J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Aug;27(8):961-964. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.961.
The First Korean Case of Lysinuric Protein Intolerance: Presented with Short Stature and Increased Somnolence
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chshinpd@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1714212
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.961
Abstract
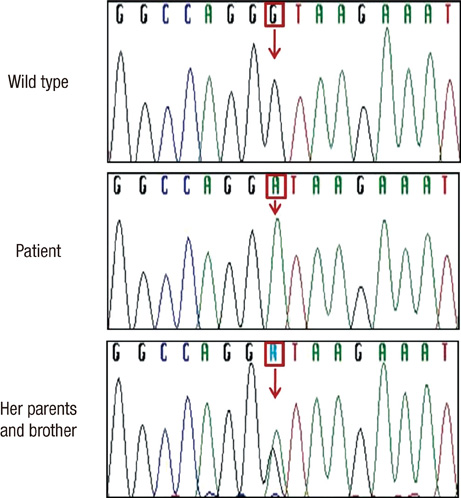
- Lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI) is a rare inherited metabolic disease, caused by defective transport of dibasic amino acids. Failure to thrive, hepatosplenomegaly, hematological abnormalities, and hyperammonemic crisis are major clinical features. However, there has been no reported Korean patient with LPI as of yet. We recently encountered a 3.7-yr-old Korean girl with LPI and the diagnosis was confirmed by amino acid analyses and the SLC7A7 gene analysis. Her initial chief complaint was short stature below the 3rd percentile and increased somnolence for several months. Hepatosplenomegaly was noted, as were anemia, leukopenia, elevated levels of ferritin and lactate dehydrogenase, and hyperammonemia. Lysine, arginine, and ornithine levels were low in plasma and high in urine. The patient was a homozygote with a splicing site mutation of IVS4+1G > A in the SLC7A7. With the implementation of a low protein diet, sodium benzoate, citrulline and L-carnitine supplementation, anemia, hyperferritinemia, and hyperammonemia were improved, and normal growth velocity was observed.
MeSH Terms
-
Amino Acid Metabolism, Inborn Errors/complications/diet therapy/*genetics
Antifungal Agents/therapeutic use
Antigens, CD98 Light Chains/genetics
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Carnitine/therapeutic use
Child, Preschool
Citrulline/therapeutic use
Diet, Protein-Restricted
Disorders of Excessive Somnolence/complications/*diagnosis/drug therapy
Female
Growth Disorders/complications/*diagnosis
Homozygote
Humans
Hypercalcemia/complications/*diagnosis
Metabolic Diseases/complications/*diagnosis
Mutation
Nephrocalcinosis/complications/*diagnosis
Republic of Korea
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Sodium Benzoate/therapeutic use
Vitamin B Complex/therapeutic use
Antifungal Agents
Antigens, CD98 Light Chains
Vitamin B Complex
Citrulline
Sodium Benzoate
Carnitine
Figure
Reference
-
1. Palacín M, Bertran J, Chillarón J, Estévez R, Zorzano A. Lysinuric protein intolerance: mechanisms of pathophysiology. Mol Genet Metab. 2004. 81:S27–S37.2. Sebastio G, Sperandeo MP, Andria G. Lysinuric protein intolerance: reviewing concepts on a multisystem disease. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2011. 157:54–62.3. Perheentupa J, Visakorpi JK. Protein intolerance with deficient transport of basic aminoacids. Another inborn error of metabolism. Lancet. 1965. 2:813–816.4. Palacín M, Borsani G, Sebastio G. The molecular bases of cystinuria and lysinuric protein intolerance. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001. 11:328–335.5. Sperandeo MP, Andria G, Sebastio G. Lysinuric protein intolerance: update and extended mutation analysis of the SLC7A7 gene. Hum Mutat. 2008. 29:14–21.6. Mykkänen J, Torrents D, Pineda M, Camps M, Yoldi ME, Horelli-Kuitunen N, Huoponen K, Heinonen M, Oksanen J, Simell O, et al. Functional analysis of novel mutations in y(+)LAT-1 amino acid transporter gene causing lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI). Hum Mol Genet. 2000. 9:431–438.7. Sperandeo MP, Bassi MT, Riboni M, Parenti G, Buoninconti A, Manzoni M, Incerti B, Larocca MR, Di Rocco M, Strisciuglio P, et al. Structure of the SLC7A7 gene and mutational analysis of patients affected by lysinuric protein intolerance. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. 66:92–99.8. Koizumi A, Shoji Y, Nozaki J, Noguchi A, E X, Dakeishi M, Ohura T, Tsuyoshi K, Yasuhiko W, Manabe M, et al. A cluster of lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI) patients in a northern part of Iwate, Japan due to a founder effect. The Mass Screening Group. Hum Mutat. 2000. 16:270–271.9. Tringham M, Kurko J, Tanner L, Tuikkala J, Nevalainen OS, Niinikoski H, Näntö-Salonen K, Hietala M, Simell O, Mykkänen J. Exploring the transcriptomic variation caused by the Finnish founder mutation of lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI). Mol Genet Metab. 2012. 105:408–415.10. Noguchi A, Shoji Y, Koizumi A, Takahashi T, Matsumori M, Kayo T, Ohata T, Wada Y, Yoshimura I, Maisawa S, et al. SLC7A7 genomic structure and novel variants in three Japanese lysinuric protein intolerance families. Hum Mutat. 2000. 15:367–372.11. Gordon WC, Gibson B, Leach MT, Robinson P. Haemophagocytosis by myeloid precursors in lysinuric protein intolerance. Br J Haematol. 2007. 138:1.12. Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, McClain K, Webb D, Winiarski J, et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007. 48:124–131.13. Tanner LM, Näntö-Salonen K, Niinikoski H, Jahnukainen T, Keskinen P, Saha H, Kananen K, Helanterä A, Metso M, Linnanvuo M, et al. Nephropathy advancing to end-stage renal disease: a novel complication of lysinuric protein intolerance. J Pediatr. 2007. 150:631–634.14. Simell O, Sipilä I, Rajantie J, Valle DL, Brusilow SW. Waste nitrogen excretion via amino acid acylation: benzoate and phenylacetate in lysinuric protein intolerance. Pediatr Res. 1986. 20:1117–1121.15. Tanner LM, Näntö-Salonen K, Venetoklis J, Kotilainen S, Niinikoski H, Huoponen K, Simell O. Nutrient intake in lysinuric protein intolerance. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007. 30:716–721.16. Botschner J, Smith DW, Simell O, Scriver CR. Comparison of ornithine metabolism in hyperornithinaemia-hyperammonaemia-homocitrullinuria syndrome, lysinuric protein intolerance and gyrate atrophy fibroblasts. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1989. 12:33–40.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A new era of genetic diagnosis for short stature children: A review
- Influences of Socioeconomic Status on Short Stature in Childhood
- A Case of Hypocortisolemia Presented by Short Stature
- Differences in Dietary Intakes between Normal and Short Stature Korean Children Visiting a Growth Clinic
- Deciphering short stature in children