J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Apr;23(2):324-327. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.2.324.
Central Pontine Myelinolysis in a Patient with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kim_dajung@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1713469
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.2.324
Abstract
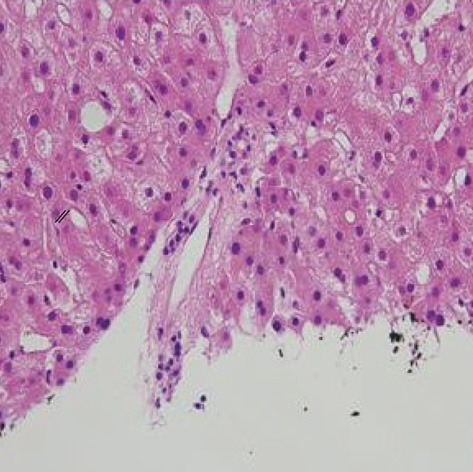
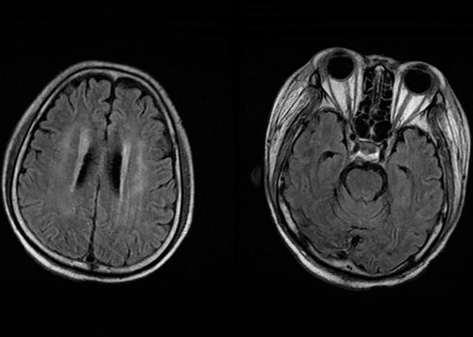
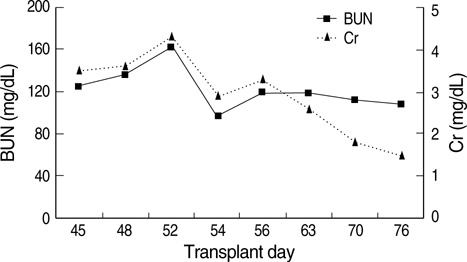
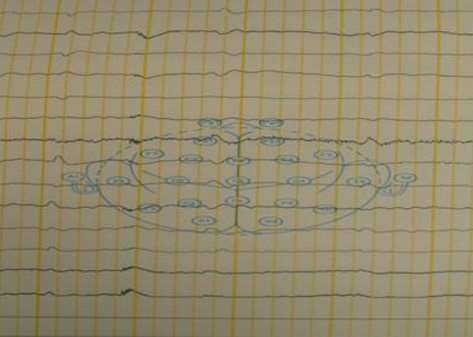
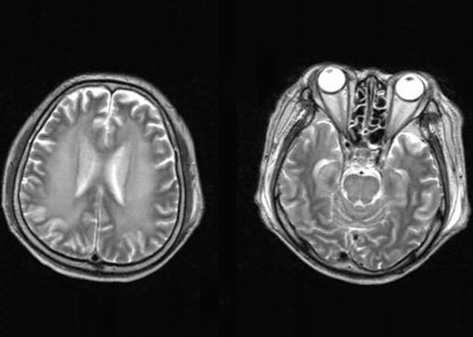
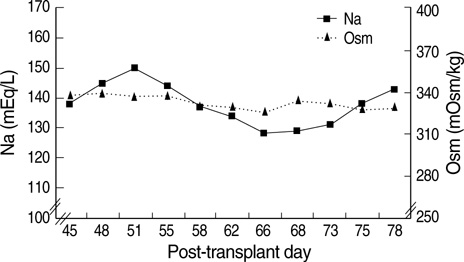
- We describe a 37-yr-old man who developed central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. After HSCT, desquamation developed on the whole body accompanied by hyperbilirubinemia. The liver biopsy of the patient indicated graft-versus-host disease- related liver disease, and the dose of methylprednisolone was increased. Then, the patient developed altered mentality with eye ball deviation to the left, for which electroencephalogram and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans were done. Brain MRI scan demonstrated the imaging findings consistent with central pontine myelinolysis and extrapontine myelinolysis. He did not have any hyponatremia episode during hospitalization prior to the MRI scan. To the best of our knowledge, presentation of CPM after allogeneic HSCT is extremely rare in cases where patients have not exhibited any episodes of significant hyponatremia. We report a rare case in which hepatic dysfunction due to graft-versus-host disease has a strong association with CPM after HSCT.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Biopsy
Brain/pathology
Electroencephalography
Graft vs Host Disease
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation/*adverse effects
Humans
Hyperbilirubinemia/etiology
Liver/pathology
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Myelinolysis, Central Pontine/complications/*etiology
Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma/complications/*therapy
Time Factors
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Reference
-
1. Messert B, Orrison WW, Hawkins MJ, Quaglieri CE. Central pontine myelinolysis. Considerations on etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurology. 1979. 29:147–160.
Article2. Lampl C, Yazdi K. Central pontine myelinolysis. Eur Neurol. 2002. 47:3–10.
Article3. Ashrafian H, Davey P. A review of the causes of central pontine myelinolysis: yet another apoptotic illness? Eur J Neurol. 2001. 8:103–109.4. Fraser C, Charnas L, Orchard P. Central pontine myelinolysis following bone marrow transplantation complicated by severe hepatic veno-occlusive disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005. 36:733–734.
Article5. McCormick WF, Danneel CM. Central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Intern Med. 1967. 119:444–478.
Article6. Karp BI, Laureno R. Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: a neurologic disorder following rapid correction of hyponatremia. Medicine (Baltimore). 1993. 72:359–373.7. Sterns RH, Cappuccio JD, Silver SM, Cohen EP. Neurologic sequelae after treatment of severe hyponatremia: a multicenter perspective. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1994. 4:1522–1530.
Article8. Bronster DJ, Emre S, Boccagni P, Sheiner PA, Schwartz ME, Miller CM. Central nervous system complications in liver transplant recipients-incidence, timing, and long-term follow-up. Clin Transplant. 2000. 14:1–7.9. Singh N, Yu VL, Gayowski T. Central nervous system lesions in adult liver transplant recipients: clinical review with implications for management. Medicine (Baltimore). 1994. 73:110–118.10. Fryer JP, Fortier MV, Metrakos P, Verran DJ, Asfar SK, Pelz DM, Wall WJ, Grant DR, Ghent CN. Central pontine myelinolysis and cyclosporine neurotoxicity following liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1996. 61:658–661.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unusual isolated extramedullary relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the breast despite complete donor hematopoietic chimerism after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- A Case of Ovarian-Relapse Sparing of the Marrow in a Patient with Acute T Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Nutritional Intervention for a Patient with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia on Allogeneic Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
- Isolated Breast Relapse of Early T-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia after Stem Cell Transplantation: A Pediatric Case and Literature Review
- A case of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis with early hypermetabolism on 18FDG-PET scan