J Korean Acad Nurs.
2012 Dec;42(7):1009-1018. 10.4040/jkan.2012.42.7.1009.
Effectiveness of Home Health Care Service for Elders after Spinal Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Nursing, Daejeon University, Daejeon, Korea & University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, Milwaukee, USA.
- 2Department of Nursing, Wonkwang Health Science University, Iksan, Korea. jio110@wu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1739539
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.7.1009
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was done to evaluate effectiveness of home healthcare services (HHCS) specialized for elders who received spinal surgeries.
METHODS
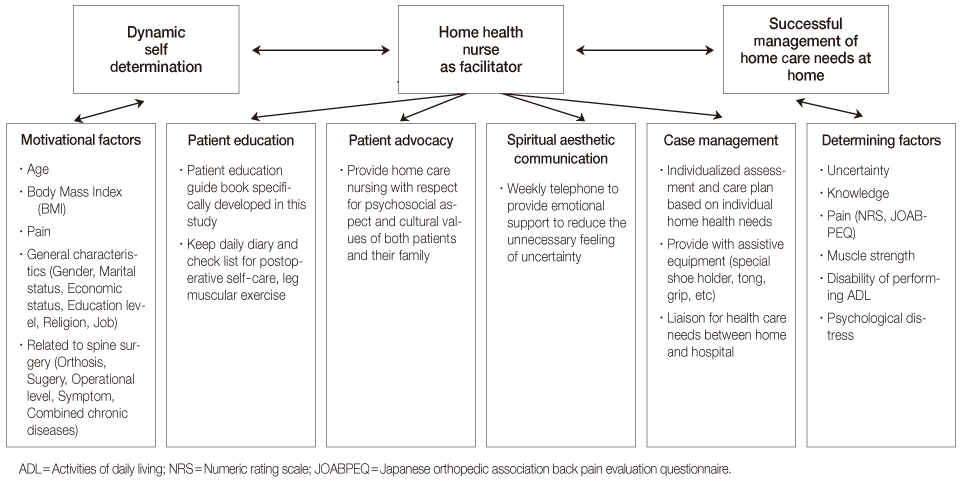
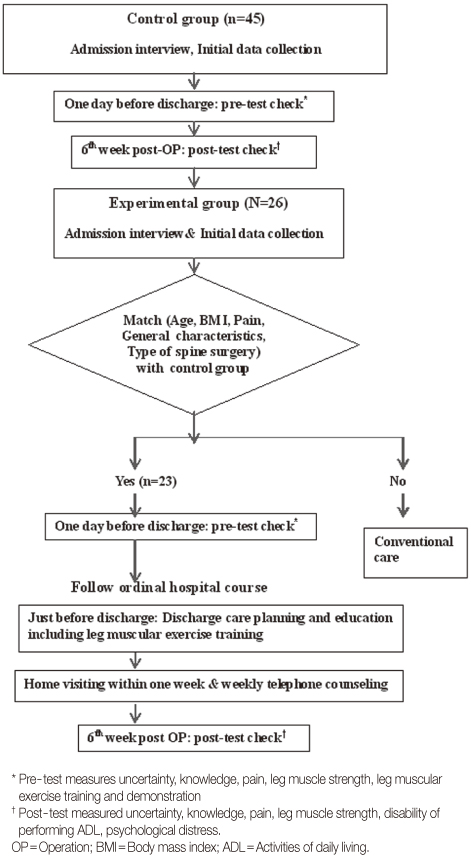
A non-equivalent control group pre-post test quasi-experimental study was performed. HHCS was developed based on the Rice model of dynamic self-determination for self-care. For data collection, a control group (n=23) and an experimental group (n=23) were selected by matching age, BMI, pain, general characteristics and type of spine surgery. Measurement tools to evaluate uncertainty and knowledge were developed by the authors. The Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) and Japanese Orthopedic Association Back Pain Evaluation Questionnaire (JOABPEQ) were used to evaluate pain levels. Muscular strength in the legs was measured using a digital muscle tester and tape ruler. Questionnaires were used to evaluate disability in performing ADL and psychological distress levels.
RESULTS
The experimental group showed significant decrease in uncertainty (p=.028), increased knowledge (p=.038), and partially decreased pain (p=.003-.331). Partial muscle strength increased significantly (p=.021-.644). Disability in performing ADL and psychological distress in the experimental group decreased significantly compared to control group (p=.002, p=.004).
