J Bacteriol Virol.
2014 Dec;44(4):326-335. 10.4167/jbv.2014.44.4.326.
Characterization of the Repeat Sequences of Varicella-Zoster Virus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. chlee@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 1737321
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2014.44.4.326
Abstract
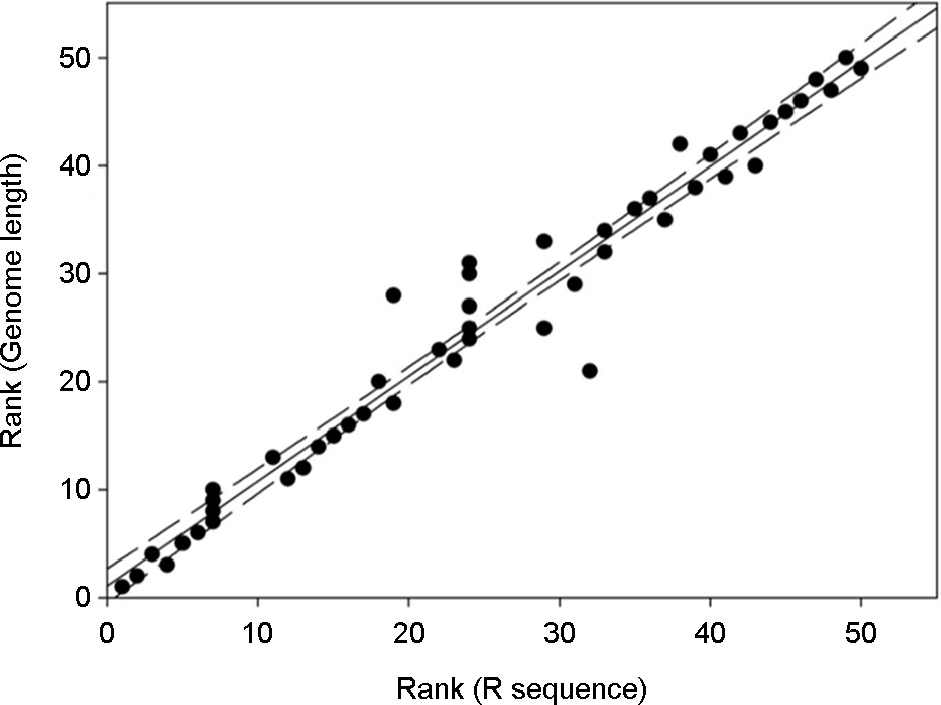
- Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a causative agent for shingles and herpes zoster. The genomes of VZV contain five reiteration (R) sequences and an origin of replication (ORI) sequences composed of tandem repeats whose numbers vary among different strains. Variation of the genome lengths among VZV strains could be attributed by the lengths of R sequences. There was a strong correlation between the lengths of VZV genome and R sequences, while variation of ORI did not contribute the variation of VZV genome length. The high G+C contents of The R sequences in ORF11, 14 and 22 influenced the codon usage of VZV in these ORFs. None of the most frequent 5 codons in R sequences was included in the top 5 most frequent codon in ORF11-14-22 or VZV genome, and vice versa.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Weller TH, Witton HM, Bell EJ. The etiologic agents of varicella and herpes zoster; isolation, propagation, and cultural characteristics in vitro. J Exp Med. 1958; 108:843–68.2). Davison AJ, Scott JE. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986; 67:1759–816.
Article3). Arvin AM. Varicella-zoster virus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996; 9:361–81.
Article4). Norberg P, Liljeqvist JA, Bergström T, Sammons S, Schmid DS, Loparev VN. Complete-genome phylogenetic approach to varicella-zoster virus evolution: genetic divergence and evidence for recombination. J Virol. 2006; 80:9569–76.
Article5). Peters GA, Tyler SD, Grose C, Severini A, Gray MJ, Upton C, et al. A full-genome phylogenetic analysis of varicella-zoster virus reveals a novel origin of replication-based genotyping scheme and evidence of recombination between major circulating clades. J Virol. 2006; 80:9850–60.
