J Korean Acad Nurs.
2014 Feb;44(1):64-74. 10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.64.
A Development and Evaluation of Nursing KMS using QFD in Outpatient Departments
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing Science, East-West Nursing Research Institute, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. ekyun@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1730907
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.64
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was done to develop and implement the Nursing KMS (knowledge management system) in order to improve knowledge sharing and creation among clinical nurses in outpatient departments.
METHODS
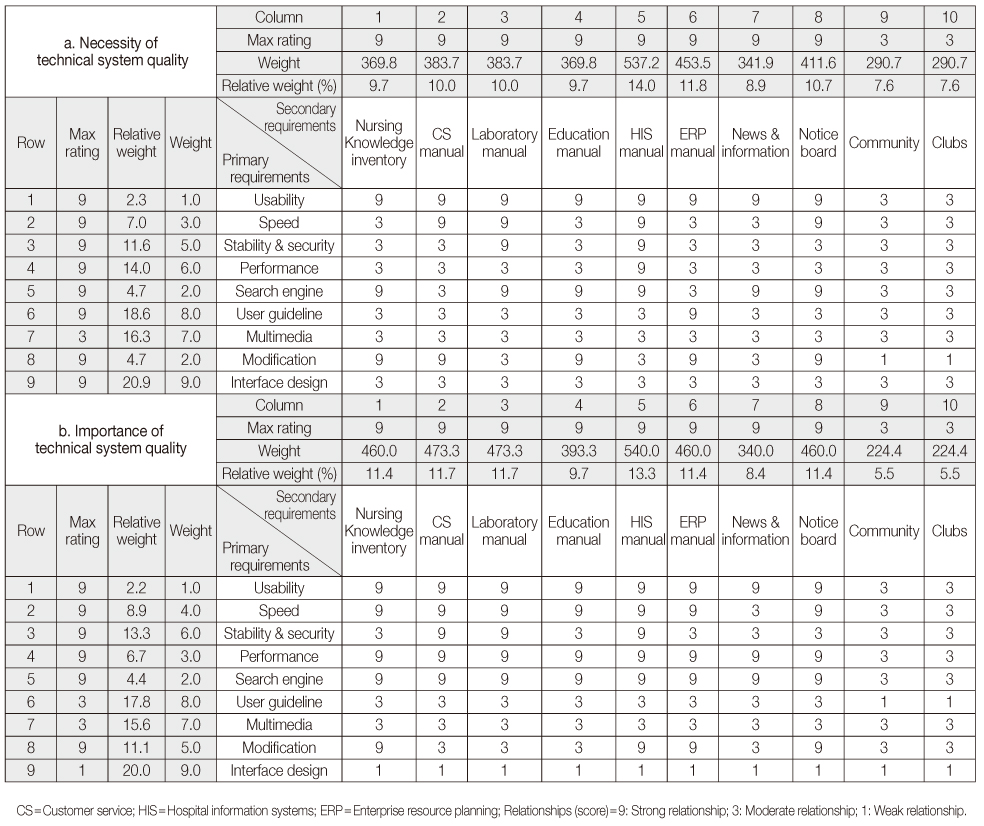
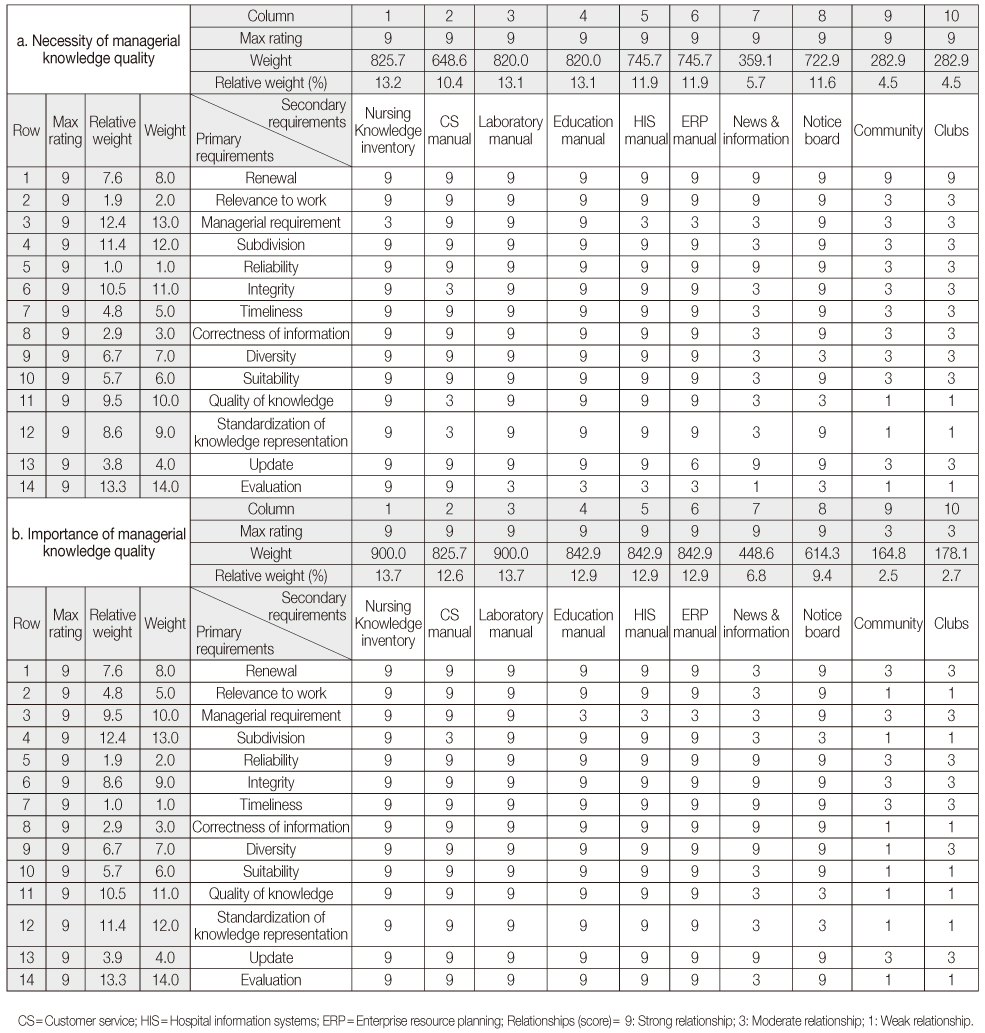
This study was a methodological research using the 'System Development Life Cycle': consisting of planning, analyzing, design, implementation, and evaluation. Quality Function Deployment (QFD) was applied to establish nurse requirements and to identify important design requirements. Participants were 32 nurses and for evaluation data were collected pre and post intervention at K Hospital in Seoul, a tertiary hospital with over 1,000 beds.
RESULTS
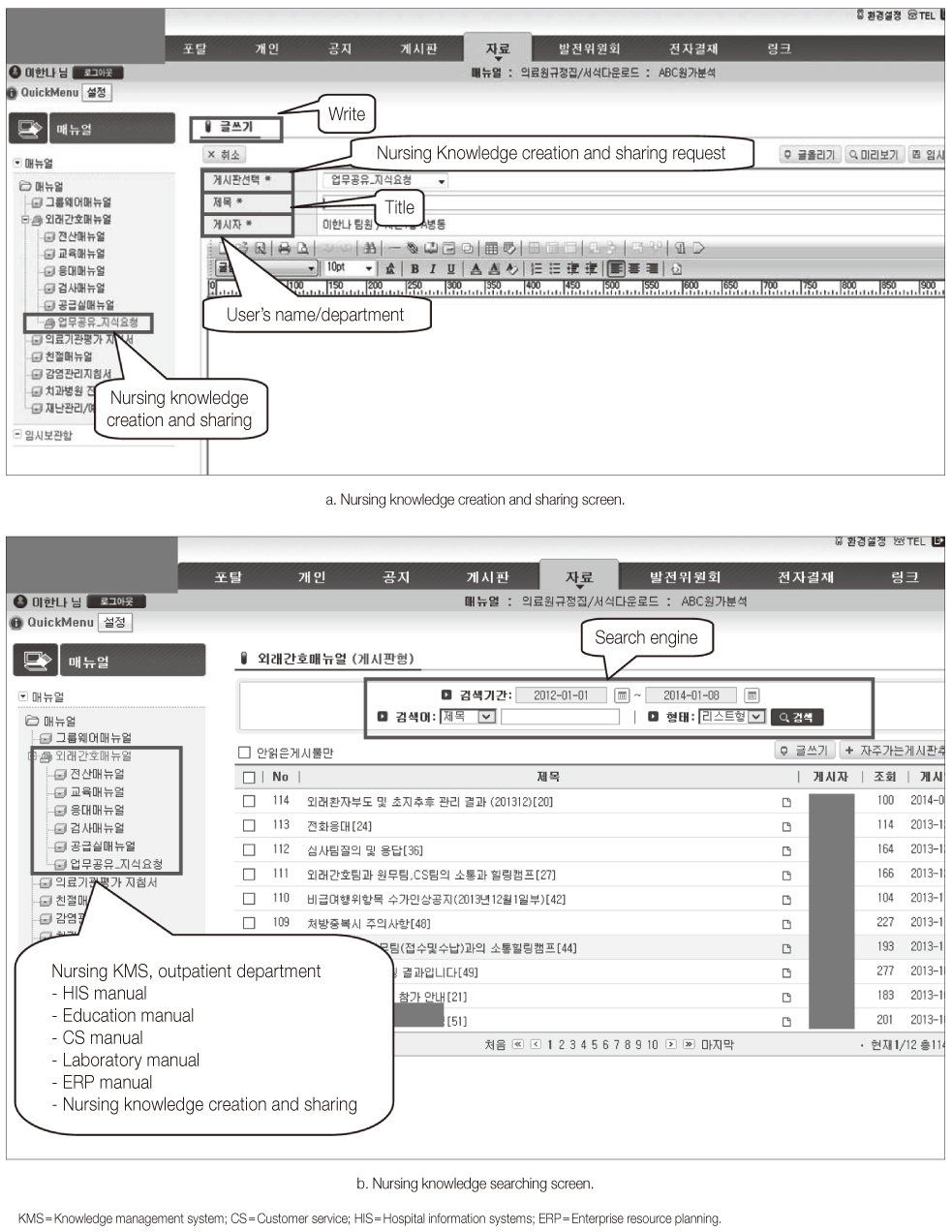
The Nursing KMS was built using a Linux-based operating system, Oracle DBMS, and Java 1.6 web programming tools. The system was implemented as a sub-system of the hospital information system. There was statistically significant differences in the sharing of knowledge but creating of knowledge was no statistically meaningful difference observed. In terms of satisfaction with the system, system efficiency ranked first followed by system convenience, information suitability and information usefulness.
CONCLUSION
The results indicate that the use of Nursing KMS increases nurses' knowledge sharing and can contribute to increased quality of nursing knowledge and provide more opportunities for nurses to gain expertise from knowledge shared among nurses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi JH, Jeong JH. The effect of readiness to self-directed learning on nursing practice competence. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2011; 17(1):16–26.2. Anderson JA, Willson P. Knowledge management: Organizing nursing care knowledge. Crit Care Nurs Q. 2009; 32(1):1–9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.cnq.0000343127.04448.13.3. Nonaka I, Takeuchi H. The knowledge-creating company: How Japanese companies create the dynamics of innovation. New York, NY: Oxford University Press;1995.4. Jang KS. Strategy for introduction of knowledge management into nursing sector in hospital. Korean J Nurs Query. 1999; 8(1):170–181.5. Ruggies R. The state of the notion: Knowledge management in practice. Calif Manage Rev. 1998; 40(3):80–89.6. Rangachari P. Knowledge sharing networks related to hospital quality measurement and reporting. Health Care Manage Rev. 2008; 33(3):253–263.7. Williams C. Can you help me?: Knowledge sharing within the nursing profession. Nurs Womens Health. 2013; 17(2):139–142. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1751-486x.12022.8. Lau AS. Hospital-based nurses' perceptions of the adoption of Web 2.0 tools for knowledge sharing, learning, social interaction and the production of collective intelligence. J Med Internet Res. 2011; 13(4):e92. http://dx.doi.org/10.2196/jmir.1398.9. Kim JA. Development of a knowledge management system for clinical application of the nursing process. Korean J Nurs Query. 2001; 10(1):110–138.10. Kim DY, Park MH. Intermediate evaluation after the introduction of electronic nursing record system in a general hospital. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2010; 16(3):133–144.11. Park I, Choi J, Han J, Keum KL, Sim H, Lee Y, et al. Development of standard nursing statements to establish an electronic nursing record system in wards of the military hospitals. J Mil Nurs Res. 2012; 30(1):60–76.12. Earl M. Knowledge management strategies: Toward a taxonomy. J Manage Inf Syst. 2001; 18(1):215–233.13. Petter S, DeLone WH, McLean ER. Information systems success: The quest for the independent variables. J Manage Inf Syst. 2013; 29(4):7–62. http://dx.doi.org/10.2753/MIS0742-1222290401.14. Ghani RA, Elias NF, Mohd M. A comprehensive instrument for measuring knowledge management system satisfaction. GSTF J Comput. 2013; 2(4):93–102. http://dx.doi.org/10.5176/2251-3043_2.4.214.15. Swanson EB. Management information systems: Appreciation and involvement. Manag Sci. 1974; 21(2):178–188. http://dx.doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.21.2.178.16. Jung SC. A study on the key success factors of knowledge management. Paper presented at: 2008 Spring Conference of Korean Association of Business Education. 2008 April 26; Gunsan: Kunsan National University;p. 175–184.17. Kim SS, Kim YW. An exploratory study on the critical success factors of knowledge management systems. Rev Ind Econ Manag. 2000; 12:65–82.18. Roh JR, Lee KC. Case study on the knowledge management system in state-run corporation: Emphasis on K-wings of Korea asset management corporation (KAMCO). J Korean Soc Libr Inf Sci. 2002; 36(2):243–264.19. Lee H, You TY. Critical success factors from POSCO engineering & construction company's knowledge management experiences. Knowl Manag Res. 2003; 4(2):95–105.20. Jeong CS, Kim SR. A study on effective requirement traceability management method in implementation project of information system. J Korea Soc Comput Inf. 2012; 17(5):115–126.21. Lee ET, Lee JK. The development of evaluating instruments and validity test on KBWA: Kant epistemological perspective. J Organ Manage. 