Yonsei Med J.
2013 May;54(3):785-787. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.785.
Characteristics of Corticospinal Tract Area According to Pontine Level
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea. strokerehab@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1727898
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.785
Abstract
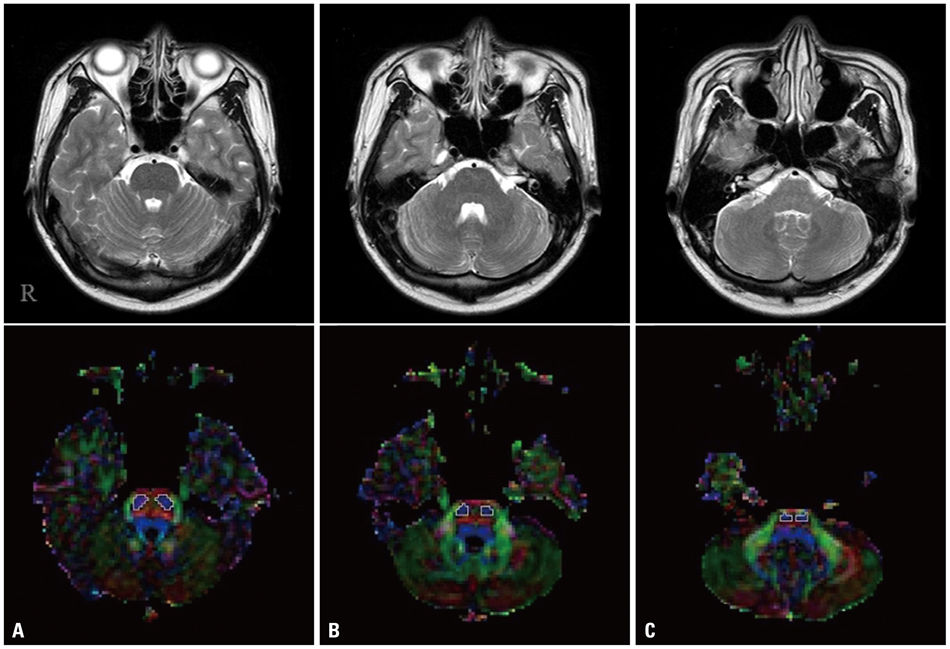
- Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) allows to isolate the corticospinal tract (CST) area from adjacent structures. Using DTI, we investigated the characteristics of the CST areas according to the pontine level in the normal human brain. We recruited 33 healthy subjects and DTIs were acquired using a sensitivity-encoding head coil on a 1.5-T Philips Gyroscan Intera. We measured the size and fractional anisotropy (FA) value of the CST area at the upper, middle, and lower pons. The size of the CST area in the lower pons was smaller than those of the mid-pons and upper pons, and the size of the CST area in the mid-pons was smallerthan that of the upper pons (p<0.05). FA values of the lower pons were larger than those of the mid-pons and upper pons, and the FA value of the mid-pons was also larger than that of the upper pons (p<0.05). In summary, we found a smaller size and higher FA value of the CST area from rostral to caudal direction in the pons. These results suggest a more compact neural structure of CST areas from rostral to caudal direction in the pons.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jang SH. Somatotopic arrangement and location of the corticospinal tract in the brainstem of the human brain. Yonsei Med J. 2011. 52:553–557.
Article2. Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, van Zijl PC. Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 1999. 45:265–269.
Article3. Ferbert A, Vielhaber S, Meincke U, Buchner H. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in pontine infarction: correlation to degree of paresis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992. 55:294–299.
Article4. Biller J, Adams HP Jr, Dunn V, Simmons Z, Jacoby CG. Dichotomy between clinical findings and MR abnormalities in pontine infarction. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1986. 10:379–385.5. Kim JS, Lee JH, Im JH, Lee MC. Syndromes of pontine base infarction. A clinical-radiological correlation study. Stroke. 1995. 26:950–955.6. Kataoka S, Hori A, Shirakawa T, Hirose G. Paramedian pontine infarction. Neurological/topographical correlation. Stroke. 1997. 28:809–815.7. Ahn S, Lee SK. Diffusion tensor imaging: exploring the motor networks and clinical applications. Korean J Radiol. 2011. 12:651–661.
Article8. Assaf Y, Pasternak O. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-based white matter mapping in brain research: a review. J Mol Neurosci. 2008. 34:51–61.
Article9. Lee SK, Kim DI, Kim J, Kim DJ, Kim HD, Kim DS, et al. Diffusion-tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: a new method of describing aberrant fiber connections in developmental CNS anomalies. Radiographics. 2005. 25:53–65.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Corticospinal Tract and Pontocerebellar Fiber of Central Pontine Myelinolysis
- Somatotopic Arrangement and Location of the Corticospinal Tract in the Brainstem of the Human Brain
- Joubert Syndrome Presenting With Normal Pyramidal Decussation: A Case Report
- Restricted Spinothalamic Sensory Loss Below Thoracic Dermatomal Level Caused by Pontine Infarction
- Corticospinal Tract Compression by Hematoma in a Patient with Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Diffusion Tensor Tractography and Functional MRI Study