Article6). Loparev VN, Rubtcova EN, Bostik V, Tzaneva V, Sauerbrei A, Robo A, et al. Distribution of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) wild-type genotypes in northern and southern Europe: evidence for high conservation of circulating genotypes. Virology. 2009; 383:216–25.
Article7). Tang JW. Phylogenetic studies of frequently diagnostically sampled herpesviruses–possibilities for clinical applications? Infect Genet Evol. 2013; 18:379–86.8). Barrett-Muir W, Scott FT, Aaby P, John J, Matondo P, Chaudhry QL, et al. Genetic variation of varicella-zoster virus: evidence for geographical separation of strains. J Med Virol. 2003; 70:S42–7.
Article9). Firth C, Kitchen A, Shapiro B, Suchard MA, Holmes EC, Rambaut A. Using time-structured data to estimate evolutionary rates of double-stranded DNA viruses. Mol Biol Evol. 2010; 27:2038–51.
Article10). Gomi Y, Sunamachi H, Mori Y, Nagaike K, Takahashi M, Yamanishi K. Comparison of the complete DNA sequences of the Oka varicella vaccine and its parental virus. J Virol. 2002; 76:11447–59.
Article11). Tyler SD, Peters GA, Grose C, Severini A, Gray MJ, Upton C, et al. Genomic cartography of varicella-zoster virus: a complete genome-based analysis of strain variability with implications for attenuation and phenotypic differences. Virology. 2007; 359:447–58.
Article12). Cohen JI. The varicella-zoster virus genome. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010; 342:1–14.
Article13). Peters GA, Tyler SD, Carpenter JE, Jackson W, Mori Y, Arvin AM, et al. The attenuated genotype of varicella-zoster virus includes an ORF0 transitional stop codon mutation. J Virol. 2012; 86:10695–703.
Article14). Chow VT, Tipples GA, Grose C. Bioinformatics of varicella-zoster virus: single nucleotide polymorphisms define clades and attenuated vaccine genotypes. Infect Genet Evol. 2013; 18:351–6.
Article15). Straus SE, Hay J, Smith H, Owens J. Genome differences among varicella-zoster virus isolates. J Gen Virol. 1983; 64:1031–41.
Article16). Che X, Oliver SL, Reichelt M, Sommer MH, Haas J, Roviš TL, et al. ORF11 protein interacts with the ORF9 essential tegument protein in varicella-zoster virus infection. J Virol. 2013; 87:5106–17.
Article17). Che X, Oliver SL, Sommer MH, Rajamani J, Reichelt M, Arvin AM. Identification and functional characterization of the Varicella zoster virus ORF11 gene product. Virology. 2011; 412:156–66.
Article18). Yoshida M, Tamura T, Miyasaka K, Shimizu A, Ohashi N, Itoh M. Analysis of numbers of repeated units in R2 region among varicella-zoster virus strains. J Dermatol Sci. 2003; 31:129–33.
Article19). Sauerbrei A, Zell R, Wutzler P. Analysis of repeat units in the R2 region among different Oka varicella-zoster virus vaccine strains and wild-type strains in Germany. Intervirology. 2007; 50:40–4.
Article20). Sandbaumhüter M, Döhner K, Schipke J, Binz A, Pohlmann A, Sodeik B, et al. Cytosolic herpes simplex virus capsids not only require binding inner tegument protein pUL36 but also pUL37 for active transport prior to secondary envelopment. Cell Microbiol. 2013; 15:248–69.
Article21). Böttcher S, Klupp BG, Granzow H, Fuchs W, Michael K, Mettenleiter TC. Identification of a 709-amino-acid internal nonessential region within the essential conserved tegument protein (p)UL36 of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 2006; 80:9910–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Genetic Diversity among Varicella-Zoster Virus Vaccine Strains
- Herpes zoster complicated by deep vein thrombosis : a case report
- Two cases of varicella zoster meningitis in immunocompetent children
- Association of Herpes Zoster and Lymphosarcoma: Report of one Case
- A clinical study on varicella zoster virus infection and treatment in children with malignant lymphoproliferative disease