Yonsei Med J.
2006 Feb;47(1):113-121. 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.1.113.
Psychiatric Comorbidity in Korean Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Psychopathology According to Subtype
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Department of Psychiatry, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yschoung@smc.samsung.co.kr
- KMID: 1715880
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2006.47.1.113
Abstract
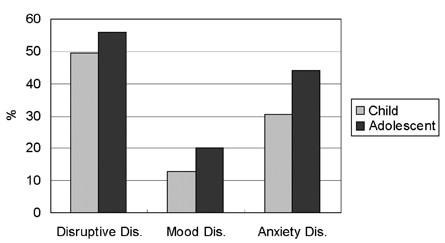
- It is well-known that more than 50% of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) cases also have comorbid psychiatric disorders. We evaluated the comorbid psychopathology of Korean children and adolescents with ADHD using a standardized diagnostic instrument. The Korean Kiddie-Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia-Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL-K) was administered and completed in 105 patients who had been referred to the outpatient and inpatient clinics at the Samsung Medical Center from March 2004 to May 2005. All of the cases were diagnosed as ADHD according to DSM-IV criteria. We analyzed their clinical characteristics and psychiatric comorbidities, and assessed the correlation of any comorbidity with gender, age and ADHD subtype. Among our 105 participants, 70 (66.7%) subjects were diagnosed with combined-type ADHD, 22 (21.0%) were the predominantly inattentive type, only 1 (1.0%) was determined to have the predominantly hyperactive-impulsive type of ADHD, and 12 (11.4%) were classified as not otherwise specified (NOS) ADHD. Eighty (76.2%) subjects had at least one comorbid disorder such as oppositional defiant disorder (n = 53, 50.5%), anxiety disorders (n = 35, 33.3%) and affective disorders (n = 15, 14.3%). Our patients ranged in age from five to 16 years. Among the factors including gender, age, and ADHD subtype, ADHD subtype was the only one significant to comorbidity in our study. The results of this study suggest that psychiatric comorbidity in Korean children with ADHD is similar to the results of previous studies in western countries. Out of all the ADHD subtypes, the combined-type group had a significantly higher ratio of comorbid disorders and psychopathologies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Major Comorbid Disorders with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Gi Jung Hyun, Bongseog Kim, Bung-Nyun Kim, Johanna Inhyang Kim, Jeong Ha Park, Geon Ho Bahn, Moon-Soo Lee, Soyoung Irene Lee, Young Sik Lee, Doug Hyun Han
J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2016;55(4):343-356. doi: 10.4306/jknpa.2016.55.4.343.
Reference
-
1. Popper CW, Gammon GD, West SA, Bailey CE. Hales RE, Yudofsky SC, editors. Disorders usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence. Textbook of psychiatry. 2003. 4 ed. Washington, D. C.: American Psychiatric Press;833–974.2. Goldman LS, Genel M, Bezman RJ, Slanetz PJ. Diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Council on Scientific Affairs, American Medical Association. JAMA. 1998. 279:1100–1107.3. Association AP. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 1994. 4 ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.4. Biederman J, Faraone S, Lapey K. Comorbidity of diagnosis in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1992. 1:335–360.5. Biederman J, Newcorn J, Sprich S. Comorbidity of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder with conduct, depressive, anxiety, and other disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 1991. 148:564–577.6. August GJ, Realmuto GM, MacDonald AW 3rd, Nugent SM, Crosby R. Prevalence of ADHD and comorbid disorders among elementary school children screened for disruptive behavior. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1996. 24:571–595.7. Bird HR, Canino G, Rubio-Stipec M, Gould MS, Ribera J, Sesman M, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of childhood maladjustment in a community survey in Puerto Rico. The use of combined measures. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988. 45:1120–1126.8. Bird HR, Gould MS, Staghezza BM. Patterns of diagnostic comorbidity in a community sample of children aged 9 through 16 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1993. 32:361–368.9. MTA Cooperative Group. A 14-month randomized clinical trial of treatment strategies for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. The MTA Cooperative Group. Multimodal Treatment Study of Children with ADHD. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999. 56:1073–1086.10. Pliszka SR. Comorbidity of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with psychiatric disorder: an overview. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998. 59:Suppl 7. 50–58.11. Jensen PS, Shervette RE 3rd, Xenakis SN, Richters J. Anxiety and depressive disorders in attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity: new findings. Am J Psychiatry. 1993. 150:1203–1209.12. Biederman J, Klein RG, Pine DS, Klein DF. Resolved: mania is mistaken for ADHD in prepubertal children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1998. 37:1091–1096. discussion 6-9.13. Biederman J, Faraone S, Mick E, Wozniak J, Chen L, Ouellette C, et al. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and juvenile mania: an overlooked comorbidity? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1996. 35:997–1008.14. Hechtman L. ADHD and bipolar diorder. ADHD Report. 1999. 