Yonsei Med J.
2009 Aug;50(4):493-504. 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.4.493.
Immunoglobulin VH Chain Gene Analysis of Peripheral Blood IgM-Producing B Cells in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Microbiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dskim6634@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1758607
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2009.50.4.493
Abstract
- PURPOSE
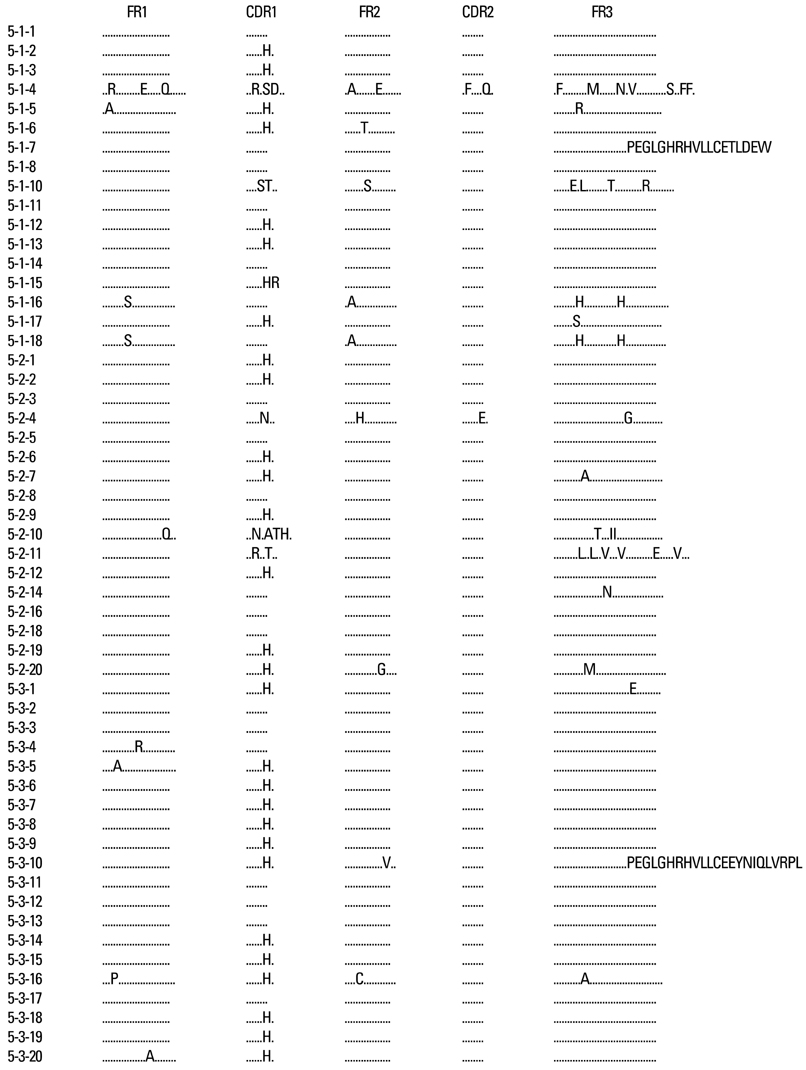
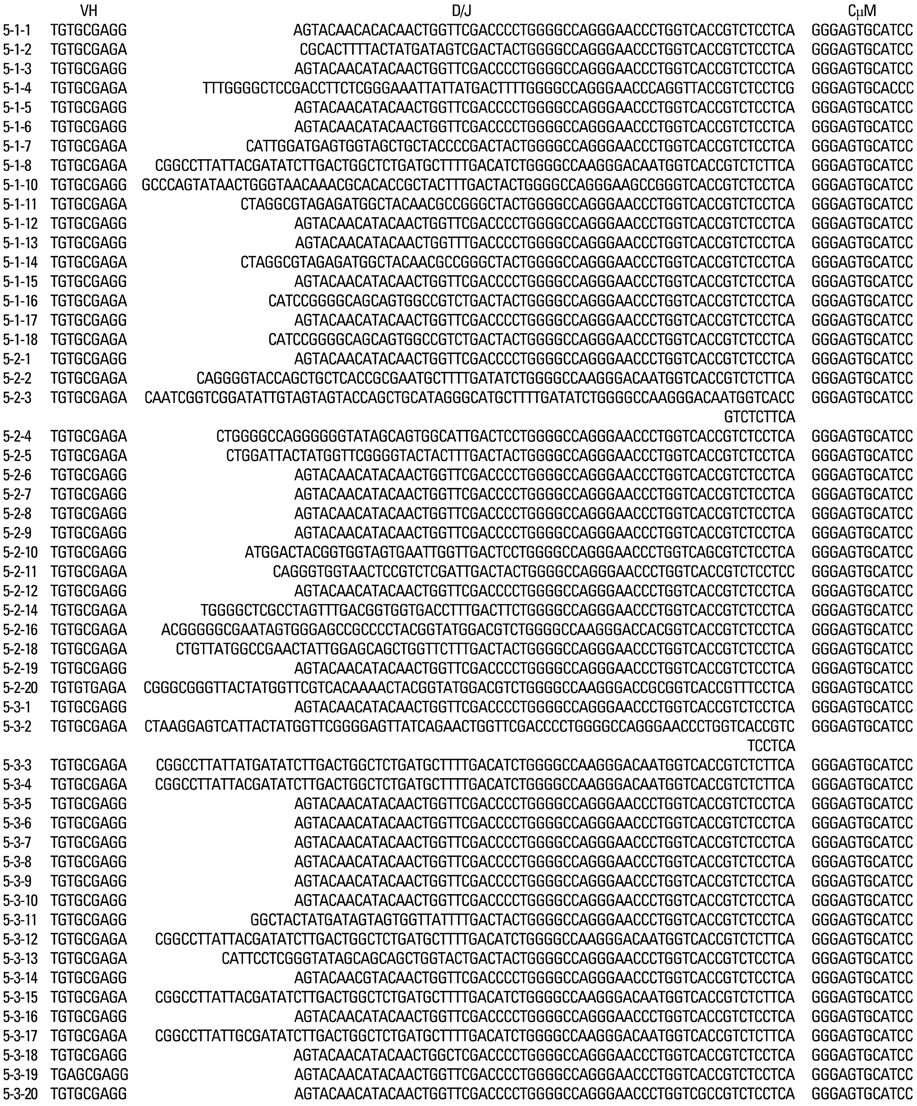
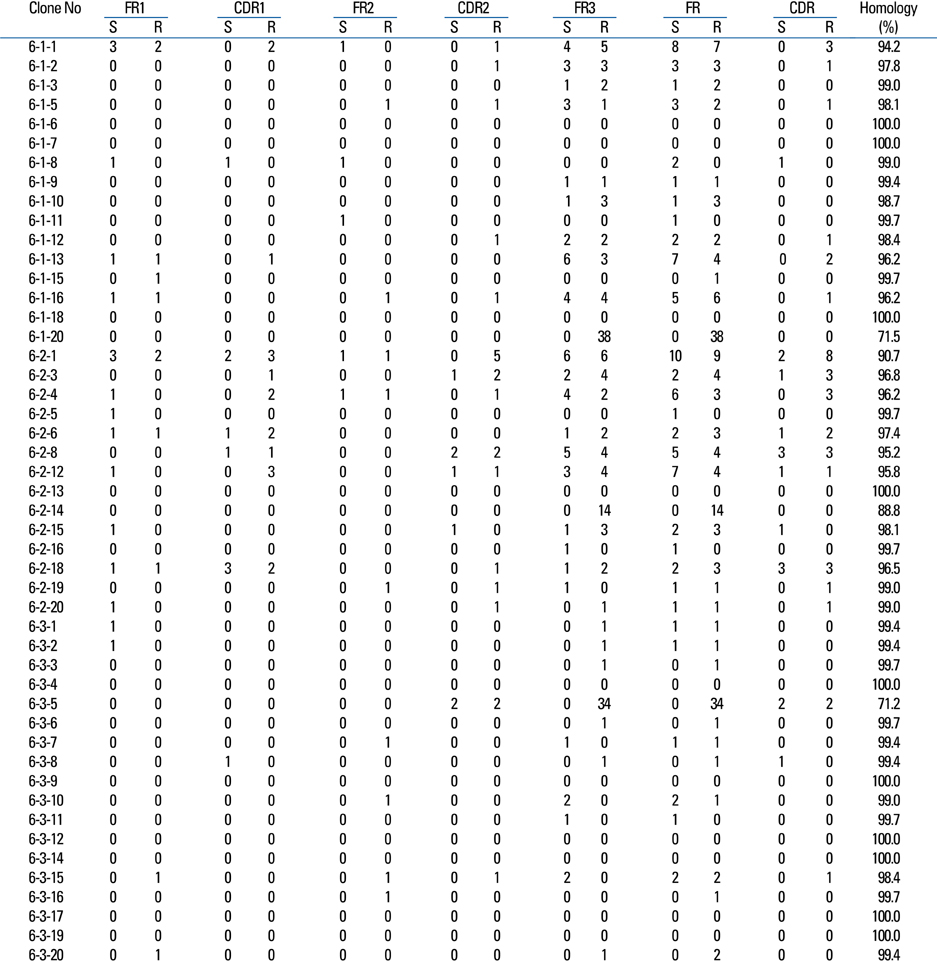
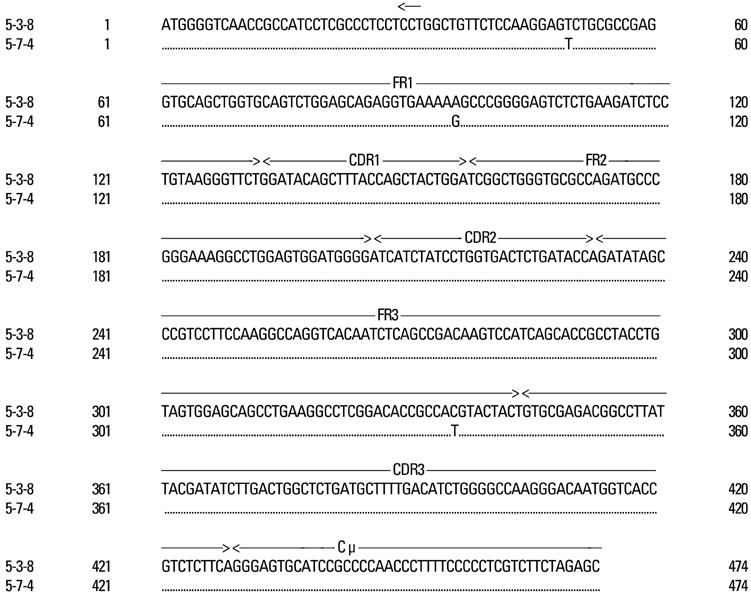
Kawasaki disease is a systemic vasculitis, and its etiology and pathogenesis are still not clear. Our study was undertaken to investigate the characteristics of the activation of B cells in the peripheral blood of Kawasaki disease (KD) patients and evidence of stimulation by superantigens. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Blood samples were obtained from three patients (2 males, 1 female) with KD, who were admitted to our Hospital, Seoul, Korea. The mean age was 1.2 years. Distribution of B cells was studied in the acute and subacute phases of KD patients. From the RNA of B cells, we obtained complementary DNA (cDNA) and performed polymerase chain reaction (PCR). To determine the oligoclonal expansion of immunoglobulin