J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Jan;25(1):97-103. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.97.
Clinical Efficacy of Organ-Preserving Pancreatectomy for Benign or Low-Grade Malignant Potential Lesion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sunkim@plaza.snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1713838
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.97
Abstract
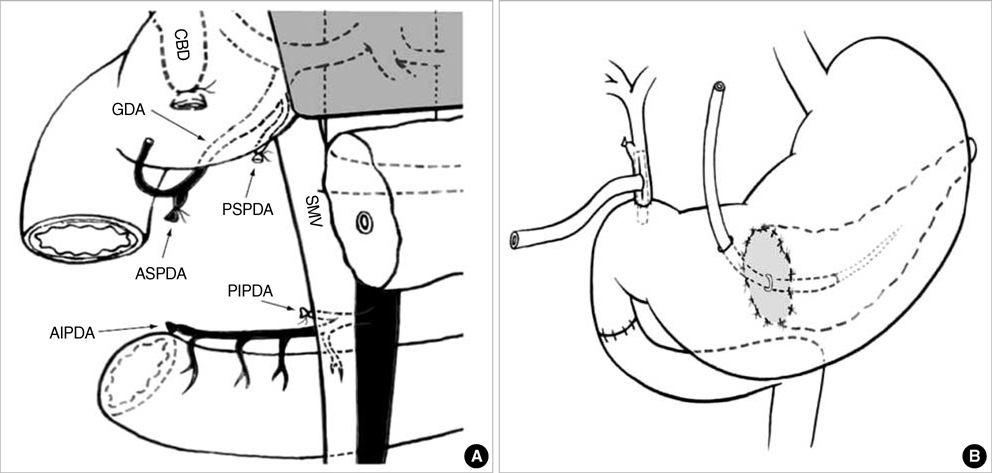
- The clinical usefulness of organ-preserving pancreatectomy is not well established due to technical difficulty and ambiguity of functional merit. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical efficacy of organ-preserving pancreatectomy such as duodenum-preserving resection of the head of the pancreas (DPRHP), pancreatic head resection with segmental duodenectomy (PHRSD), central pancreatectomy (CP) and spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy (SPDP). Between 1995 and 2007, the DPRHP were performed in 14 patients, the PHRSD in 16 patients, the CP in 13 patients, and the SPDP in 45 patients for preoperatively diagnosed benign lesions or tumors with low-grade malignant potential. The clinical outcomes including surgical details, postoperative complications and long-term functional outcomes were compared between organ-preserving pancreatectomy and conventional pancreatectomy group. Major postoperative complications constituted the following: bile duct stricture (7.1% [1/14]) in DPRHP, delayed gastric emptying (31.2% [5/16]) in PHRSD, pancreatic fistula (21.4% [3/14]) in CP. There were no significant differences in postoperative complications and long-term functional outcomes between two groups. Organ-preserving pancreatectomy is associated with tolerable postoperative complications, and good long-term outcome comparing to conventional pancreatectomy. Organ-preserving pancreatectomy could be alternative treatment for benign or low-grade malignant potential lesion of the pancreas or ampullary/parapapillary duodenum.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ryu M, Takayama W, Watanabe K, Honda I, Yamamoto H, Arai Y. Ventral pancreatic resection for adenoma and low-grade malignancies of the head of the pancreas. Surg Today. 1996. 26:476–481.2. Asanuma Y, Koyama K, Saito K, Tanaka J. An appraisal of segmental pancreatectomy for benign tumors of the pancreatic body: a report of two cases. Surg Today. 1993. 23:733–736.3. Yamaguchi K, Shimizu S, Yokohata K, Noshiro H, Chijiiwa K, Tanaka M. Ductal branch-oriented minimal pancreatectomy: two cases of successful treatment. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999. 6:69–73.4. Sperti C, Pasquali C, Ferronato A, Pedrazzoli S. Median pancreatectomy for tumors of the neck and body of the pancreas. J Am Coll Surg. 2000. 190:711–716.5. Yamaguchi K, Yokohata K, Ohkido M, Watanabe M, Ogawa Y, Chijiiwa K, Tanaka M. Which is less invasive--distal pancreatectomy or segmental resection? Int Surg. 2000. 85:297–302.6. Beger HG, Schlosser W, Friess HM, Büchler MW. Duodenum-preserving head resection in chronic pancreatitis changes the natural course of the disease: a single-center 26-year experience. Ann Surg. 1999. 230:512–519.7. Izbicki JR, Bloechle C, Knoefel WT, Kuechler T, Binmoeller KF, Broelsch CE. Duodenum-preserving resection of the head of the pancreas in chronic pancreatitis. A prospective, randomized trial. Ann Surg. 1995. 221:350–358.8. Aranha GV, Shoup M. Nonstandard pancreatic resections for unusual lesions. Am J Surg. 2005. 189:223–228.9. Ahn YJ, Kim SW, Park YC, Jang JY, Yoon YS, Park YH. Duodenal-preserving resection of the head of the pancreas and pancreatic head resection with second-portion duodenectomy for benign lesions, low-grade malignancies, and early carcinoma involving the periampullary region. Arch Surg. 2003. 138:162–168.10. Kim SW, Youk EG, Park YH. Comparison of pancreatogastrostomy and pancreatojejunostomy after pancreatoduodenectomy performed by one surgeon. World J Surg. 1997. 