Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2014 Apr;2(1):36-38. 10.14791/btrt.2014.2.1.36.
Glioblastoma in a Patient with Neurofibromatosis Type 1: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea. gtyee@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 1734666
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2014.2.1.36
Abstract
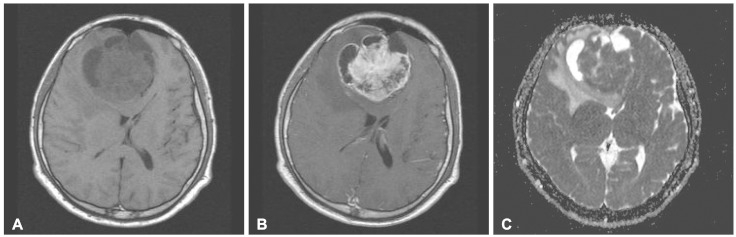
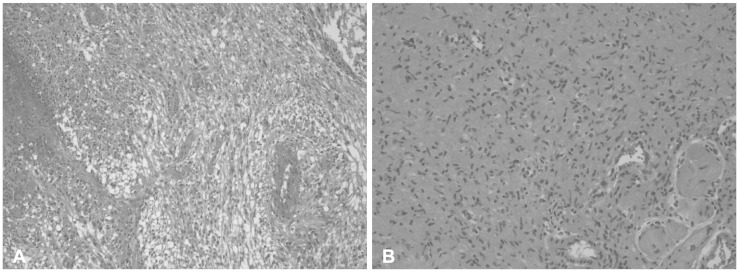
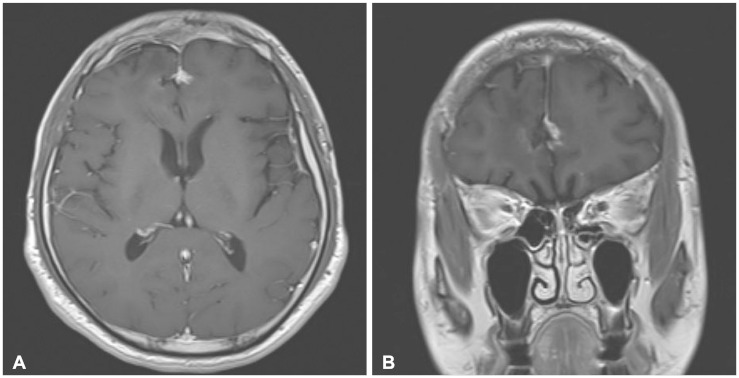
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominantly inherited familial tumor syndrome. Benign tumors such as pilocytic astrocytoma, optic glioma make up the majority of intracranial neoplasms in patients with NF1. There have only been a handful of cases in which adult glioblastoma presented with NF1. A 32-year-old male presented with headache and radiological studies showing a high grade intra-axial tumor. The patient underwent gross total surgical excision and the pathology revealed glioblastoma. After the surgery, he received concomitant chemo-radiotherapy with temozolomide and adjuvant temozolomide chemotherapy. We report a NF1 patient who developed glioblastoma and reviewed related articles.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Glioblastoma Cellular Origin and the Firework Pattern of Cancer Genesis from the Subventricular Zone
Seon-Jin Yoon, Junseong Park, Dong-Su Jang, Hyun Jung Kim, Joo Ho Lee, Euna Jo, Ran Joo Choi, Jin-Kyung Shim, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui-Hyun Kim, Jong Hee Chang, Jeong Ho Lee, Seok-Gu Kang
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63(1):26-33. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2019.0129.
Reference
-
1. Friedman JM. Epidemiology of neurofibromatosis type 1. Am J Med Genet. 1999; 89:1–6. PMID: 10469430.
Article2. Blatt J, Jaffe R, Deutsch M, Adkins JC. Neurofibromatosis and childhood tumors. Cancer. 1986; 57:1225–1229. PMID: 3080222.
Article3. Korf BR. Malignancy in neurofibromatosis type 1. Oncologist. 2000; 5:477–485. PMID: 11110599.
Article4. Huttner AJ, Kieran MW, Yao X, et al. Clinicopathologic study of glioblastoma in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010; 54:890–896. PMID: 20310005.
Article5. Farmer JP, Khan S, Khan A, et al. Neurofibromatosis type 1 and the pediatric neurosurgeon: a 20-year institutional review. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2002; 37:122–136. PMID: 12187057.
Article6. Guillamo JS, Créange A, Kalifa C, et al. Prognostic factors of CNS tumours in Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1): a retrospective study of 104 patients. Brain. 2003; 126(Pt 1):152–160. PMID: 12477702.
Article7. Walther MM, Herring J, Enquist E, Keiser HR, Linehan WM. von Recklinghausen's disease and pheochromocytomas. J Urol. 1999; 162:1582–1586. PMID: 10524872.
Article8. Pál E, Gömöri E E, Gáti I. Neurofibromatosis and glioblastoma in a case of multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol. 2001; 8:717–718. PMID: 11784359.
Article9. Mehta RS, Abraham M, Plesa C, Ennis P. Glioblastoma multiforme in an adult with von Recklinghusen disease. Commun Oncol. 2008; 5:544–548.10. Hakan T, Aker FV. Case report on a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1 and a frontal cystic glioblastoma. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2008; 42:362–365. PMID: 18975243.11. Broekman ML, Risselada R, Engelen-Lee J, Spliet WG, Verweij BH. Glioblastoma multiforme in the posterior cranial fossa in a patient with neurofibromatosis type I. Case Rep Med. 2009; 2009:757898. PMID: 20029672.
Article12. Gutmann DH, James CD, Poyhonen M, et al. Molecular analysis of astrocytomas presenting after age 10 in individuals with NF1. Neurology. 2003; 61:1397–1400. PMID: 14638962.
Article13. Reilly KM, Loisel DA, Bronson RT, McLaughlin ME, Jacks T. Nf1; Trp53 mutant mice develop glioblastoma with evidence of strain-specific effects. Nat Genet. 2000; 26:109–113. PMID: 10973261.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Orbital Neurilemoma Associated with Neurofibroma tosis
- A Novel c.6766_6767insAA Mutation in the Neurofibromin Gene in a Patient with Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Glioblastoma
- Bilateral Segmental Neurofibromatosis with Partial Unilateral Lentiginosis: Case Report with Review of the Literature
- A Case of Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia associated with Neurofibromatosis
- Clitoral Involvement by Neurofibromatosis: A Case Report