Yonsei Med J.
2011 Jul;52(4):686-691. 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.4.686.
Clinical Features of Re-Emerging Hepatitis A: An Analysis of Patients Hospitalized during an Urban Epidemic in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. seran@yuhs.ac
- 2AIDS Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1728005
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2011.52.4.686
Abstract
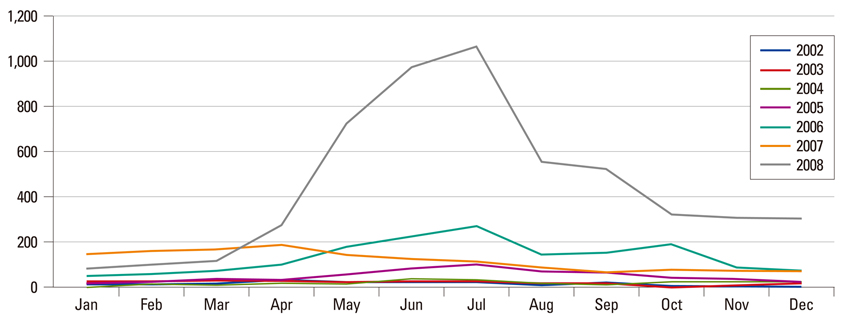
- From April 2008 to November 2008, many cases of hepatitis A were reported in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province in Korea. Furthermore, the rate of severe or fulminant hepatitis have significantly increased during the latest epidemic (13.4% vs. 5.2%, p=0.044). Therefore, widespread use of vaccine is warranted to reduce the burden of hepatitis A in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Prognostic Indicators for Acute Liver Failure Development and Mortality in Patients with Hepatitis A: Consecutive Case Analysis
Hye Sun Shin, Sae Pyul Kim, Sang Hoon Han, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Chae Yoon Chon, Jun Yong Park
Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(4):953-959. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.4.953.
Reference
-
2. Takahashi Y, Shimizu M. The Study Group of Fulminant Hepatitis. Aetiology and prognosis of fulminant viral hepatitis in Japan: a multicentre study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991. 6:159–164.
Article3. Fujiwara K, Yokosuka O, Ehata T, Saisho H, Saotome N, Suzuki K, et al. Association between severity of type A hepatitis and nucleotide variations in the 5' non-translated region of hepatitis A virus RNA: strains from fulminant hepatitis have fewer nucleotide substitutions. Gut. 2002. 51:82–88.
Article4. Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV. Acute renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1996. 334:1448–1460.
Article5. Gordon SC, Reddy KR, Schiff L, Schiff ER. Prolonged intrahepatic cholestasis secondary to acute hepatitis A. Ann Intern Med. 1984. 101:635–637.
Article6. Barros H, Oliveira F, Miranda H. A survey on hepatitis A in Portuguese children and adolescents. J Viral Hepat. 1999. 6:249–253.
Article7. Sohn YM, Rho HO, Park MS, Park JH, Choi BY, Ki M, et al. The changing epidemiology of hepatitis A in children and the consideration of active immunization in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2000. 41:34–39.
Article8. Choi W, Eom HS, Kim IH, Lee DH, Kim PS, Kim HG, et al. Patterns of acute hepatitis A and anti-HAV seroprevalence of kyungin province. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1999. 34:69–75.9. Kim TY, Sohn JH, Ahn SB, Son BK, Lee HL, Eun CS, et al. [Comparison of recent IgG anti-HAV prevalence between two hospitals in Seoul and Gyeonggi area]. Korean J Hepatol. 2007. 13:363–369.
Article10. Song HJ, Kim TH, Song JH, Oh HJ, Ryu KH, Yeom HJ, et al. Emerging need for vaccination against hepatitis A virus in patients with chronic liver disease in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. 22:218–222.
Article11. Lee D, Cho YA, Park Y, Hwang JH, Kim JW, Kim NY, et al. Hepatitis a in Korea: epidemiological shift and call for vaccine strategy. Intervirology. 2008. 51:70–74.
Article12. Lee EJ, Kwon SY, Seo TH, Yun HS, Cho HS, Kim BK, et al. [Clinical features of acute hepatitis A in recent two years]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008. 52:298–303.13. Rakela J, Redeker AG, Edwards VM, Decker R, Overby LR, Mosley JW. Hepatits A virus infection in fulminant hepatitis and chronic active hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1978. 74:879–882.
Article14. Poovorawan Y, Theamboonlers A, Sinlaparatsamee S, Chaiear K, Siraprapasiri T, Khwanjaipanich S, et al. Increasing susceptibility to HAV among members of the young generation in Thailand. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2000. 18:249–253.15. Byun KS, Kim JH, Song KJ, Baek LJ, Song JW, Park SH, et al. Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis A virus in Korea. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001. 16:519–524.
Article16. Yun H, Kim S, Lee H, Byun KS, Kwon SY, Yim HJ, et al. Genetic analysis of HAV strains isolated from patients with acute hepatitis in Korea, 2005-2006. J Med Virol. 2008. 80:777–784.
Article17. Jenson HB. The changing picture of hepatitis A in the United States. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2004. 16:89–93.
Article18. Shaw FE Jr, Sudman JH, Smith SM, Williams DL, Kapell LA, Hadler SC, et al. A Community-wide epidemic of hepatitis A in Ohio. Am J Epidemiol. 1986. 123:1057–1065.
Article19. Skinner JT. Community-wide epidemic of hepatitis A--Shelby County, Tennessee. J Tenn Med Assoc. 1995. 88:468–469.20. Tong MJ, el-Farra NS, Grew MI. Clinical manifestations of hepatitis A: recent experience in a community teaching hospital. J Infect Dis. 1995. 171:Suppl 1. S15–S18.
Article21. Cuthbert JA. Hepatitis A: old and new. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001. 14:38–58.
Article22. Lemon SM, Shapiro CN. The value of immunization against hepatitis A. Infect Agents Dis. 1994. 3:38–49.23. Brown GR, Persley K. Hepatitis A epidemic in the elderly. South Med J. 2002. 95:826–833.
Article24. Lednar WM, Lemon SM, Kirkpatrick JW, Redfield RR, Fields ML, Kelley PW. Frequency of illness associated with epidemic hepatitis A virus infections in adults. Am J Epidemiol. 1985. 122:226–233.
Article25. Halliday ML, Kang LY, Zhou TK, Hu MD, Pan QC, Fu TY, et al. An epidemic of hepatitis A attributable to the ingestion of raw clams in Shanghai, China. J Infect Dis. 1991. 164:852–859.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An epidemic outbreak of hepatitis C transmitted via nonparenteral routes: diagnosed by genomic sequencing of the hepatitis C virus
- Epidemiological Characteristics of Scrub Typhus in Korea, 2009
- Post COVID-19 Emerging Infectious Diseases: What is the Next Pandemic Agent?
- Epidemic modeling and Table-top Exercise for Emerging Infectious Diseases in Korea
- 2017 KASL clinical practice guidelines management of hepatitis C: Treatment of chronic hepatitis C