7:1–4.15. Hinshaw SP. Externalizing behavior problems and academic underachievement in childhood and adolescence: causal relationships and underlying mechanisms. Psychol Bull. 1992. 111:127–155.16. Hechtman L. Assessment and diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2000. 9:481–498.17. Barkley RA, Anastopoulos AD, Guevremont DC, Fletcher KE. Adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: mother-adolescent interactions, family beliefs and conflicts, and maternal psychopathology. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1992. 20:263–288.18. Gresham FM, MacMillan DL, Bocian KM, Ward SL, Forness SR. Comorbidity of hyperactivity-impulsivity-inattention and conduct problems: risk factors in social, affective, and academic domains. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1998. 26:393–406.19. Kuhne M, Schachar R, Tannock R. Impact of comorbid oppositional or conduct problems on attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997. 36:1715–1725.20. Biederman J, Faraone S, Milberger S, Curtis S, Chen L, Marrs A, et al. Predictors of persistence and remission of ADHD into adolescence: results from a four-year prospective follow-up study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1996. 35:343–351.21. DuPaul GJ, Barkley RA, McMurray MB. Response of children with ADHD to methylphenidate: interaction with internalizing symptoms. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1994. 33:894–903.22. Tannock R, Ickowicz A, Schachar R. Differential effects of methylphenidate on working memory in ADHD children with and without comorbid anxiety. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1995. 34:886–896.23. Diamond IR, Tannock R, Schachar RJ. Response to methylphenidate in children with ADHD and comorbid anxiety. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1999. 38:402–409.24. MTA Cooperative Group. Moderators and mediators of treatment response for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: the Multimodal Treatment Study of children with Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999. 56:1088–1096.25. Cho SC, Shin YO. Prevalence of disruptive behavior disorders. Korean J Child Adol Psychiatr. 1994. 5:141–149.26. Lee KS, Ryu YJ, Ahn DH, Shin YJ. A study of psychosocial variables within ADHD with of without externalizing symptom. Korean J Child Adol Psychiatr. 1996. 7:203–212.27. Joung YS, Song DH, Lee MH. The Correlation between aggression and depressive symptom in patient with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1995. 34:148–155.28. Kim JY, Ahn DH, Shin YJ. An epidemiological study of attention-deficits hyperactivity disorder and learning disabilities in a rural area. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1999. 38:784–793.29. Kim YS, Cheon KA, Kim BN, Chang SA, Yoo HJ, Kim JW, et al. The reliability and validity of Kiddie-Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia-Present and Lifetime Version-Korean version (K-SADS-PL-K). Yonsei Med J. 2004. 45:81–89.30. Kim S, Kim J, Song D, Lee H, Chu Y, Hong C, et al. The Manual of Korean Personality Inventory for Children(KPI-C). 1997. Seoul: Korea Guidance.31. Oh K, Lee H, Hong K, Ha E. Korean version of Child Behavior Checklist (K-CBCL). 1997. Seoul: ChungAng Aptitude Publishing Co. Ltd..32. Wilens TE, Biederman J, Brown S, Tanguay S, Monuteaux MC, Blake C, et al. Psychiatric comorbidity and functioning in clinically referred preschool children and school-age youths with ADHD. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2002. 41:262–268.33. Keenan K, Wakschlag LS. More than the terrible twos: the nature and severity of behavior problems in clinic-referred preschool children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2000. 28:33–46.34. Ha EH, Lee SJ, Oh KJ, Hong KE. Parent-adolescent agreement in the assessment of behavior problems of adolescents: Comparison of factor structures of K-CBCL and YSR. Korean J Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1998. 9:3–12.35. Kim J. Min S, editor. Society and psychiatry. Modern psychiatry. 1999. 4 ed. Seoul: Ilchokak;92–106.36. American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. Practice parameters for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with depressive disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1998. 37(10):Suppl. 63S–83S.37. McClellan J, Werry J. Practice parameters for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997. 36(10):Suppl. 157S–176S.38. Kim J, So Y, Joung Y, Lee I, Hong S. A validity study of parent behavioral rating scales as diagnostic tools of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Korean J Child Adol Psychiatr. 2000. 11:282–289.39. Weiss G. Lewis M, editor. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Child and adolescent psychiatry: A comprehensive textbook. 2002. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Williams & Wilkins;664.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis and Comorbidity of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in School-Aged Children
- Evaluation of Oxidative Metabolism in Child and Adolescent Patients with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
- A Comparison of Comorbidity and Psychological Outcomes in Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
- Medical and Psychiatric Comorbidities in Korean Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
- Use of Atypical Antipsychotics in Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder