Clin Nutr Res.
2012 Jul;1(1):23-29. 10.7762/cnr.2012.1.1.23.
Differences in Dietary Intakes between Normal and Short Stature Korean Children Visiting a Growth Clinic
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Sungshin Women's University, Seoul 147-732, Korea. smlee@sungshin.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Sanggye-Paik Hospital, Inje University School of Medicine, Seoul 139-707, Korea.
- KMID: 2279749
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7762/cnr.2012.1.1.23
Abstract
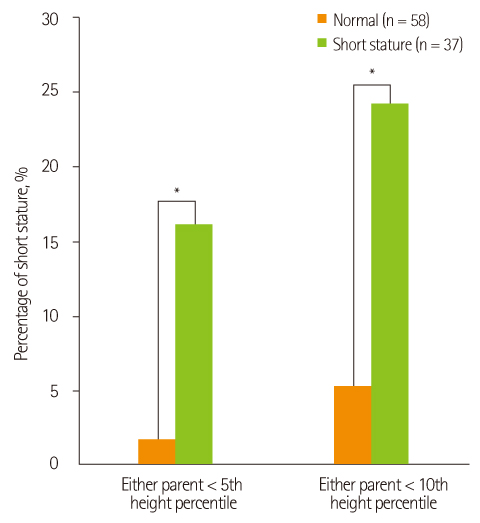
- This study compared birth stature, parents' stature, and food and nutrient intakes between normal and short stature Korean children visiting a growth clinic. A total of 143 growth clinic visitors agreed to participate in the study. Out of the 143 subjects, 37 children with height below the fifth percentile (short stature group) and 58 children with height above the twenty-fifth percentile (normal group) were included in the study analysis. Data were collected through a survey of parents or guardians of children and anthropometric measurements. The ratio of short stature in either parent was significantly higher in short stature group. The mean intakes of protein, fat, calcium, and iron were lower in short stature children compared to normal children. Among five major food groups, the intake frequency of vegetables and fruits was significantly lower in short stature group and that of meat.fish.egg.legume group was also significantly lower in short stature group. In further analysis categorized into 11 detail food groups, the intake frequency of fruit group and legume group was significantly lower in short stature group. Nutritional counseling should be provided to emphasize adequate intake of various food groups including vegetables, fruits, and legumes to short stature children visiting a growth clinic.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korean Statistical Information Service: Student Health Examination Statistics Report. 2005. cited 2011 Dec 10. Available from http://kosis.kr/nsportal/abroad/abroad_01List.jsp.2. Shin JH. Evaluation of short stature and Growth Hormone Treatment. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 1993. 14:97–112.3. Fernald LC, Grantham-McGregor SM. Growth Retardation is associated with changes in the stress response system and behavior in school-aged jamaican children. J Nutr. 2002. 132:3674–3679.
Article4. Silventoinen K, Sammalisto S, Perola M, Boomsma DI, Cornes BK, Davis C, Dunkel L, De Lange M, Harris JR, Hjelmborg JV, Luciano M, Martin NG, Mortensen J, Nisticò L, Pedersen NL, Skytthe A, Spector TD, Stazi MA, Willemsen G, Kaprio J. Heritability of adult body height: a comparative study of twin cohorts in eight countries. Twin Res. 2003. 6:399–408.
Article5. Hammond GK, Barr SI, McCargar LJ. Teacher's perception and use of an innovative early childhood nutrition education program. J Nutr Educ. 1994. 26:233–237.
Article6. Thibault H, Souberbielle JC, Taieb C, Brauner R. Idiopathic prepubertal short stature is associated with low body mass index. Horm Res. 1993. 40:136–140.
Article7. Lee KH. Growth assessment and diagnosis of growth disorders in childhood. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2003. 46:1171–1177.8. Choi MJ, Yoon JS. The effect of eating habits and nutrient intake on the physical growth indices in preschool children. Korean J Community Nutr. 2003. 8:3–14.9. Wudy SA, Hagemann S, Dempfle A, Ringler G, Blum WF, Berthold LD, Alzen G, Gortner L, Hebebrand J. Children with idiopathic short stature are poor eaters and have decreased body mass index. Pediatrics. 2005. 116:e52–e57.
Article10. Huh K, Park MJ. Questionnaire-based analysis of growth-promoting attempts among children visiting a university growth chlinic. Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:576–580.
Article11. Zadik Z, Sinai T, Zung A, Reifen R. Effect of nutrition on growth in short stature before and during growth-hormone therapy. Pediatrics. 2005. 116:68–72.
Article12. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. the Korean Pediatric Society. 2007 Children and Adolescent Growth Chart Report. 2009. Seoul: Seoul Press.13. Size Korea. Report on the 5th Korean Body Size Examination. 2004. cited 2009 Dec 10. Available from http://sizekorea.kats.go.kr/.14. Hermanussen M, Sunder M, Voigt M, Tresguerres JA. Morbid obesity is associated with short stature. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2005. 18:647–650.
Article15. Mendez MA, Adair LS. Severity and timing of stunting in the first two years of life affect performance on cognitive tests in late childhood. J Nutr. 1999. 129:1555–1562.
Article16. Ferreira HS, Moura FA, Cabral CR Jr, Florêncio TM, Vieira RC, de Assunção ML. Short stature of mothers from an area endemic for undernutrition is associated with obesity, hypertension and stunted children: a population-based study in the semi-arid region of Alagoas, Northeast Brazil. Br J Nutr. 2009. 101:1239–1245.
Article17. Hernandez-Diaz S, Peterson KE, Dixit S, Hernández B, Parra S, Barquera S, Sepúlveda J, Rivera JA. Association of maternal short stature with stunting in Mexican children: common genes vs common environment. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1999. 53:938–945.
Article18. Lee SS. The important function of calcium in relation to children's growth. J Korean Diet Assoc. 1999. 5:238–242.19. Black RE, Williams SM, Jones LE, Goulding A. Children who avoid drinking cow milk have low dietary calcium intakes and poor bone health. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002. 76:675–680.
Article20. Bae YJ, Sung CJ. A comparison between postmenopausal osteoporotic women and normal women of their nutrient intakes and the evaluation of diet quality. Korean J Community Nutr. 2005. 10:205–215.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Etiologies and characteristics of children with chief complaint of short stature
- Overnight Growth Hormone Secretions and Sleep Patterns in Idiopathic Short Stature Children
- Status of Alternative Therapies Used by the Children Visiting the 'Growth Clinic'
- Etiological Classifications of Children with Chief Complaint of Short Stature
- Influences of Socioeconomic Status on Short Stature in Childhood