J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Oct;19(5):735-738. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.5.735.
Detection Rates of Bacteria in Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. shleemd@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1733518
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.5.735
Abstract
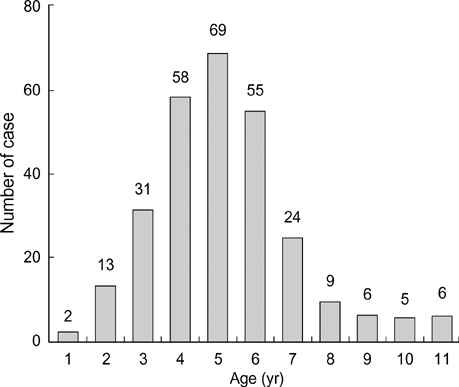
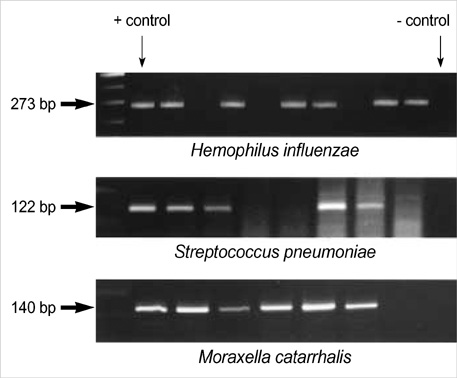
- This study was performed to investigate polymerase chain reaction-based detection of bacterial DNA in middle ear fluid and assess the correlation between the PCR-positive rate with several factors associated with middle ear effusion. The purpose was to gain a further understanding of bacterial infection as a major cause of otitis media with effusion. Of the 278 specimens of middle ear fluid, 39 (14%) tested positive by ordinary culture. The overall detection rate of bacterial DNA using the PCR method was 36.7% for middle ear effusion, and bacterial DNA detection rates of Hemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis in the middle ear effusion were 29.1%, 4.7% and 10.8%, respectively. The bacterial DNA detection rate was higher in ears with a history of acute otitis media than those without the history. High detection rates were observed in patients younger than 48 months who have had a higher tendency to present with acute otitis media. We concluded that PCR is a more sensitive method for the detection of bacteria in middle ear effusion than ordinary culture, and acute otitis media is a major contributor to the pathogenesis of otitis media with effusion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Child
Child, Preschool
Chronic Disease
DNA, Bacterial/analysis
Haemophilus Infections/*diagnosis
Haemophilus influenzae/genetics/*isolation & purification
Humans
Infant
Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis/genetics/isolation & purification
Moraxellaceae Infections/diagnosis
Otitis Media with Effusion/*diagnosis/*microbiology
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
Streptococcal Infections/diagnosis
Streptococcus pneumoniae/genetics/isolation & purification
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Microbiological Results From Middle Ear Effusion in Pediatric Patients Receiving Ventilation Tube Insertion: Multicenter Registry Study on the Effectiveness of Ventilation Tube Insertion in Pediatric Patients With Chronic Otitis Media With Effusion: Part I
Myung Hoon Yoo, Yang-Sun Cho, June Choi, Yun Hoon Choung, Jae-Ho Chung, Jong Woo Chung, Gyu Cheol Han, Eun-Ju Jeon, Beom Cho Jun, Dong-Kee Kim, Kyu Sung Kim, Jun Ho Lee, Kyu-Yup Lee, Seung Hwan Lee, In Seok Moon, Hong Ju Park, Shi Nae Park, Jihye Rhee, Jae Hyun Seo, Seung Geun Yeo
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;11(3):181-185. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2017.01473.
Reference
-
1. Rayner MG, Zhang Y, Gorry MC, Chen Y, Post JC, Ehrlich GD. Evidence of bacterial metabolic activity in culture-negative otitis media with effusion. JAMA. 1998. 279:296–299.
Article2. Liu YS, Lim DJ, Lang RW, Brick HG. Chronic middle ear effusions: Immunochemical and bacteriological investigations. Arch Otolaryngol. 1975. 101:278–286.
Article3. Senturia BH, Gessert CF, Carr CD, Baumann ES. Studies concerned with tubotympanitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1958. 67:440–467.4. Park HJ, Park KH, Kim BC, Yoo YJ, Park K. Detection of bacteria in the middle ear effusion and adenoid tissue of chronic otitis media patient using PCR method. Korean J Otolaryngol. 2000. 43:913–917.5. Jero J, Virolainen A, Salo P, Leinonen M, Eskola J, Karma P. PCR assay for detecting Streptococcus pneumoniae in the middle ear of children with otitis media with effusion. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh). 1996. 116:288–292.
Article6. Ueyama T, Kurono Y, Shirabe K, Takeshita M, Mogi G. High incidence of Haemophilus influenzae in nasopharyngeal secretions and middle ear effusions as detected by PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. 33:1835–1838.
Article7. Virolainen A, Salo P, Jero J, Karma P, Eskola J, Leinonen M. Comparison of PCR assay bacterial culture for detecting Streptococcus pneumoniae in middle ear fluid of children with acute otitis media. J Clin Microbiol. 1994. 32:2667–2670.8. Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988. 239:487–491.
Article9. Bluestone CD. Recent advances in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of otitis media. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1981. 28:727–755.
Article10. Lim DJ, Lewis DM, Schram JL, Birk HG. Otitis media with effusion: Cytological and microbiological correlates. Arch Otolaryngol. 1979. 105:404–412.
Article11. Qvarnberg Y, Holopainen E, Palva T. Aspiration cytology in acute otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh). 1984. 97:443–449.
Article12. Choi YC, Park YS, Yeo SW, Chae SY, Jung DG, Kim SW. Detection of Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in chronic otitis media with effusion (OME). Korean J Otolaryngol. 1998. 41:846–850.13. Post JC, Aul JJ, White GJ, Wadowsky RM, Zavoral T, Tabari R, Kerber B, Doyle WJ, Ehrlich GD. PCR-based detection of bacterial DNA after antimicrobial treatment is indicative of persistent, viable bacteria in the chinchilla model of otitis media. Am J Otolaryngol. 1996. 17:106–111.
Article14. Post JC, Preston RA, Aul JJ, Larkins-Pettigrew M, Rydquist-White J, Anderson KW, Wadowsky RM, Reagan DR, Walker ES, Kingsley LA. Molecular analysis of bacterial pathogens in otitis media with effusion. JAMA. 1995. 273:1598–1604.
Article15. Gok U, Bulut Y, Keles E, Yalcin S, Doymaz MZ. Bacteriological and PCR analysis of clinical material aspirated from otitis media with effusions. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2001. 60:49–54.
Article16. Suzuki M, Watanabe T, Mogi G. Clinical, bacteriological, and histological study of adenoids in children. Am J Otolaryngol. 1999. 20:85–90.
Article17. Mills RP, Irani BS, Vaughan-Jones RJ, Padgham ND. Maxillary sinusitis in children with otitis media with effusion. J Laryngol Otol. 1994. 108:842–844.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of Bacteria in the Middle Ear Effusion and Adenoid Tissue of Chronic Otitis Media Patient Using PCR Method
- Efficiency of Tympanostomy Tube Insertion in Children with Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion
- Relationship between Effusion Bacteria and Concentrations of Immunoglobulin in Effusion Fluid in Recurrent Otitis Media with Effusion Patients
- Middle ear histopathology in children with otitis media with effusion
- Management of Otitis Media in Children