, Kim JD, Woo HY, et al. Impact of adherence to peginterferon-ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients on achieving a sustained virologic response. Korean J Hepatol. 2009. 15:338–349.15. Kang MJ, Jung EU, Park SW, et al. Effects of pegylated interferon and ribavirin in Korean patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Korean J Hepatol. 2008. 14:318–330.16. Kim CH, Park BD, Lee JW, et al. Durability of a sustained virologic response in combination therapy with interferon/peginterferon and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Hepatol. 2009. 15:70–79.17. Kim JI, Kim SH, Lee BS, et al. Efficacy of initial treatment with peginterferon alpha-2a versus peginterferon alpha-2b in combination with ribavirin in naive chronic hepatitis C patients living in Daejeon and Chungcheong Province in Korea: a comparative study. Korean J Hepatol. 2008. 14:493–502.18. Kim KT, Han SY, Kim JH, et al. Clinical outcome of pegylated interferon and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Hepatol. 2008. 14:36–45.19. Kim MN, Yoon KT, Park JY, et al. A comparison of 24- vs. 48-week peginterferon plus ribavirin in patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Hepatol. 2009. 15:496–503.20. Lee HJ, Eun JR, Choi JW, Kim KO, Moon HJ. Comparison of therapeutic results between combination therapy of peginterferon alpha-2a plus ribavirin and interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin according to treatment duration in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Hepatol. 2008. 14:46–57.21. Sinn DH, Shin SR, Kil JS, et al. Efficacy of peg-interferon-α-2a plus ribavirin for patients aged 60 years and older with chronic hepatitis C in Korea. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. 26:469–476.22. Bitetto D, Fattovich G, Fabris C, et al. Complementary role of vitamin D deficiency and the interleukin-28B rs12979860 C/T polymorphism in predicting antiviral response in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2011. 53:1118–1126.23. Escudero A, Rodríguez F, Serra MA, Del Olmo JA, Montes F, Rodrigo JM. Pegylated alpha-interferon-2a plus ribavirin compared with pegylated alpha-interferon-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus: prospective, non-randomized study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. 23:861–866.24. Reddy KR, Messinger D, Popescu M, Hadziyannis SJ. Peginterferon alpha-2a (40 kDa) and ribavirin: comparable rates of sustained virological response in sub-sets of older and younger HCV genotype 1 patients. J Viral Hepat. 2009. 16:724–731.25. Vutien P, Nguyen NH, Trinh HN, et al. Similar treatment response to peginterferon and ribavirin in Asian and Caucasian patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010. 105:1110–1115.26. Borroni G, Andreoletti M, Casiraghi MA, et al. Effectiveness of pegylated interferon/ribavirin combination in 'real world' patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008. 27:790–797.27. Sebastiani G, Ferrari A, Boccato S, Pistis R, Alberti A. Clinical trial: comparison of weekly once versus twice half-dose weekly administration of pegylated interferon alpha 2b in combination with ribavirin for the treatment of HCV-1 positive patients with chronic hepatitis C. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007. 26:1077–1082.28. Rodriguez-Torres M, Jeffers LJ, Sheikh MY, et al. Latino Study Group. Peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin in Latino and non-Latino whites with hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2009. 360:257–267.29. Grasso A, Malfatti F, De Leo P, et al. Insulin resistance predicts rapid virological response in non-diabetic, non-cirrhotic genotype 1 HCV patients treated with peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin. J Hepatol. 2009. 51:984–990.30. Romero-Gómez M, Diago M, Andrade RJ, et al. Spanish Treatment of Resistance to Insulin in Hepatitis C Genotype 1 Group. Treatment of insulin resistance with metformin in naïve genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C patients receiving peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin. Hepatology. 2009. 50:1702–1708.31. Yu S, Douglass JM, Qualls C, Arora S, Dunkelberg JC. Response to therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C in hispanics compared to non-Hispanic whites. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. 104:1686–1692.32. Puoti C, Barbarini G, Picardi A, et al. Club Epatologico Ospedaliero (Hospital Liver Club, CLEO). Rapid virological response as a predictor of sustained response in HCV-infected patients with persistently normal alanine aminotransferase levels: A multicenter study. J Viral Hepat. 2011. 18:393–399.33. Fung J, Lai CL, Hung I, et al. Chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 6 infection: response to pegylated interferon and ribavirin. J Infect Dis. 2008. 198:808–812.34. Tsang OT, Zee JS, Chan JM, et al. Chronic hepatitis C genotype 6 responds better to pegylated interferon and ribavirin combination therapy than genotype 1. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. 25:766–771.35. Lee SD, Yu ML, Cheng PN, et al. Comparison of a 6-month course peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin and interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin in treating Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis C in Taiwan. J Viral Hepat. 2005. 12:283–291.36. Chu CJ, Lee SD, Hung TH, et al. Insulin resistance is a major determinant of sustained virological response in genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C patients receiving peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009. 29:46–54.37. Hsu CS, Liu CH, Liu CJ, et al. Factors affecting early viral load decline of Asian chronic hepatitis C patients receiving pegylated interferon plus ribavirin therapy. Antivir Ther. 2009. 14:45–54.38. Miyase S, Haraoka K, Ouchida Y, Morishita Y, Fujiyama S. Randomized trial of peginterferon α-2a plus ribavirin versus peginterferon α-2b plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C in Japanese patients. J Gastroenterol. 2012. 47:1014–1021.39. Roberts SK, Weltman MD, Crawford DH, et al. Chariot Study Group. Impact of high-dose peginterferon alfa-2A on virological response rates in patients with hepatitis C genotype 1: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 2009. 50:1045–1055.40. Liu CH, Liu CJ, Lin CL, et al. Pegylated interferon-alpha-2a plus ribavirin for treatment-naive Asian patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 47:1260–1269.41. Dimitroulopoulos D, Petroulaki E, Manolakopoulos S, et al. Peginterferon/ribavirin treatment achieves a higher compliance rate than interferon/ribavirin combination in patients chronically infected with HCV on methadone maintenance. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. 21:1407–1412.42. Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, et al. PEGASYS International Study Group. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004. 140:346–355.43. Ferenci P, Shiffman ML, Fried MW, et al. Early prediction of response to 40 KDA peginterferon alfa-2a (PEGASYS) plus ribavirin (PBV) in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2001. 34:351A.44. Kotenko SV, Gallagher G, Baurin VV, et al. IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat Immunol. 2003. 4:69–77.45. Sheppard P, Kindsvogel W, Xu W, et al. IL-28, IL-29 and their class II cytokine receptor IL-28R. Nat Immunol. 2003. 4:63–68.46. Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, et al. Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature. 2009. 461:399–401.47. Lyoo K, Song MJ, Hur W, et al. Polymorphism near the IL28B gene in Korean hepatitis C virus-infected patients treated with peg-interferon plus ribavirin. J Clin Virol. 2011. 52:363–366.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Peginterferon-alpha and Ribavirin Combination Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis C
- Treatment of chronic hepatitis C: Efficacy of initial treatment of peginterferon alpha-2a versus peginterferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin in naive chronic hepatitis C patients
- Permanent sudden hearing loss associated with peginterferon and ribavirin combination therapy during hepatitis C treatment
- Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin in the Retreatment of Chronic Hepatitis C in Korea
- Importance of Medication Adherence to Peginterferon-Ribavirin Combination Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C