Korean J Radiol.
2008 Jun;9(3):243-249. 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.3.243.
Evaluation of Tumor Angiogenesis with a Second-Generation US Contrast Medium in a Rat Breast Tumor Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shlee@amc.seoul.kr
- 3Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1758458
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2008.9.3.243
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
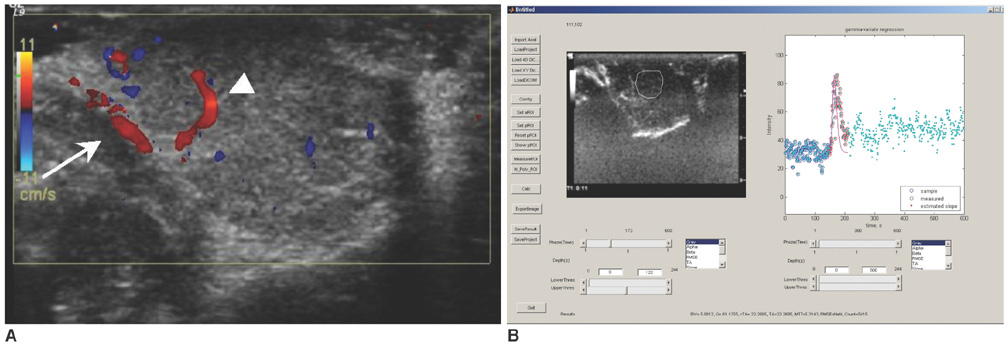
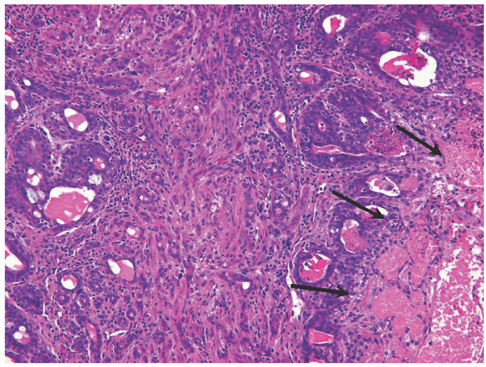
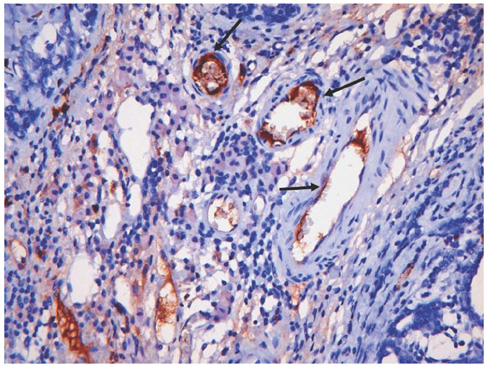
Tumor angiogenesis is an important factor for tumor growth, treatment response and prognosis. Noninvasive imaging methods for the evaluation of tumor angiogenesis have been studied, but a method for the quantification of tumor angiogenesis has not been established. This study was designed to evaluate tumor angiogenesis in a rat breast tumor model by the use of a contrast-enhanced ultrasound (US) examination with a second-generation US contrast agent. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The alkylating agent 19N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU) was injected into the intraperitoneal cavity of 30-day-old female Sprague-Dawley rats. Three to four months later, breast tumors were detected along the mammary lines of the rats. A total of 17 breast tumors larger than 1 cm in nine rats were evaluated by gray-scale US, color Doppler US and contrast-enhanced US using SonoVue. The results were recorded as digital video images; time-intensity curves and hemodynamic parameters were analyzed. Pathological breast tumor specimens were obtained just after the US examinations. The tumor specimens were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) and the expression of CD31, an endothelial cell marker, was determined by immunohistochemical staining. We also evaluated the pathological diagnosis of the tumors and the microvessel density (MVD). Spearman's correlation and the Kruskal-Wallis test were used for the analysis. RESULTS: The pathological diagnoses were 11 invasive ductal carcinomas and six benign intraductal epithelial proliferations. The MVD did not correlate with the pathological diagnosis. However, blood volume (BV) showed a statistically significant correlation with MVD (Spearman's correlation, p < 0.05). CONCLUSION: Contrast-enhanced US using a second-generation US contrast material was useful for the evaluation of tumor angiogenesis of breast tumors in the rat.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua P, Allred EN, Moore DH, et al. Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992. 84:1875–1887.2. Bosari S, Lee AK, DeLellis RA, Wiley BD, Heatley GJ, Silverman ML. Microvessel quantitation and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1992. 23:755–761.3. Toi M, Bando H, Kuroi K. The predictive value of angiogenesis for adjuvant therapy in breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2007. 7:311–314.4. Delille JP, Slanetz PJ, Yeh ED, Kopans DB, Garrido L. Breast cancer: regional blood flow and blood volume measured with magnetic susceptibility-based MR imaging-initial results. Radiology. 2002. 223:558–565.5. Brix G, Kiessling F, Lucht R, Darai S, Wasser K, Delorme S, et al. Microcirculation and microvasculature in breast tumors: pharmacokinetic analysis of dynamic MR image series. Magn Reson Med. 2004. 