2005; 29(1):1–33.22. Bock GW, Kim YG. Breaking the myths of rewards: An exploratory study of attitudes about knowledge sharing. Inf Resour Manag J. 2002; 15(2):14–21. http://dx.doi.org/10.4018/irmj.2002040102.23. Kang M, Lee JU, Yoon S. Investigating the predicting power of team characteristics and knowledge sharing level on team performance. J Corp Educ. 2011; 13(1):51–74.24. Ahn SK, Kim SS. A study on the user's satisfaction of agriculture information system. Agrolnformatics J. 1999; 1(1):1–11.25. Lee HJ, Park HA. Development of telephone consultation algorithm for patient discharged with ophthalmic disease. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2011; 17(3):336–348. http://dx.doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2011.17.3.336.26. Seo NR, Lee MH. Evaluation of nursing information systems in a general hospital. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2001; 7(1):111–126.27. Jaegal D, Park TJ, Saplan VJ. A study on factors influencing for knowledge sharing on the use of knowledge management system in central government. Korean Public Adm Rev. 2009; 43(1):247–272.28. Hamilton S, Chervany NL. Evaluating information systems effectiveness-part ii: Comparing evaluator viewpoints. MIS Q. 1981; 5(4):79–86. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/249329.29. Liu C, Arnett KP. Exploring the factors associated with web site success in the context of electronic commerce. Inf Manag. 2000; 38(1):23–33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7206(00)00049-5.30. Chang YS. The effects of organizational culture type on the knowledge sharing. Daehan J Bus. 2010; 23(5):2793–2813.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Kabuki Make-up Syndrome Including One Case Associated with Xq Isochromosome
- The analysis of patient visit pattern in a university hospital before and after implementation of health care delivery system
- Kissing molars class III detected at a young age
- Strategic Planning for the Contract-Managed Hospital Foodservice Through QFD Methodology
- Effects of the Mind Map for Emotional Labor and Burnout: A Survey of Nurses in Outpatient Departments of Cancer Hospitals