21:640–643.11. Park YC, Kim SW, Jang JY, Ahn YJ, Park YH. Factors influencing delayed gastric emptying after pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2003. 196:859–865.12. Balcom JH 4th, Rattner DW, Warshaw AL, Chang Y, Fernandez-del Castillo C. Ten-year experience with 733 pancreatic resections: changing indications, older patients, and decreasing length of hospitalization. Arch Surg. 2001. 136:391–398.13. Bassi C, Falconi M, Salvia R, Mascetta G, Molinari E, Pederzoli P. Management of complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy in a high volume centre: results on 150 consecutive patients. Dig Surg. 2001. 18:453–457.14. Marcus SG, Cohen H, Ranson JH. Optimal management of the pancreatic remnant after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann Surg. 1995. 221:635–645.15. van Berge Henegouwen MI, De Wit LT, Van Gulik TM, Obertop H, Gouma DJ. Incidence, risk factors, and treatment of pancreatic leakage after pancreaticoduodenectomy: drainage versus resection of the pancreatic remnant. J Am Coll Surg. 1997. 185:18–24.16. Yeh TS, Jan YY, Jeng LB, Hwang TL, Wang CS, Chen SC, Chao TC, Chen MF. Pancreaticojejunal anastomotic leak after pancreaticoduodenectomy--multivariate analysis of perioperative risk factors. J Surg Res. 1997. 67:119–125.17. Sauvanet A, Partensky C, Sastre B, Gigot JF, Fagniez PL, Tuech JJ, Millat B, Berdah S, Dousset B, Jaeck D, Le Treut YP, Letoublon C. Medial pancreatectomy: a multi-institutional retrospective study of 53 patients by the French Pancreas Club. Surgery. 2002. 132:836–843.18. Christein JD, Smoot RL, Farnell MB. Central pancreatectomy: a technique for the resection of pancreatic neck lesions. Arch Surg. 2006. 141:293–299.19. Braasch JW, Deziel DJ, Rossi RL, Watkins E Jr, Winter PF. Pyloric and gastric preserving pancreatic resection. Experience with 87 patients. Ann Surg. 1986. 204:411–418.20. Itani KM, Coleman RE, Meyers WC, Akwari OE. Pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy. A clinical and physiologic appraisal. Ann Surg. 1986. 204:655–664.21. Jimenez RE, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Rattner DW, Chang Y, Warshaw AL. Outcome of pancreaticoduodenectomy with pylorus preservation or with antrectomy in the treatment of chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 2000. 231:293–300.22. Isaji S, Kawarada Y. Pancreatic head resection with second-portion duodenectomy for benign lesions, low-grade malignancies, and early stage carcinomas involving the pancreatic head region. Am J Surg. 2001. 181:172–176.23. Robey E, Mullen JT, Schwab CW. Blunt transection of the pancrease treated by distal pancreatectomy, splenic salvage and hyperalimentation. Four cases and review of the literature. Ann Surg. 1982. 196:695–699.24. Cooper MJ, Williamson RC. Conservative pancreatectomy. Br J Surg. 1985. 72:801–803.25. Cooper MJ, Williamson RC. Splenectomy: indications, hazards and alternatives. Br J Surg. 1984. 71:173–180.26. Billiar TR, West MA, Hyland BJ, Simmons RL. Splenectomy alters Kupffer cell response to endotoxin. Arch Surg. 1988. 123:327–332.27. Stone WM, Sarr MG, Nagorney DM, McIlrath DC. Chronic pancreatitis. Results of Whipple's resection and total pancreatectomy. Arch Surg. 1988. 123:815–819.28. Bittner R, Butters M, Buchler M, Nagele S, Roscher R, Beger HG. Glucose homeostasis and endocrine pancreatic function in patients with chronic pancreatitis before and after surgical therapy. Pancreas. 1994. 9:47–53.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical course of pancreas cancer diagnosed after spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy with borderline lesion: two case reports
- Duodenum-preserving pancreatic head resection in benign and low-grade malignant pancreatic tumors
- Dual-incision laparoscopic spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy
- Robotic central pancreatectomy: a surgical technique
- Current status of robotic surgery for pancreatic tumors