M (IgM) VH family, we cloned and sequenced the PCR products from each group and analyzed DNA. RESULTS: In the peripheral blood of acute phase patients, T cells were significantly decreased (p < 0.05), whereas B cells were significantly increased (p < 0.05). When the first PCR was done on the B cell chains, VH1 to VH6 were all found to be expressed. The number of micro gene clones obtained from 3 patients was 312, and they belonged to VH3, VH4 and VH5 family. M99686 germ line was most frequently used and the next most frequently used, were X92224/J, L21967 and L21964. A similar order was seen in patients. Among the clones, 20 sets of clones showed the same base sequence and this was frequent between VH2 and VH5. There was one set, which showed almost the same base sequence between different patients, and the homology was 99.5%. Twenty sets of clones that had the same base sequence showed high similarity to the germ line (94 - 100%). Among these, the clones that utilized the M99686 germ line were 4 sets which were most frequent. The 3-dimensional structure of one of these clones showed typical beta, sheet structure of immunoglobulin chains. CONCLUSION: The IgM transcripts expressed by the B cells in the peripheral blood of KD patients in the acute phase of the disease clearly showed an oligoclonal expansion, suggesting that KD is caused not by stimulation of a superantigen, but rather by a conventional antigen.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Recent Advances in Kawasaki Disease
Kyu Yeun Kim, Dong Soo Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(1):15-21. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.15.
Reference
-
1. Kawasaki T. Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children: Clinical observations of 50 cases. Jpn J Allergol. 1967. 16:178–222.2. Freeman AF, Shulman ST. Recent developments in Kawasaki disease. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2001. 14:357–361.
Article3. Abe J, Kotzin BL, Jujo K, Melish ME, Glode MP, Kohsaka T, et al. Selective expansion of T cells expressing T-Cell receptor variable regions V beta 2 and V beta 8 in Kawasaki disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. 89:4066–4070.
Article4. Leung DY, Meissner HC, Fulton DR, Murray DL, Kotzin BL, Schlievert PM. Toxic shock syndrome toxin-secreting Staphylococcus aureus in Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet. 1993. 342:1385–1388.
Article5. Rowley AH, Eckerley CA, Jäck HM, Shulman ST, Baker SC. IgA plasma cells in vascular tissue of patients with Kawasaki syndrome. J Immunol. 1997. 159:5946–5955.6. Andersson U. Development of B lymphocyte function in childhood. Acta Paediatr Ascand. 1985. 74:568–573.
