Yonsei Med J.
2013 May;54(3):739-746. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.739.
Effect-Site Concentration of Remifentanil for Minimizing Cardiovascular Changes by Inhalation of Desflurane
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Armed Forces Capital Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. baikhj@ewha.ac.kr
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1727892
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.739
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aims to investigate the most appropriate effect-site concentration of remifentanil to minimize cardiovascular changes during inhalation of high concentration desflurane.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
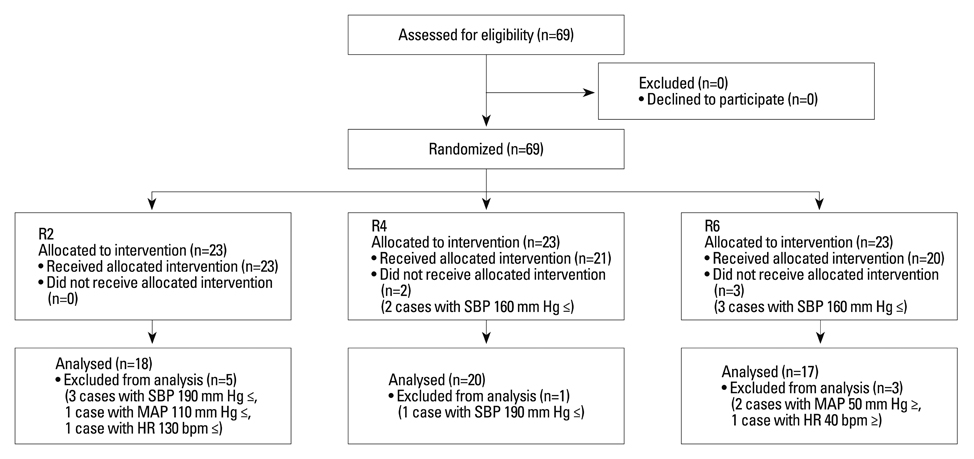
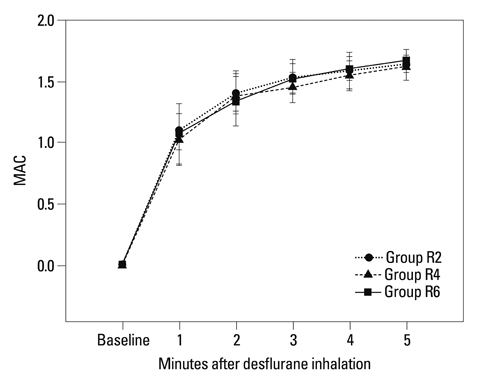
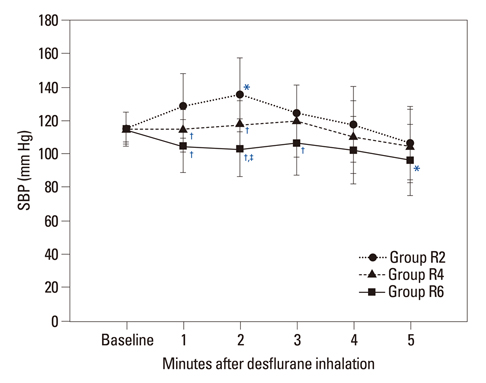
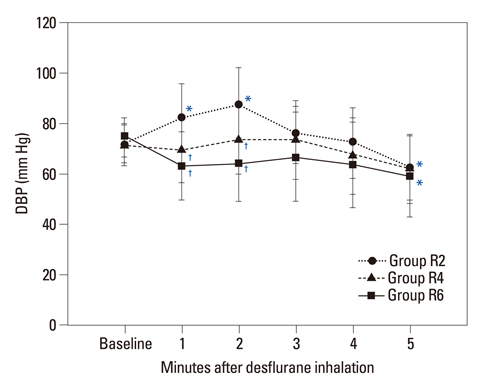
Sixty-nine American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status class I patients aged 20-65 years were randomly allocated into one of three groups. Anesthesia was induced with etomidate and rocuronium. Remifentanil was infused at effect-site concentrations of 2, 4 and 6 ng/mL in groups R2, R4 and R6, respectively. After target concentrations of remifentanil were reached, desflurane was inhaled to maintain the end-tidal concentration of 1.7 minimum alveolar concentrations for 5 minutes (over-pressure paradigm). The systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR) and end-tidal concentration of desflurane were measured for 5 minutes.