52:420–429.6. Teifke A, Behr O, Schmidt M, Victor A, Vomweg TW, Thelen M, et al. Dynamic MR imaging of breast lesions: correlation with microvessel distribution pattern and histologic characteristics of prognosis. Radiology. 2006. 239:351–360.7. Frouge C, Guinebretiere JM, Contesso G, Di Paola R, Blery M. Correlation between contrast enhancement in dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of the breast and tumor angiogenesis. Invest Radiol. 1994. 29:1043–1049.8. Esserman L, Hylton N, George T, Weidner N. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging to assess tumor histopathology and angiogenesis in breast carcinoma. Breast J. 1999. 5:13–21.9. Buadu LD, Murakami J, Murayama S, Hashiguchi N, Sakai S, Masuda K, et al. Breast lesions: correlation of contrast medium enhancement patterns on MR images with histopathologic findings and tumor angiogenesis. Radiology. 1996. 200:639–649.10. Buckley DL, Drew PJ, Mussurakis S, Monson JR, Horsman A. Microvessel density of invasive breast cancer assessed by dynamic Gd-DTPA enhanced MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1997. 7:461–464.11. Hulka CA, Edmister WB, Smith BL, Tan L, Sgroi DC, Campbell T, et al. Dynamic echo-planar imaging of the breast: experience in diagnosing breast carcinoma and correlation with tumor angiogenesis. Radiology. 1997. 205:837–842.12. Su MY, Wang Z, Carpenter PM, Lao X, Muhler A, Nalcioglu O. Characterization of N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea-induced malignant and benign breast tumors in rats by using three MR contrast agents. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1999. 9:177–186.13. Thompson HK Jr, Starmer CF, Whalen RE, McIntosh HD. Indicator transit time considered as a gamma variate. Circ Res. 1964. 14:502–515.14. Wilke N, Simm C, Zhang J, Ellermann J, Ya X, Merkle H, et al. Contrast-enhanced first pass myocardial perfusion imaging: correlation between myocardial blood flow in dogs at rest and during hyperemia. Magn Reson Med. 1993. 29:485–497.15. Wilke N, Jerosch-Herold M, Stillman AE, Kroll K, Tsekos N, Merkle H, et al. Concepts of myocardial perfusion imaging in magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Q. 1994. 10:249–286.16. Miller JC, Pien HH, Sahani D, Sorensen AG, Thrall JH. Imaging angiogenesis: applications and potential for drug development. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005. 97:172–187.17. Less JR, Skalak TC, Sevick EM, Jain RK. Microvascular architecture in a mammary carcinoma: branching patterns and vessel dimensions. Cancer Res. 1991. 51:265–273.18. Peters-Engl C, Medl M, Mirau M, Wanner C, Bilgi S, Sevelda P, et al. Color-coded and spectral Doppler flow in breast carcinomas-relationship with the tumor microvasculature. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998. 47:83–89.19. Kim EA, Yoon KH, Lee YH, Kim HW, Juhng SK, Won JJ. Focal hepatic lesions: contrast-enhancement patterns at pulse-inversion harmonic US using a microbubble contrast agent. Korean J Radiol. 2003. 4:224–233.20. Yamaguchi A, Hayashi Y, Kojima Y, Miyagawa H, Ito M, Kohri K. Testicular torsion: usefulness of contrast-enhanced power Doppler sonography. Int J Urol. 2005. 12:849–851.21. Tani T, Tanabe K, Tani M, Ono F, Katayama M, Tamita K, et al. Quantitative assessment of harmonic power doppler myocardial perfusion imaging with intravenous Levovist in patients with myocardial infarction: comparison with myocardial viability evaluated by coronary flow reserve and coronary flow pattern of infarct-related artery. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2005. 3:22.22. Greis C. Technology overview: SonoVue (Bracco, Milan). Eur Radiol. 2004. 14:Suppl 8. P11–P15.23. Schneider M, Arditi M, Barrau MB, Brochot J, Broillet A, Ventrone R, et al. BR1: a new ultrasonographic contrast agent based on sulfur hexafluoride-filled microbubbles. Invest Radiol. 1995. 30:451–457.24. Lim A, Cosgrove D. Functional studies. Eur Radiol. 2004. 14:Suppl 8. P110–P115.25. Bokor D. Diagnostic efficacy of SonoVue. Am J Cardiol. 2000. 86:19G–24G.26. Ding H, Wang WP, Huang BJ, Wei RX, He NA, Qi Q, et al. Imaging of focal liver lesions: low-mechanical-index real-time ultrasonography with SonoVue. J Ultrasound Med. 2005. 24:285–297.27. Rosen L. Antiangiogenic strategies and agents in clinical trials. Oncologist. 2000. 5:20–27.28. Davis DW, McConkey DJ, Abbruzzese JL, Herbst RS. Surrogate markers in antiangiogenesis clinical trials. Br J Cancer. 2003. 89:8–14.29. Anderson H, Price P, Blomley M, Leach MO, Workman P. Measuring changes in human tumour vasculature in response to therapy using functional imaging techniques. Br J Cancer. 2001. 85:1085–1093.30. Turetschek K, Preda A, Novikov V, Brasch RC, Weinmann HJ, Wunderbaldinger P, et al. Tumor microvascular changes in antiangiogenic treatment: assessment by magnetic resonance contrast media of different molecular weights. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004. 20:138–144.31. Kuhl CK, Bieling H, Gieseke J, Ebel T, Mielcarek P, Far F, et al. Breast neoplasms: T2* susceptibility-contrast, first-pass perfusion MR imaging. Radiology. 1997. 202:87–95.32. Mussurakis S, Buckley DL, Horsman A. Prediction of axillary lymph node status in invasive breast cancer with dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 1997. 203:317–321.33. Szabo BK, Aspelin P, Kristoffersen Wiberg M, Tot T, Bone B. Invasive breast cancer: correlation of dynamic MR features with prognostic factors. Eur Radiol. 2003. 13:2425–2435.34. Stomper PC, Herman S, Klippenstein DL, Winston JS, Budnick RM, Stewart CC. Invasive breast carcinoma: analysis of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging enhancement features and cell proliferative activity determined by DNA S-phase percentage. Cancer. 1996. 77:1844–1849.35. Kvistad KA, Lundgren S, Fjosne HE, Smenes E, Smethurst HB, Haraldseth O. Differentiating benign and malignant breast lesions with T2*-weighted first pass perfusion imaging. Acta Radiol. 1999. 40:45–51.36. Cosgrove D. Future prospects for SonoVue and CPS. Eur Radiol. 2004. 14:Suppl 8. P116–P124.37. Tang MX, Eckersley RJ, Noble JA. Pressure-dependent attenuation with microbubbles at low mechanical index. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2005. 31:377–384.38. Chen Q, Zagzebski J, Wilson T, Stiles T. Pressure-dependent attenuation in ultrasound contrast agents. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2002. 28:1041–1051.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation between Tumor Angiogenesis and Metastasis in Invasive Breast Carcinoma
- Up-to-date Doppler techniques for breast tumor vascularity: superb microvascular imaging and contrast-enhanced ultrasound
- Correlation between Tumor Angiogenesis and Metastasis in Invasive Breast Carcinoma
- Visualization of Tumor Angiogenesis Using MR Imaging Contrast Agent Gd-DTPA-anti-VEGF Receptor 2 Antibody Conjugate in a Mouse Tumor Model
- Development of Experimental 9L Gliosarcoma Rat Brain Tumor Model