Article7. Andersson U, Bird AG, Britton BS, Palacios R. Humoral and cellular immunity in humans studied at the cell level from birth to two years of age. Immunol Rev. 1981. 57:1–38.
Article8. Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. Committee on Rheumatic Fever, and Kawasaki Disease. American Heart Association. Diagnostic guidelines for Kawasaki disease. Circulation. 2001. 103:335–336.9. Brezinschek HP, Brezinschek RI, Lipsky PE. Analysis of the heavy chain repertoire of human peripheral B cells using single-cell polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol. 1995. 155:190–202.10. Meissner HC, Leung DY. Superantigens, conventional antigens and the etiology of Kawasaki syndrome. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000. 19:91–94.
Article11. Rowley AH. The etiology of Kawasaki disease: superantigen or conventional antigen? Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999. 18:69–70.
Article12. Leucht S, Uttenreuther-Fischer MM, Gaedicke G, Fischer P. The B cell superantigen-like interaction of intravenous immunoglobin (IVIG) with Fab fragments of V(H) 3-23 and 3-30/3-30.5 germline gene origin cloned from a patient with Kawasaki disease is enhanced after IVIG therapy. Clin Immunol. 2001. 99:18–29.
Article13. Duong TT, Silverman ED, Bissessar MV, Yeung RS. Superantigenic activity is responsible for induction of coronary arteritis in mice: an animal model of Kawasaki disease. Int Immunol. 2003. 15:79–89.
Article14. Choi IH, Chwae YJ, Shim WS, Kim DS, Kwon DH, Kim JD, et al. Clonal expansion of CD8+ T cells in Kawasaki disease. J Immunol. 1997. 159:481–486.15. Rowley AH, Shulman ST, Spike BT, Mask CA, Baker SC. Oligoclonal IgA response in the vascular wall in acute Kawasaki disease. J Immunol. 2001. 166:1334–1343.
Article16. Rowley AH, Baker SC, Orenstein JM, Shulman ST. Searching for the cause of Kawasaki disease--cytoplasmic inclusion bodies provide new insight. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008. 6:394–401.
Article17. Barron K, DeCunto C, Montalvo J, Orson F, Lewis D. Abnormalities of immunoregulation in Kawasaki syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1988. 15:1243–1249.18. Leung DY, Geha RS, Newburger JW, Burns JC, Fiers W, Lapierre LA, et al. Two monokines, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor, render cultured vascular endothelial cells susceptible to lysis by antibodies circulating during Kawasaki syndrome. J Exp Med. 1986. 164:1958–1972.
Article19. Leung DY. The potential role of cytokine-mediated vascular endothelial activation in the pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1991. 33:739–744.
Article20. Lee TJ, Kim KH, Chun JK, Kim DS. Low-dose methotrexate therapy for intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. Yonsei Med J. 2008. 49:714–718.
Article21. Hillson JL, Karr NS, Oppliger IR, Mannik M, Sasso EH. The structural basis of germline-encoded VH3 immunoglobulin binding to staphylococcal protein A. J Exp Med. 1993. 178:331–336.
Article22. Silverman GJ. Unconventional B-cell antigens and human immune repertoires. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. 764:342–355.23. Jukes TH, King JL. Evolutionary nucleotide replacements in DNA. Nature. 1979. 281:605–606.
Article24. Shlomchik MJ, Marshak-Rothstein A, Wolfowicz CB, Rothstein TL, Weigert MG. The role of clonal selection and somatic mutation in autoimmunity. Nature. 1987. 328:805–811.
Article25. Shlomchik MJ, Nemazee DA, Sato VL, Van Snick J, Carson DA, Weigert MG. Variable region sequences of murine IgM anti-IgG monoclonal autoantibodies (rheumatoid factors). A structural explanation for the high frequency of IgM anti-IgG B cells. J Exp Med. 1986. 164:407–427.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum to "Immunoglobulin VH Chain Gene Analysis of Peripheral Blood IgM-Producing B Cells in Patients with Kawasaki Disease" by Lee HH, et al. (Yonsei Med J 50(4):493-504, 2009)
- Oligoclonal Expansion of the VH Family in Kawasaki Disease
- Clonal Expansion of Peripheral B Cells in Kawasaki Disease
- Overexpression and unique rearrangement of VH2 transcripts in immunoglobulin variable heavy chain genes in ankylosing spondylitis patients
- Canges of Peripheral IFN-r-Producing CD4(+) and CD4(-) Cell Frequencies in Kawasaki Disease