RESULTS
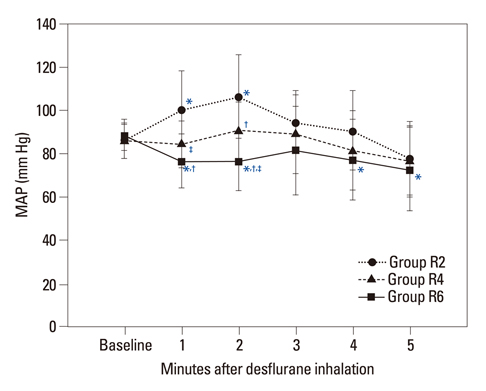
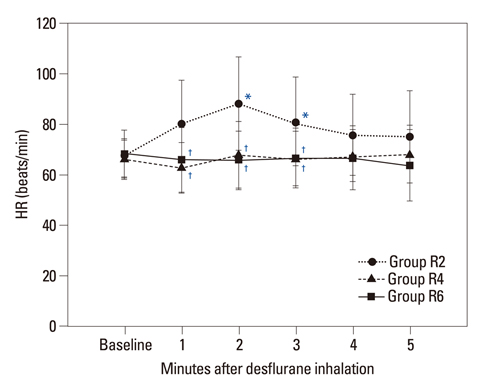
The end-tidal concentration of desflurane increased similarly in all groups. The SBP, DBP, MAP and HR within group R4 were not significantly different as compared with baseline values. However, measured parameters within group R2 increased significantly 1-3 minutes after desflurane inhalation. The MAP within group R6 decreased significantly at 1, 2, 4, and 5 minutes (p<0.05). There were significant differences in SBP, DBP, MAP and HR among the three groups 1-3 minutes after inhalation (p<0.05). The incidence of side effects such as hyper- or hypo-tension, and tachy- or brady-cardia in group R4 was 4.8% compared with 21.8% in group R2 and 15.0% in group R6.
CONCLUSION
The most appropriate effect-site concentration of remifentanil for blunting hemodynamic responses by inhalation of high concentration desflurane is 4 ng/mL.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Androstanols/adverse effects/pharmacology
Anesthetics/adverse effects/pharmacology
Anesthetics, Inhalation/adverse effects/*pharmacology
Blood Pressure/drug effects
Etomidate/adverse effects/pharmacology
Female
Heart/*drug effects
Heart Rate/drug effects
Humans
Isoflurane/adverse effects/*analogs & derivatives/pharmacology
Male
Middle Aged
Piperidines/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Protective Agents/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Androstanols
Anesthetics
Anesthetics, Inhalation
Piperidines
Protective Agents
Isoflurane
Etomidate
Figure
Reference
-
1. Eger EI 2nd. New inhaled anesthetics. Anesthesiology. 1994. 80:906–922.
Article2. Patel SS, Goa KL. Desflurane. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and its efficacy in general anaesthesia. Drugs. 1995. 50:742–767.3. Morgan GE, Mikhail MS, Murray MJ. Strauss M, Lebowitz H, Boyle PJ, editors. Inhalation anesthetics. Clinical Anesthesiology. 2006. 4th ed. New York: McGraw Hill Inc;155–178.4. Bennett JA, Lingaraju N, Horrow JC, McElrath T, Keykhah MM. Elderly patients recover more rapidly from desflurane than from isoflurane anesthesia. J Clin Anesth. 1992. 4:378–381.
Article5. Dupont J, Tavernier B, Ghosez Y, Durinck L, Thevenot A, Moktadir-Chalons N, et al. Recovery after anaesthesia for pulmonary surgery: desflurane, sevoflurane and isoflurane. Br J Anaesth. 1999. 82:355–359.
Article6. Sutton TS, Koblin DD, Gruenke LD, Weiskopf RB, Rampil IJ, Waskell L, et al. Fluoride metabolites after prolonged exposure of volunteers and patients to desflurane. Anesth Analg. 1991. 73:180–185.
Article7. Ebert TJ, Muzi M. Sympathetic hyperactivity during desflurane anesthesia in healthy volunteers. A comparison with isoflurane. Anesthesiology. 1993. 79:444–453.
Article8. Weiskopf RB, Eger EI 2nd, Noorani M, Daniel M. Fentanyl, esmolol, and clonidine blunt the transient cardiovascular stimulation induced by desflurane in humans. Anesthesiology. 1994. 81:1350–1355.