CONCLUSION
Results indicate HHCS is an efficient home care nursing program for these elders. Further experimental studies with larger samples are required to confirm effects of HHCS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi WJ, Kim DO, Jun MH, Jung JY. A comparative study of the level of pain, knowledge, and uncertainty between pre and post spinal operation. Poster session presented at the International Council of Nurses. 2011. 05. Malta:2. Cohen J. A power primer. Psychol Bull. 1992. 112(1):155–159. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.155.3. Deyo RA. Back surgery-who needs it? N Engl J Med. 2007. 356(22):2239–2243. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp078052.4. Djurasovic M, Glassman SD, Carreon LY, Dimar JR. Contemporary management of sumptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 2010. 41(2):183–191. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ocl.2009.12.003.5. Fukui M, Chiba K, Kawakami M, KiKuchi S, Konno S, Miyamoto M, et al. JOA back pain evaluation questionnaire(JOABPEQ)/JOA cervical myelopathy evaluation questionnaire (JOACMEQ) the report on the development of revised versions April 16, 2007. J Orthop Sci. 2009. 14(3):348–365. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00776-009-1337-8.6. Harvey CV. Spinal surgery patient care. Orthop Nurs. 2005. 24(6):426–440.7. Jun MH, Choi CR, Lim EJ. Experience of Korean elderly patients undergoing lumbar spinal surgery: Inventive adaptation to postsurgical lives. Poster session presented at the Canadian Association of Neuroscience Nurses 41st annual meeting and scientific sessions. 2010. 06. Quebec, Canada:8. Jun MH, Jung JY. A follow up study for elderly's disabilities in performing activities of daily life after lumbar spinal surgery. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2010a. 16(1):140–149.9. Jun MH, Jung JY. Elderly patient guide: Spinal surgery for low back pain. 2010b. Seoul: Daehak Publisher.10. Jung JY. Effects of legs muscular strengthening exercises on pain, muscular strength of legs, disability of daily living activity, and isoenzyme of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. 2010. Daejeon: Daejeon University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.11. Lee CS, Lee CG. Lumbar spinal disease beyond common sense, Tale about lumbar disc. 2000. Goyang: KSI.12. Lee JN. The effect and client satisfaction of home care nursing services for the aging: Focused on the poor aged in Yongin. 2007. Youngin: Gangnam University;Unpublished master's thesis.13. Lee JS. Easy prevention and treatment for lumbar disc. 2004. Seoul: Garim Publisher.14. McClune A. Predictors of improved quality of life 12 months after lumbar spinal fusion surgery. 2001. Pittsburg: University of Pittsburg;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.15. Mekhail N, Vallejo R, Coleman MH, Benyamin RM. Long-term results of percutaneous lumbar decompression mild for spinal stenosis. Pain Pract. 2012. 12(3):184–193. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1533-2500.2011.00481.x.16. Mishel MH. Uncertainty in illness. J Nurs scholarsh. 1988. 20(4):225–232. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.1988.tb00082.x.17. National Health Insurance Corporation. Major operation statistics 2010. 2011. Retrieved April 30, 2012. from http://www.nhic.or.kr/portal/site/main/menuitem.b3d33d790bae4b404bf15151062310a0.18. Nielsen PR, Jørgensen LD, Dahl B, Pedersen T, Tønnesen H. Prehabilitation and early rehabilitation after spinal surgery: Randomized clinical trial. Clin Rehabil. 2010. 24:137–148. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0269215509347432.19. Rice R. Home care nursing practice: Concepts and application. 2006. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby.20. Saban KL, Penckofer SM. Patient expectations of quality of life following lumbar spinal surgery. J Neurosci Nurs. 2007. 39(3):180–189. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01376517-200706000-00009.21. Sobottke R, Aghayev E, Roder C, Eysel P, Delank SK, Zweig T. Predictors of surgical, general and follow-up complications in lumbar spinal stenosis relative to patient age as emerged from the spine tango registry. Eur Spine J. 2012. 21(3):411–417. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-2016-y.22. Statistics Korea. Population projections for Korea: 2010~2060. 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2012. From http://kostat.go.kr/wnsearch/search.jsp.23. Statistics Korea. Housing census: 2010-2035. 2012. Retrieved April 26, 2012. From http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/index.action.24. Suri P, Rainville J, Kalichman L, Katz JN. Does this older adult with lower extremity pain have the clinical syndrome of lumbar stenosis? JAMA. 2010. 304(23):2628–2636. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2010.1833.25. Yu YK, Kim SH. The effect of rehabilitation exercise program according to whether or not operation of Lumbar in patients with Low back pain. Exerc Sci. 2006. 15(4):275–282.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Home Health Care Program for Cerebrovascular Accident Patients
- Determinants of Amount of Service Use in Community-Based Long-term Care for Elders
- Elders' Health Status, Quality of Life, and Satisfaction with Customized Home Visiting Health Service Depending on Connection to Volunteerism
- An Analysis of Interrupting Factors in Collaboration between Medical Professionals in Home Health Service
- Levels of Health-related Quality of Life (EQ-5D) and Its Related Factors among Vulnerable Elders Receiving Home Visiting Health Care Services in Some Rural Areas