Article9. Yonker-Sell AE, Muzi M, Hope WG, Ebert TJ. Alfentanil modifies the neurocirculatory responses to desflurane. Anesth Analg. 1996. 82:162–166.
Article10. Glass PS, Hardman D, Kamiyama Y, Quill TJ, Marton G, Donn KH, et al. Preliminary pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of an ultra-short-acting opioid: remifentanil (GI87084B). Anesth Analg. 1993. 77:1031–1040.11. Morgan GE, Mikhail MS, Murray MJ. Strauss M, Lebowitz H, Boyle PJ, editors. Nonvolatile anesthetic agents. Clinical Anesthesiology. 2006. 4th ed. New York: McGraw Hill Inc;179–204.12. Song D, White PF. Remifentanil as an adjuvant during desflurane anesthesia facilitates early recovery after ambulatory surgery. J Clin Anesth. 1999. 11:364–367.
Article13. Gesztesi Z, Mootz BL, White PF. The use of a remifentanil infusion for hemodynamic control during intracranial surgery. Anesth Analg. 1999. 89:1282–1287.
Article14. Kim EA, Kim SK, Lim HS, Ko SH, Han YJ, Song HS. The effect of age on the cardiovascular responses induced by inhaled high concentration of desflurane. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2007. 53:435–440.
Article15. Stanski DR, Shafer SL. Miller RD, editor. Measuring depth of anesthesia. Miller's Anesthesia. 2006. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone Inc;1227–1264.16. Mapleson WW. Effect of age on MAC in humans: a meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 1996. 76:179–185.
Article17. Ahn ST, Lee JH, Cheong SH, Lee KM, Lee SE, Kim YH, et al. The effect of continuous remifentanil infusion on the airway reactivity during desflurane inhalation. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2007. 53:448–452.
Article18. Rampil IJ, Lockhart SH, Zwass MS, Peterson N, Yasuda N, Eger EI 2nd, et al. Clinical characteristics of desflurane in surgical patients: minimum alveolar concentration. Anesthesiology. 1991. 74:429–433.19. Van Hemelrijck J, Smith I, White PF. Use of desflurane for outpatient anesthesia. A comparison with propofol and nitrous oxide. Anesthesiology. 1991. 75:197–203.
Article20. Moore MA, Weiskopf RB, Eger EI 2nd, Noorani M, McKay L, Damask M. Rapid 1% increases of end-tidal desflurane concentration to greater than 5% transiently increase heart rate and blood pressure in humans. Anesthesiology. 1994. 81:94–98.
Article21. Cheung AT, Marshall BE. Longnecker DE, Murphy FL, editors. The inhaled anesthetics. Dripps/Eckenhoff/Vandam Introduction to anesthesia. 1997. 9th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Inc;75–87.22. Philip BK, Scuderi PE, Chung F, Conahan TJ, Maurer W, Angel JJ, et al. The Remifentanil/Alfentanil Outpatient TIVA Group. Remifentanil compared with alfentanil for ambulatory surgery using total intravenous anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1997. 84:515–521.
Article23. Song D, Whitten CW, White PF. Remifentanil infusion facilitates early recovery for obese outpatients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesth Analg. 2000. 90:1111–1113.
Article24. Tonner PH, Scholz J. Total intravenous or balanced anaesthesia in ambulatory surgery? Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2000. 13:631–636.
Article25. Naguib M, Lien CA. Miller RD, editor. Pharmacology of muscle relaxants and their antagonists. Miller's Anesthesia. 2006. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone Inc;481–572.
Article26. Albertin A, Casati A, Federica L, Roberto V, Travaglini V, Bergonzi P, et al. The effect-site concentration of remifentanil blunting cardiovascular responses to tracheal intubation and skin incision during bispectral index-guided propofol anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2005. 101:125–130.
Article27. Dixon WJ. Staircase bioassay: the up-and-down method. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1991. 15:47–50.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Optimal effect-site concentration of remifentanil for preventing development of hypertension during tracheal intubation with inhaled desflurane induction
- The target concentration of remifentanil to suppress the hemodynamic response to endotracheal intubation during inhalational induction with desflurane
- The median effective effect-site concentration of remifentanil for minimizing the cardiovascular changes to endotracheal intubation during desflurane anesthesia in pediatric patients
- Effect of midazolam pretreatment on desflurane MAC(BAR) at an effect-site concentration of remifentanil 1.0 ng/ml
- Optimal dose of remifentanil for the prevention of hemodynamic responses during induction of anesthesia with desflurane